Chapter: Mathematics (maths) : Fourier Series
Periodic Functions
PERIODIC FUNCTIONS
A function f (x) is called periodic if it is defined for all real „x‟ some positive number „p‟ such that
f (x + p ) = f (x) for all x.
This number „p‟ is called a period of f(x
If a periodic function f (x) has a smallest period p (>0), this is often called the fundamental period of f(x). For example, the functions cosx and sinx have fundamental period 2p.
DIRICHLET CONDITIONS
Any function f(x), defined in the interval c £x £c + 2p, can be developed as a Fourier series of the form
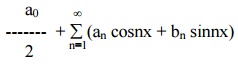
provided the following conditions are satisfied.
f (x) is periodic, single–valued and finite in [ c, c + 2 p].
f (x) has a finite number of discontinuities in [ c, c + 2p].
f (x) has at the most a finite number of maxima and minima in [ c,c+ 2p].
These conditions are known as Dirichlet conditions. When these conditions are satisfied, the Fourier series converges to f(x) at every point of continuity. At a point of discontinuity x = c, the sum of the series is given by
f(x) = (1/2) [ f (c-0) + f (c+0)] ,
where f (c-0) is the limit on the left and f (c+0) is the limit on the right.
EULER’S FORMULAE
The Fourier series for the function f(x) in the interval c < x < c + 2pis given by
