Chapter: 11th Nursing : Chapter 11 : Pharmacology
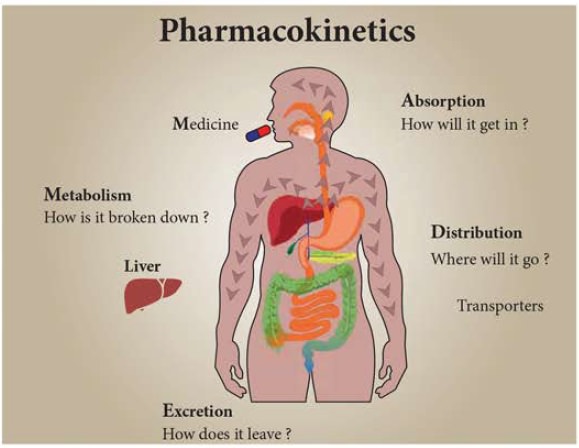
Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics
It is “what the body
does to the drug”. It includes absorption, distribution, metabolism and
excretion.
Drug Absorption:
Definition
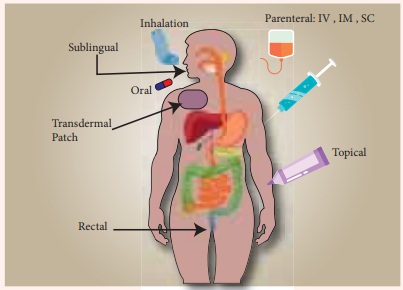
“The process of
movement of unchanged drug from the site of administration to systemic
circulation is called as drug absorption”.
It is the movement of
a drug from the site of administration into the blood stream. There are various
factors influencing drug absorption. It includes:
·
Physiological
properties of the drug. eg., lipid soluble form better absorbed than water soluble.
·
Route of drug
administration. eg., intravenous route directly enters the circulation.
·
Food eg., milk and milk
products decrease the absorption.
·
Presence of other
drugs eg.,
ascorbic acid increases the absorption of oral iron.
·
Gastrointestinal and
other diseases eg., gastroenteritis decreases drug absorption.
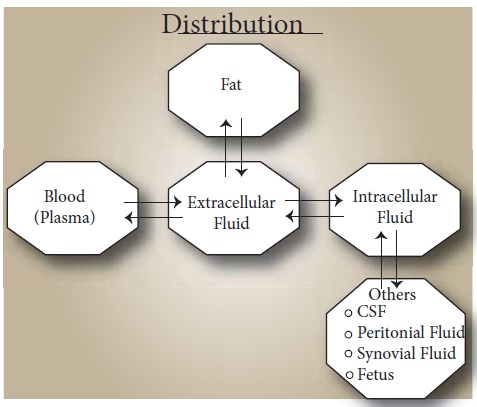
Drug Distribution
Drug distribution:
refers to the reversible transfer of a drug between the blood and the extra
vascular fluids and tissues of the body (for example, fat, muscle, and brain
tissue). Drugs come into the circulation after absorption. From plasma drugs
have to cross the capillary membrane to come to interstitial space then it
cross the cell membrane and enter into the intracellular fluids.
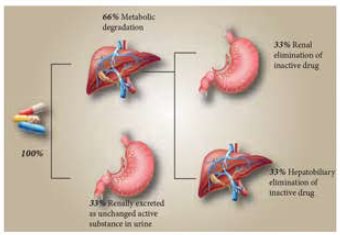
Drug Metabolism
·
Chemical alteration of the drug in a living organism is called
drug metabolism or biotransformation.
Site: Liver is the main site for drug metabolism; other sites are GI
tract, kidney, lungs, blood, skin and placenta.
Factors Affecting Drug Metabolism
Age:
Neonates and elderly metabolize to a lesser extent than adults.
Diseases: Liver diseases impair the drug metabolism.
Drug Excretion
Removal of the drug and its
metabolites from the body is known as drug excretion. The main channel of
excretion of drugs is the kidney; others include lungs, bile, faeces, sweat,
saliva, etc.
Related Topics