Chapter: Orthopaedics
Orthopaedics: Ankle
Ankle
Evaluation of Ankle and Foot Complaints
Special Tests
·
anterior drawer: examiner attempts to displace the
foot anteriorly against a fixed tibia
·
talar tilt: foot is stressed in inversion and
Bllgle oftala.r rotation is evaluated by x-ray
X-Ray
·
AP, lateral
·
mortise view: ankle at 15° of internal rotation
o
gives true view of ankle joint
o
joint space should be symmetric with no talar tilt
·
Ottawa Ankle Rules should guide use of x-ray
·
± CT to better characterize fractures
Ankle Fracture
Mechanism
·
pattern of fracture depends on the position of the
ankle when trauma occurs
·
generally involves
o
lpsilateral ligamentous tears or transverse bony
avulsion
o
contralateral shear fractures (oblique or spiral)
·
classification systems
o
Danis-Weber
o
Lauge-Hansen: based on foot's position and motion
relative to leg
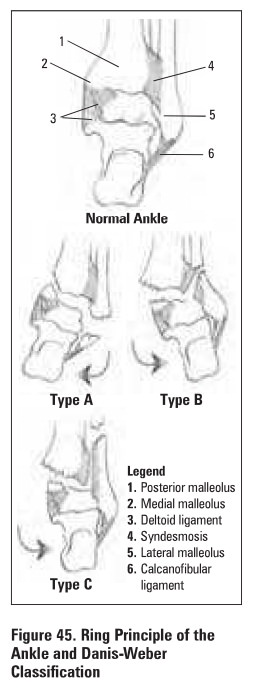
Danis-Webar Classification (Figure 45)
·
based on level offibular fracture relative to syndesmosis
·
Type A (infra-syndesmotic)
o
pure inversion injury
o
avulsion of lateral malleolus below plafond or
torn calcaneofibular ligament
o
± shear fracture of medial malleolus
·
Type B (trans-syndesmotic)
o
external rotation and eversion (most common)
o
± avulsion of medial malleolus or rupture of
deltoid ligament
o
spiral fracture of lateral malleolus starting at
plafond
·
Type C (supra-syndesmotic)
o
pure external rotation
o
avulsion of medial malleolus or tom deltoid ligament
o
± posterior malleolus may be avulsed with
posterior tibio-fibular ligament
o
fibular fracture is above plafond (called
Maisonneuve fracture if at proximal fibule)
o
frequently tears syndesmosis
Treatment
·
undisplaced: non-weight bearing below knee cast
·
indications for ORIF
o
all fracture-dislocations
o
most of type B, and all of type C
o
trimalleolar (medial, posterior; lateral)
fractures
o
talar tilt >10°
o
medial clear space on XR greater than superior
clear space
o
open fracture/open joint injury
·
high incidence of post-traumatic arthritis
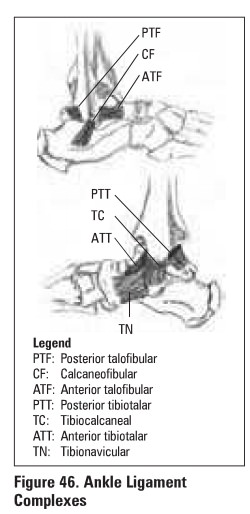
Ligamentous Injuries
Medial Ligament Complex (deltoid ligament)
·
eversion injury
·
usually avulses medial or posterior malleolus and
strains syndesmosis
Lateral Ligament Complex (ATF, CF. PTF)
·
inversion injury
·
ATF most severely injured if ankle is plantar
flexed
·
swelling and tenderness anterior to lateral
malleolus
·
++ ecchymoses
·
+ve ankle anterior drawer
·
may have significant medial talar tilt on
inversion stress x-ray
Treatment
·
microscopic tear (Grade I)
o
rest, ice, compression, elevation (RICE)
·
macroscopic tear (Grade II)
o
strap ankle in dorsi1leDon and eversion x 4--6
weeks
o
PT: strengthening and proprioceptive retraining
·
complete tear (Grade III)
o
below knee walking cast 4-6 weeks
o
PT: strengthening and proprioceptive retraining
o
surgical intervention may be required if chronic
symptomatic instability develops
Related Topics