Chapter: Basic & Clinical Pharmacology : Antiprotozoal Drugs
Parasite Life Cycle - Malaria
MALARIA
Malaria
is the most important parasitic disease of humans and causes hundreds of
millions of illnesses per year. Four species of plasmo-dium typically cause
human malaria: Plasmodium
falciparum,vivax, P malariae, and P
ovale. A fifth species, P knowlesi, is
pri-marily a pathogen of monkeys, but has recently been recognized to cause
illness, including severe disease, in humans in Asia. Although all of the
latter species may cause significant illness, P falciparum is responsible for the majority of serious
complications and deaths. Drug resistance is an important therapeutic problem,
most notably with P falciparum.
PARASITE LIFE CYCLE
An anopheline mosquito
inoculates plasmodium sporozoites to initiate human infection (Figure 52–1).
Circulating sporozoites rapidly invade liver cells, and exoerythrocytic stage
tissue schizonts mature in the liver. Merozoites are subsequently released from
the liver and invade erythrocytes. Only erythrocytic parasites cause clinical
illness. Repeated cycles of infection can lead to the infec-tion of many
erythrocytes and serious disease. Sexual stage game-tocytes also develop in
erythrocytes before being taken up by mosquitoes, where they develop into
infective sporozoites.
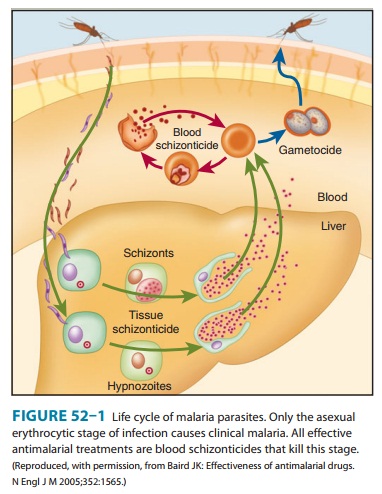
In P falciparum and P malariae infection, only one cycle of liver cell invasion and
multiplication occurs, and liver infection ceases spontaneously in less than 4
weeks. Thus, treatment that eliminates erythrocytic parasites will cure these
infections. In P vivax and P ovale infections, a dormant hepatic
stage, the hypnozoite, is not eradicated by most drugs, and subsequent
relapses can therefore occur after therapy directed against erythrocytic
parasites. Eradication of both erythrocytic and hepatic parasites is required
to cure these infections and usually requires two or more drugs.
Related Topics