Chapter: Paediatrics: Bones and joints
Paediatrics: Skeletal dysplasias
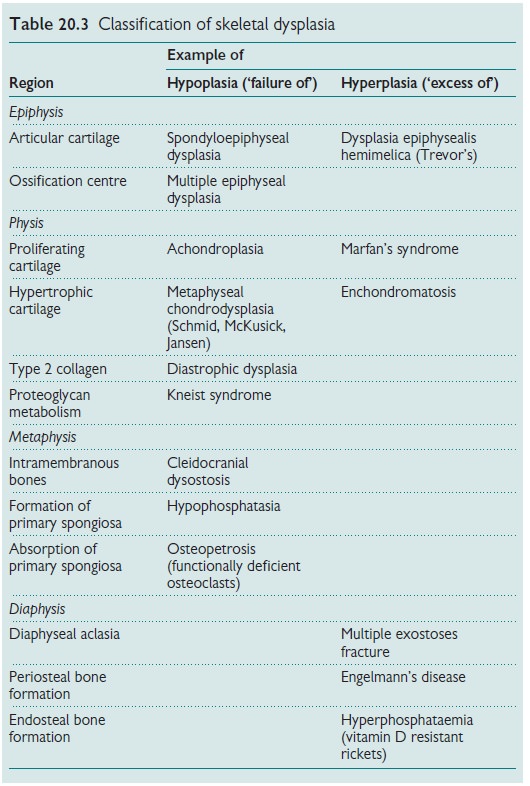
Skeletal dysplasias
This is a heterogeneous group of
conditions characterized by abnormal growth of bones. They can be classified
according to the region of bone involved or by their genotype (see Table 20.3).
Radial dysplasia
An absent or hypoplastic radius
that causes abnormal radial deviation of the hand. This is the most common form
of longitudinal upper limb deficiency and is often accompanied by a
congenitally absent thumb. Anomalies of other systems may also be associated.
ŌĆó
TAR.
ŌĆó
FA.
ŌĆó
HoltŌĆōOram syndrome: AD; cardiac anomalies, and radial
dysplasia.
ŌĆó
VACTERL
(vertebral anomalies, anal atresia, cardiac malformations, tracheo-oesophageal
fistula, renal and limb anomalies).
Management
ŌĆó
Serial
castings/splinting.
ŌĆó Surgery is usually required to place the hand in position to maximize function. If a thumb is absent, pollicization of the index finger could improve function. The index finger is reconstructed and radially positioned to form a functional ŌĆśthumbŌĆÖ.
Related Topics