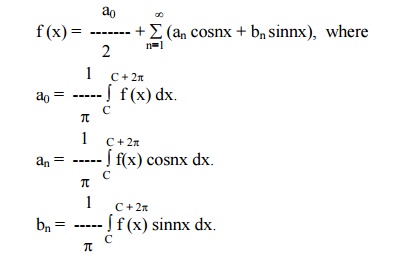
These values of a0, an, bn are known as Euler‚Äüs 0 , formula en,bn The coefficients a0, an, bn are are also termed as Fourier coefficients.
Example 1
Expand f(x) = x as Fourier Series (Fs) in the interval [ -π, π]
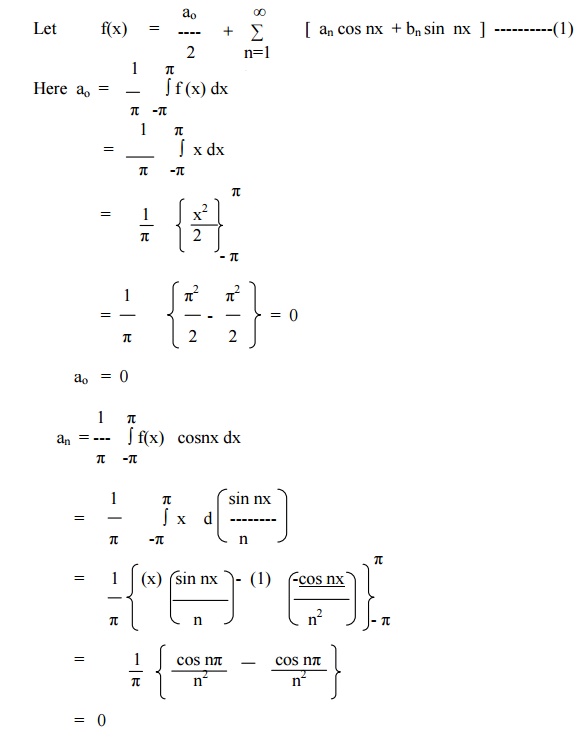
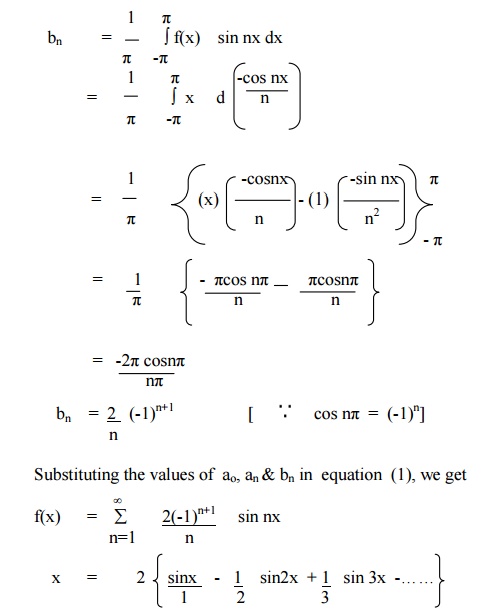
Example 2
Expand f(x) = x2 in the interval ( -p£x £p) and hence deduce that
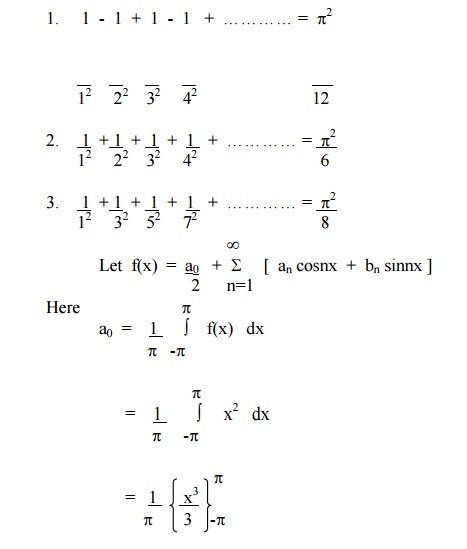
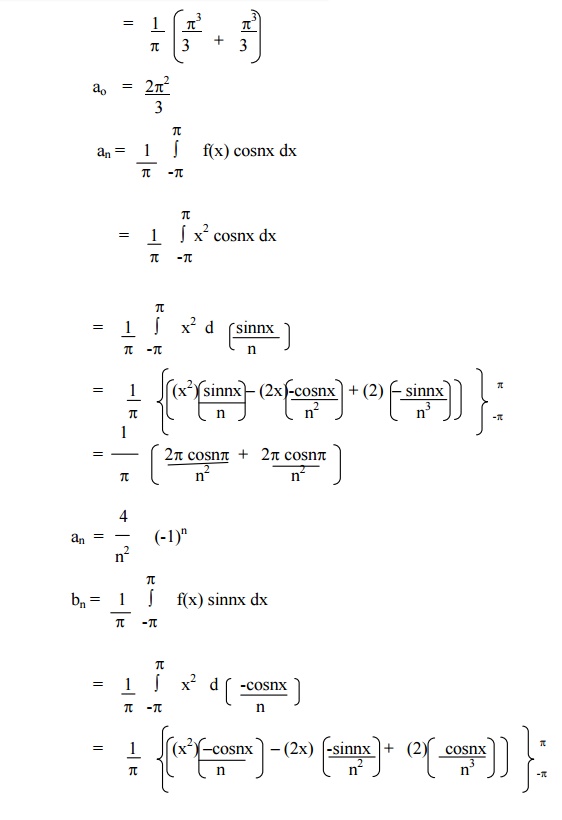
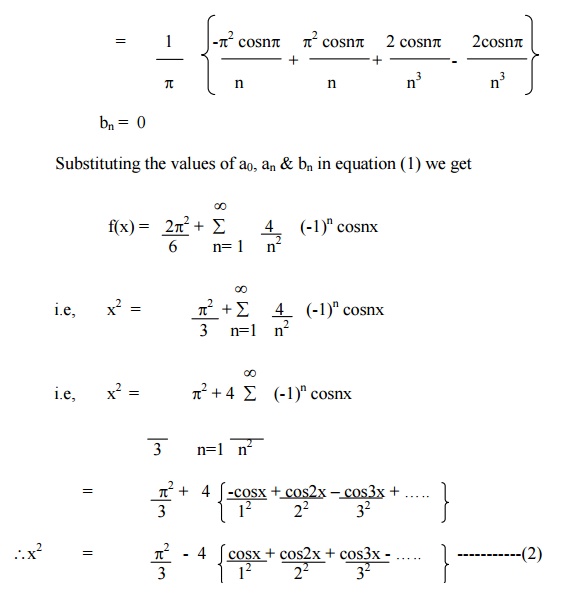
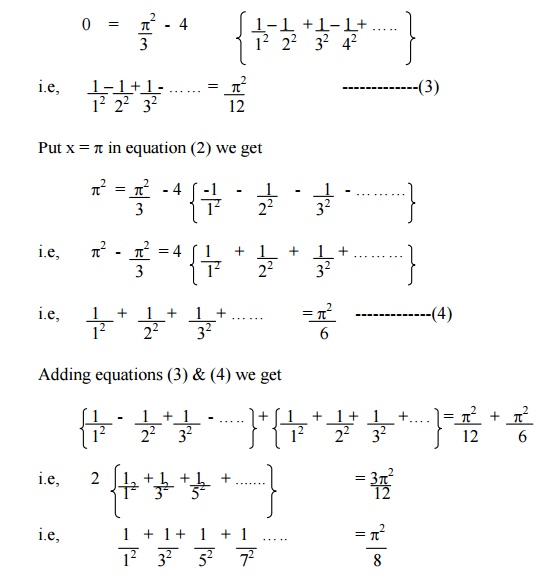
Example 3
