Chapter: BIOLOGY (ZOOLOGY) Standard XI first year 11th text book Assignment topics question and answer Explanation Definition
Pigeon : Endoskeleton : Flight muscles, Pectoralis major, Pectoralis minor or subclavius, Coracobrachialis
Pigeon - Endoskeleton : Flight muscles, Pectoralis major, Pectoralis minor or subclavius, Coracobrachialis
Pigeon
Sub phylum - Vertebrata
Class - Aves
Order - Columbiformes
Type - Columba livia
Birds are easily recongnised group of vertebrates. In birds every part of the body is modified to suit their aerial mode of life. Birds possess feathers, beak and feet modified in relation to their aerial life.
The Pigeons are flying birds(carinate). They are known both as wild and domesticated forms. The Pigeons are seen both in tropical and temperate zones. About 10 species of Pigeons are found in India. The pigeons fly in flocks and roost together. The domestic pigeons have many varieties, namely panter, fantail and tumblers. They differ in size, colouration and feather ar-rangement. All of them are, however, descendants of the rock pigeon-columba livia.
Endoskeleton :-
The endoskeleton of pigeon is strong but lightly built. The texture of the bone is often spongy. Bone marrow is absent. The air spaces from the lungs may continue into the bones, making them light. The bones are more or less devoid of bone marrow. These are called Pneumatic bones. Most of the bones except those of the tail, forearm, hand and hind limb contain air spaces. In general there is a tendency for the reduction and fusion of bones. It gives rigidity to the skeleton.
Flight muscles :-
The wings are the modified forelimbs. They are organs of flight. The musculature of the forelimbs are greatly modified in response to the function they perform. Flight is the coordinated effort of a number of paired muscles of which the following are most important.
Pectoralis major (Depressor muscles)
These are the largest breast muscles. They are about one fifth of the body weight. By the contraction of this muscle the wings are lowered during flight.
Pectoralis minor or subclavius :-
These are smaller but longer than pectoralis major. By their contrac-tion the wings are raised in flight.
Coracobrachialis :-
These small flight muscles pull the wing downwards in flight.
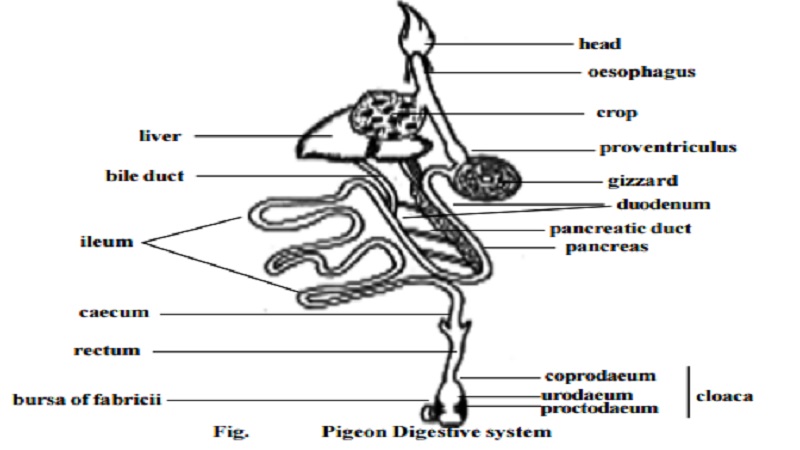
Digestive system :-
The two jaws of the mouth are modified into beak. Both the jaws are devoid of teeth. The mouth leads into the buccal cavity. The floor of the buccal cavity is provided with a narrow, triangular tongue. It has a horny covering and is provided with sensory papillae. The buccal cavity narrows behind into the Pharynx. The salivary glands are absent in the buccal cavity. Three pairs of buccal glands are present in the mouth. Their secretion is mainly mucous.
Respiratory System :-
The flight activity requires a continuous and abundant supply of oxy-gen . Hence, the respiratory system of pigeon is highly developed and well differentiated. The respiratory system consists of external nostrils, glottis, larynx, trachea, bronchus and lungs.
Related Topics