Chapter: Human Nervous System and Sensory Organs : Basic Elements of the Nervous System
Peripheral Nerve - The Nerve Fiber
Peripheral Nerve
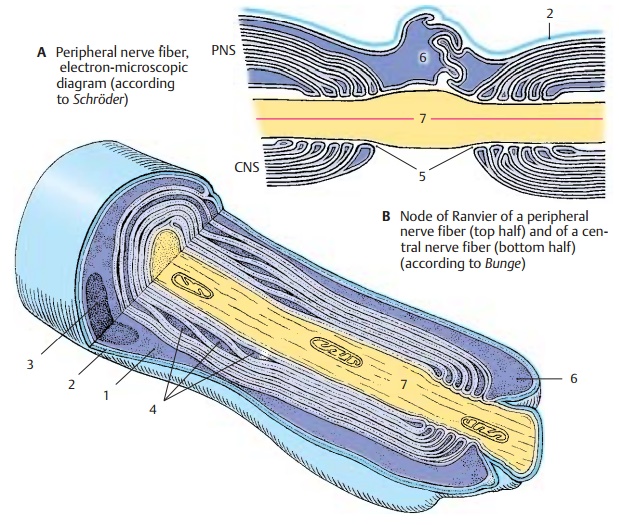
The myelin sheath of peripheral nerve fibers is surrounded by the
cytoplasm of the Schwann cell (A1). The outer cell membraneborders on
a basal lamina (AB2), which en-velops the entire peripheral nerve fiber. The
nucleus of the Schwann cell (A3) is
depicted in cross section. The Schmidt–Lantermanclefts (A4) are depicted in longitudinal sec-tion as cytoplasmic crevices
of the major pe-riod lines. In the three-dimensional recon-struction, they
appear as spirals in which the cytoplasm communicates between the inside and
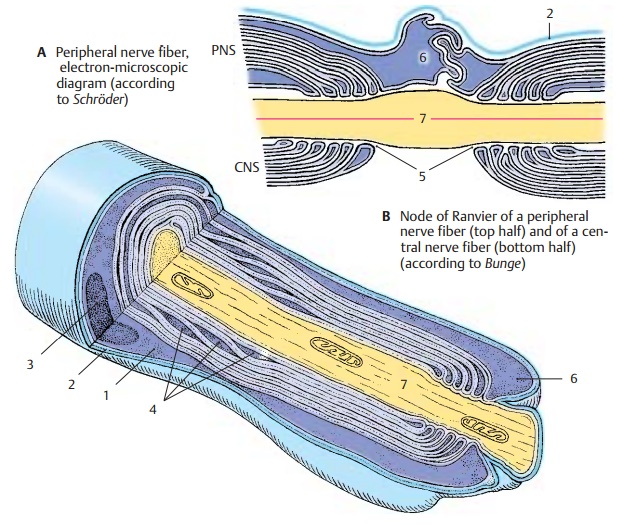
outside. At the node of Ranvier (B5), the Schwann cell processes (AB6) slide over the paranodal region
and over the axon (ABD7). They
interdigitate and thus form a dense envelope around the node of Ranvier.
Differences between the structures
of the myelin sheaths in CNS and PNS are il-lustrated in B.
There is a regular relationship
between the circumference of the axon, the thickness of its myelin sheath, the
distance between the nodes of Ranvier, and the conductionvelocity of a nerve fiber. The larger the cir-cumference
of an axon, the thicker the en-closing myelin sheath and the longer the
in-ternodes. When myelinated nerve fibers are still growing (e.g., in the
nerves of the limbs), the internodes are growing in length. The longer the
internodes, the faster the conduction velocity of the fiber.We dis-tinguish
between myelinated, poorly myeli-nated, and unmyelinated nerve fibers, also
referred to as A, B, and C fibers. The myeli-nated
A fibers have an axonal diameter of3 – 20 µm and a conduction velocity of
up to 120 m/s; the poorly myelinated B
fibers are up to 3 µm in diameter and have a conduction velocity of up to
15 m/s. Conduction velocity is the slowest in the unmyelinated C fibers (up to 2 m/s); we are dealing here with a con-tinuous spread of excitation. By
contrast,conduction in myelinated nerves is salta-tory, that is, it takes place
in jumps. The morphological basis of saltatory
conduction is the alternation of myelinated internodes and unmyelinated
nodes of Ranvier; the current inside the axon jumps from onenode to the next,
and the current circuit is closed each time at the nodes through changes in the
permeability of the ax-olemma (triggered by voltage-gated ion channels). This
mode of conduction is much faster and requires less energy than the continuous
spread of excitation.
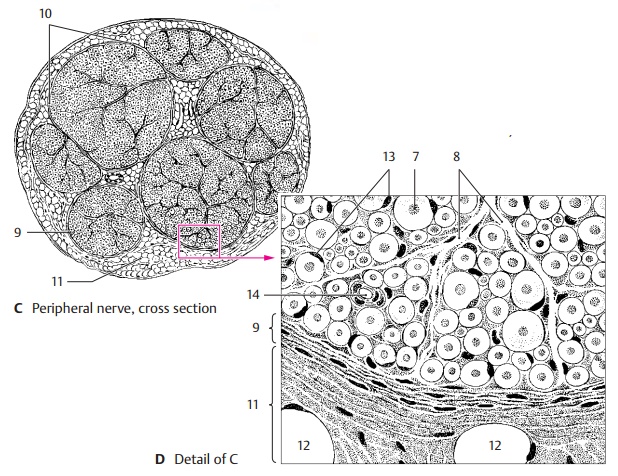
The peripheral nerve fiber is
surrounded by longitudinal collagenous connective-tissue fibrils; together with
the basal membrane, they form the endoneural
sheath. The nerve fibers are embedded in a loose con-nective tissue, the endoneurium (D8). A vari-able number of nerve fibers is collected into bundles or fascicles (C10) by theperineurium (CD9) which consists mainly of circular fibers. The innermost layer
of the per-ineurium is formed by endothelial
cells that enclose the endoneural space in several thin layers. The
perineural endothelial cells possess a basal membrane at their per-ineural and
endoneural surfaces and are joined together by zonulae occludentes(tight junctions). They represent a barrier
between nerve and surrounding tissue, sim-ilarly to the endothelial cells of
cerebral capillaries. The mechanical strength of the peripheral nerve is based
on its content of circular elastic fibers.
In the nerves of the limbs, the perineurium is rein-forced in the joint
regions. The epineurium (CD11) borders on the perineurium; its
inner layers form concentric lamellae as well. They change into loose connectivetissue containing fat cells (D12), blood ves-sels, and lymph vessels.
D13 Cell nuclei of Schwann cells.
D14 Capillaries.
Related Topics