Chapter: Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology: The Digestive System
Pancreas
PANCREAS
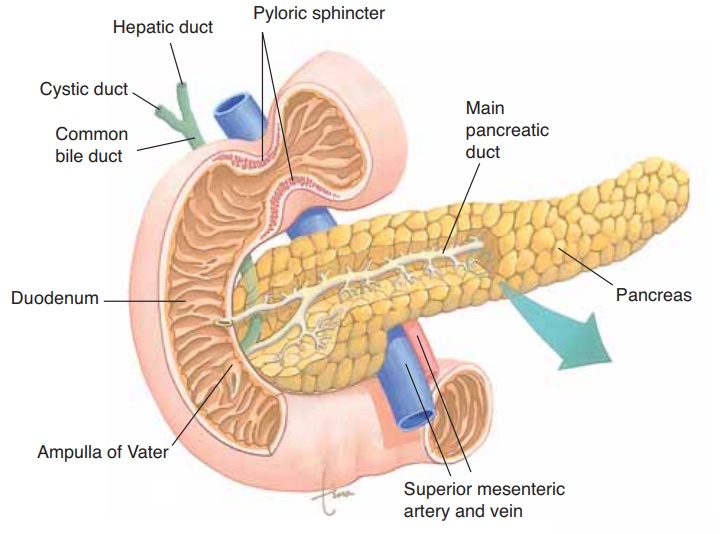
The pancreas is located in the upper left abdominal quadrant between the curve of the duodenum and the spleen and is about 6 inches (15 cm) in length. The endocrine functions of the pancreas were discussed, so only the exocrine functions will be considered here. The exocrine glands of the pancreas are called acini (singular: acinus) (Fig. 16–7). They produce enzymes that are involved in the digestion of all three types of complex food molecules.
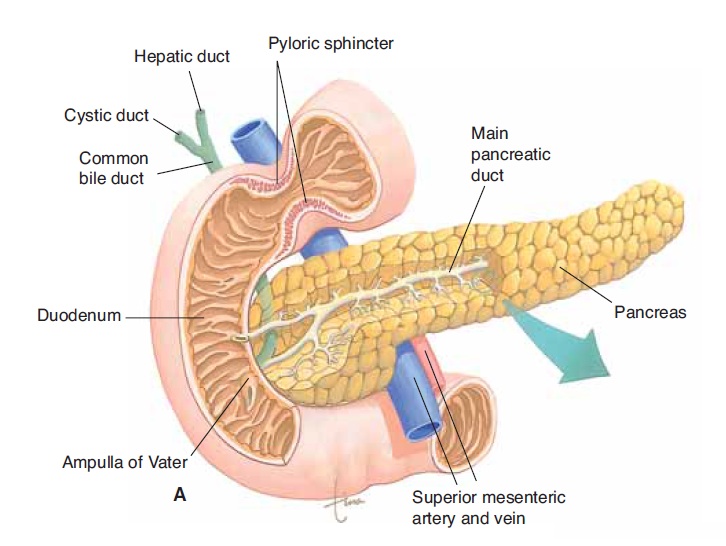
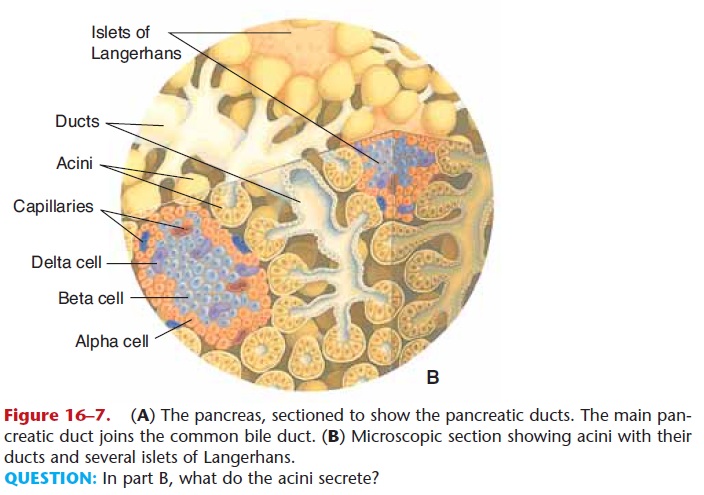
Figure 16–7. (A) The pancreas, sectioned to show the pancreatic ducts. The main pan-creatic duct joins the common bile duct. (B) Microscopic section showing acini with their ducts and several islets of Langerhans.
QUESTION: In part B, what do the acini secrete?
The pancreatic enzyme amylase digests starch to maltose. You may recall that this is the “backup” enzyme for salivary amylase, though pancreatic amy-lase is responsible for most digestion of starch. Lipase converts emulsified fats to fatty acids and glycerol. The emulsifying or fat-separating action of bile salts increases the surface area of fats so that lipase works effectively. Trypsinogen is an inactive enzyme that is changed to active trypsin in the duodenum. Trypsin digests polypeptides to shorter chains of amino acids.
The pancreatic enzyme juice is carried by small ducts that unite to form larger ducts, then finally the main pancreatic duct. An accessory duct may also be present. The main pancreatic duct emerges from the medial side of the pancreas and joins the common bile duct to the duodenum (see Fig. 16–7).
The pancreas also produces a bicarbonate juice (containing sodium bicarbonate), which is alkaline.
Because the gastric juice that enters the duodenum is very acidic, it must be neutralized to prevent dam-age to the duodenal mucosa. This neutralizing is accomplished by the sodium bicarbonate in pancreatic juice, and the pH of the duodenal chyme is raised to about 7.5.
Secretion of pancreatic juice is stimulated by the hormones secretin and cholecystokinin, which are produced by the duodenal mucosa when chyme enters the small intestine. Secretin stimulates the produc-tion of bicarbonate juice by the pancreas, and chole- cystokinin stimulates the secretion of the pancreatic enzymes.
Related Topics