Chapter: Microbiology
Poliomyelitis
POLIOMYELITIS
Introduction
Poliomyelitis is an acute illness with pain and flaccid paralysis affecting mainly lower limbs and is caused by three polio viruses.(poliovirus1,2 and 3)
Polioviruses belong to the family of enteroviruses which multiply in the gut and rarely cause intestinal symptoms.
Characteristics of enteroviruses- Polio virus
These viruses enter the body via ingestion by mouth. They mul-tiply in the lymphoid tissues of the alimentary tract including the phar-ynx. From the gut they enter the blood (viremia) or shed into the lumen of the intestine.
Virology
Polio virus belongs to Picorna virus (pico = small + RNA).
They are RNA viruses, having single stranded positive sense RNA.
Viruses are small roughly spherical particles, 25-30 nm in size, stable at acid pH.
They grow rapidly in tissue cultures and produce cytopathic effects.
Replication of polio virus
1. Polio virus attaches to the specific receptors on the cell surface. If the cell is not possessing the receptor it is not susceptible to infection
2. The virus enters the cell by micropinocytosis
3. Then uncoating of capsid proteins occurs. The viral RNA is released into the cytoplasm
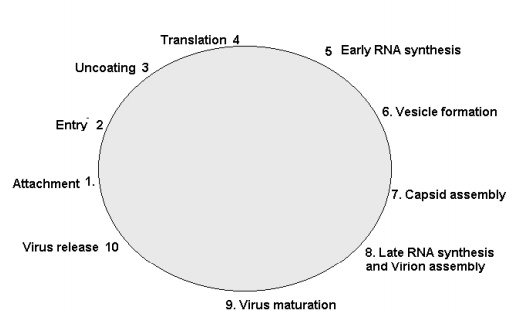
4. Viral RNA is a plus strand and it can act as a messenger RNA. So early translation (protein synthesis ) occurs.
5. At the same time Viral RNA synthesis also occurs.
6. During this time a vesicle is formed inside the cells
7. Inside the vesicle assembly of viral components occur
8. Afterwards late viral RNA translation occurs leading to further synthesis of viral proteins
9. Finally maturation of virus occurs
10. The virus is released after the rupture of the cell and the cycle continues
Pathogenesis and Clinical features
Most infections are confined to alimentary tract and are symp-tomless. A small proportion of infections show fever. Still very few cases progress to aseptic meningitis and to paralysis.
Poliomyelitis is an acute illness with pain and flaccid paralysis affecting mainly the lower legs. Some times the muscles of respiratory tract may be involved. Paralysis is an extension of aseptic meningitis and is therefore accompanied by the signs and symptoms of meningitis which include fever, head ache with stiffness of neck. Paralysis is due to viral damage to the cells of the anterior horn of the spinal cord with lower motor neurone lesions resulting in flaccid paralysis
Epidemiology
Enterovirus infections are common in children and in conditions of poor hygine. Infections spread mainly by fecal-oral route.
Laboratory diagnosis and control
Faeces, throat swab and blood are collected for viral isolation. These specimens are inoculated into monkey kidney cell cultures and observed for cytopathic effects. The virus can be identified by neutral-ization using specific antiserum
Control
Two types of vaccines are available for three polioviruses.
1. Sabin live attenuated virus vaccines. It is administered in three oral doses
2. Salk inactivated virus vaccine: It contains three polio viruses inactivated by formalin and is given in three injections.
Related Topics