Obtain the Fourier Series of periodicity 2πin [for-π, π]

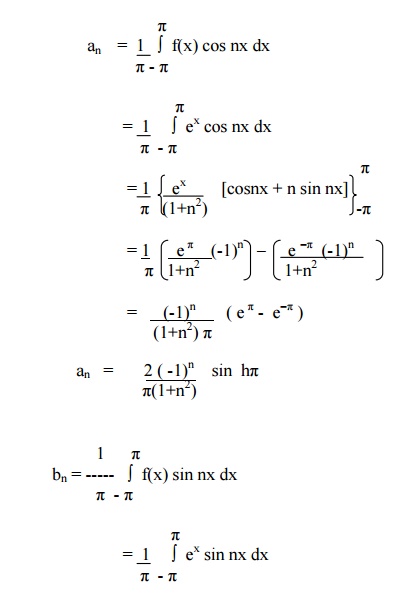
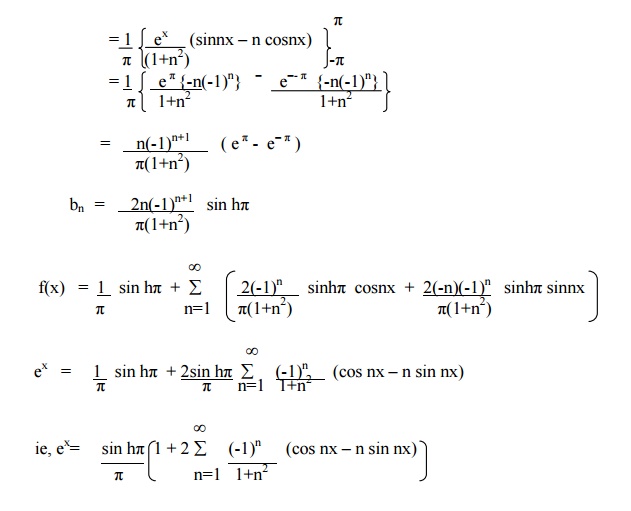
Example 4
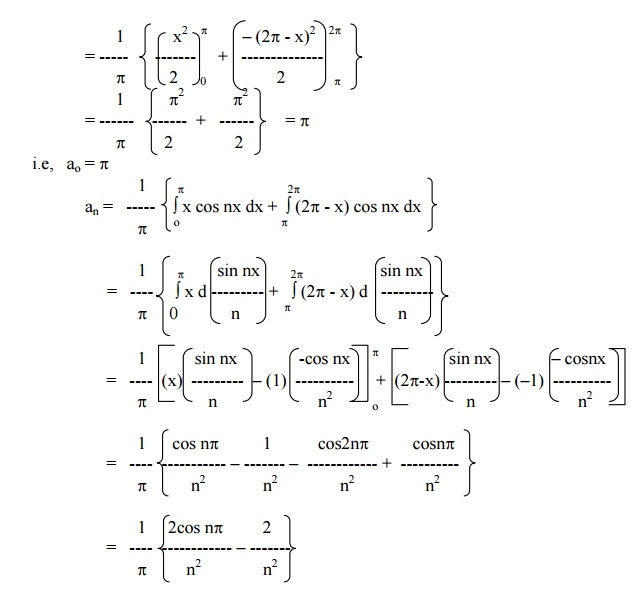
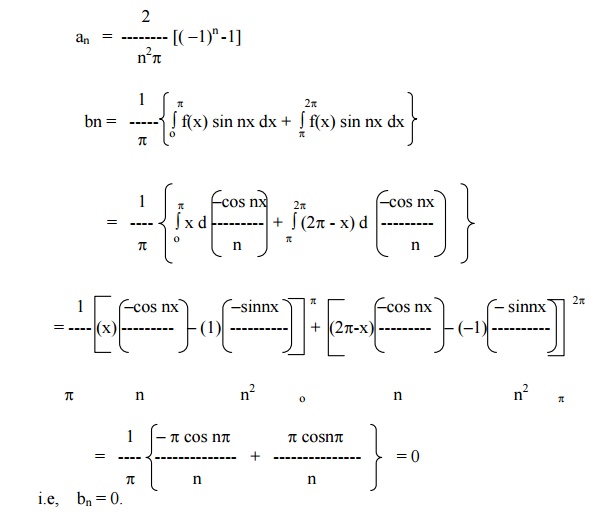
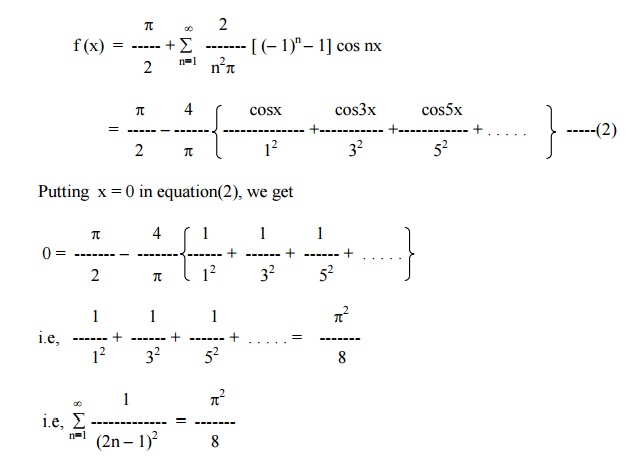
Example 5
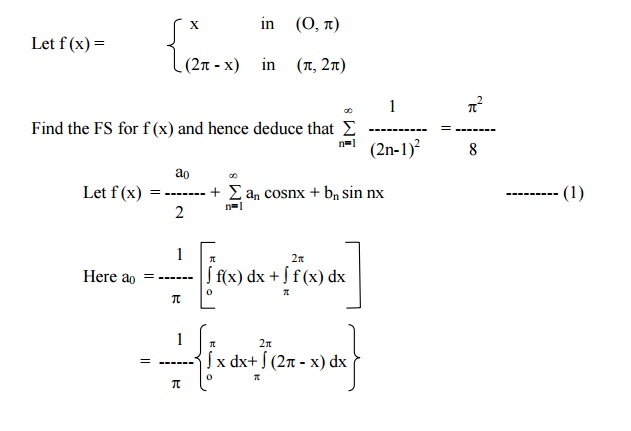
Find the Fourier series for f (x) = (x + x2) in (-p< x < p) of percodicity 2p and hence deduce that
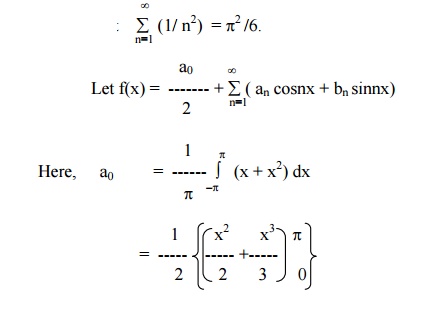
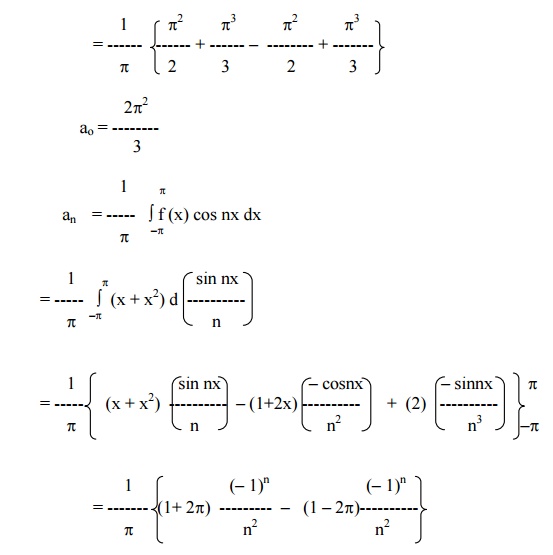
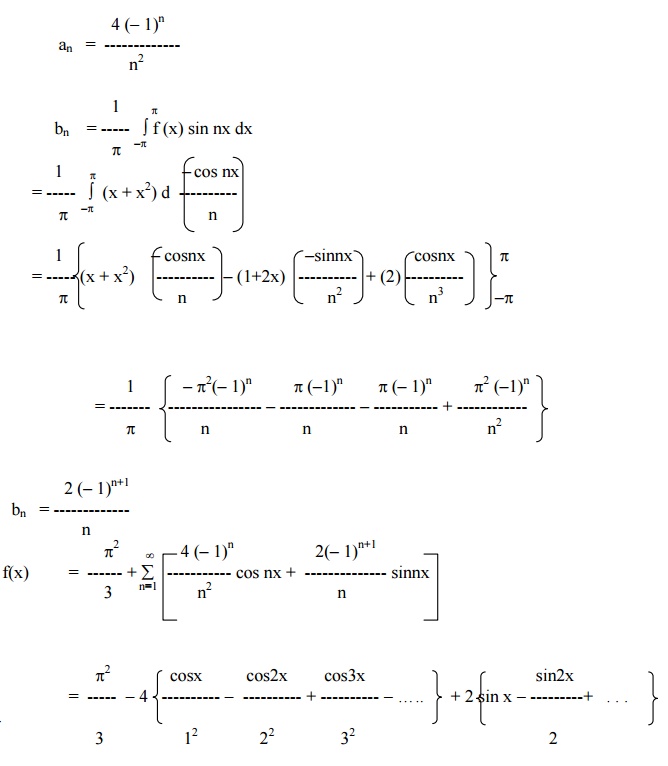
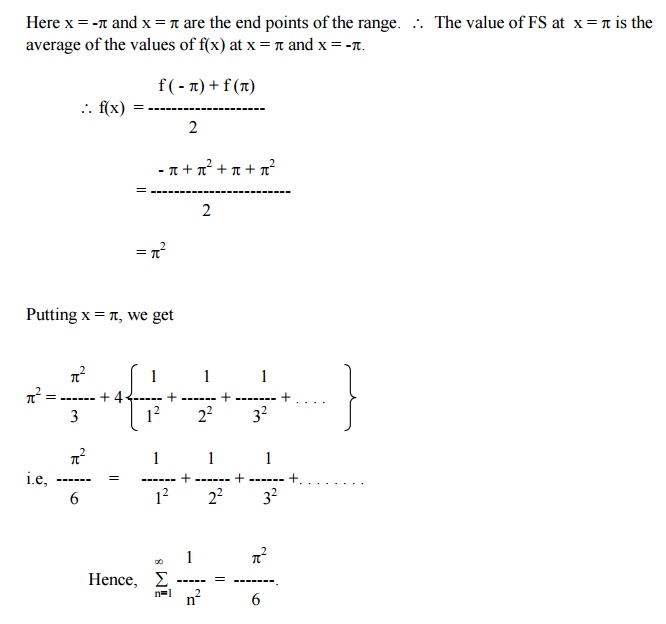
Here x = -pand x = pare the end points of the range. \ The value of FS at x = pis the average of the values of f(x) at x = pand x = -p.
Exercises:
Determine the Fourier expressions of the following functions in the given interval
1.f(x) = (p- x)2, 0 < x < 2p
2.f(x) = 0 in -p< x < 0
= pin 0 < x < p
3.f(x) = x –x2 in [-p,p]
4.f(x) = x(2p-x) in (0,2p)
5.f(x) = sinh ax in [-p, p]
6.f(x) = cosh ax in [-p, p]
7.f(x) = 1 in 0 < x < p
= 2 in p< x < 2p
8.f(x) = -p/4 when -p< x < 0
= p/4 when 0 < x < p
9.f(x) = cosax, in -p< x < p, wherea‟is„ not an integer
10.Obtain a fourier series to represent e-ax from x = -pto x = p. Hence derive the series for p/ sinhp
Related Topics