Chapter: Medical Surgical Nursing: Management of Patients With Oncologic or Degenerative Neurologic Disorders
Nursing Process: The Patient Undergoing a Cervical Discectomy
NURSING PROCESS:THE PATIENT
UNDERGOING A CERVICAL DISCECTOMY
Assessment
The patient is asked about past injuries to the neck
(whiplash) be-cause unresolved trauma may cause persistent discomfort, pain and
tenderness, and symptoms of arthritis in the injured joint of the cervical
spine. Assessment includes determining the onset, location, and radiation of
pain, paresthesias, limited movement, and diminished function of the neck,
shoulders, and upper ex-tremities. It is important to determine whether the
symptoms are bilateral because with large herniations, bilateral symptoms may
be due to cord compression. The area around the cervical spine is palpated to
assess muscle tone and tenderness. Range of motion in the neck and shoulders is
evaluated.
The patient is asked about any health concerns that may
in-fluence the postoperative course. The nurse determines the pa-tient’s need
for information about the surgical procedure and reinforces what the physician
has explained. Strategies for pain management are discussed with the patient.
Diagnosis
NURSING DIAGNOSES
Based on the assessment data, the patient’s major nursing
diag-noses may include the following:
·
Acute pain related to the
surgical procedure
·
Impaired physical mobility
related to the postoperative sur-gical regimen
·
Deficient knowledge about the
postoperative course and home care management
Other nursing diagnoses may include preoperative anxiety,
postoperative constipation, urinary retention related to surgical procedure and
dehydration, self-care deficits related to neck or-thosis, and sleep pattern
disturbance related to disruption in lifestyle.
COLLABORATIVE PROBLEMS/POTENTIAL COMPLICATIONS
Based on all the assessment data, the potential
complications may include the following:
·
Hematoma at the surgical site,
resulting in cord compres-sion and neurologic deficit
·
Recurrent or persistent pain
after surgery
Planning and Goals
The goals for the patient may include relief of pain,
improved mobility, increased knowledge and self-care ability, and preven-tion
of complications.
Nursing Interventions
RELIEVING PAIN
The patient may be kept
flat in bed for 12 to 24 hours. If the pa-tient has had a bone fusion with bone
removed from the iliac crest, considerable pain may be experienced.
Interventions consist of monitoring the donor site for hematoma formation,
adminis-tering the prescribed postoperative analgesic agent, positioning for
comfort, and reassuring the patient that the pain can be relieved. If the
patient experiences a sudden reappearance or increase of pain, extrusion of the
graft may have occurred, requiring reoperation and surgical repositioning of
the graft. This should be promptly reported to the surgeon.
The patient may experience a sore throat, hoarseness, and
dys-phagia due to temporary edema. These symptoms are relieved by throat
lozenges, voice rest, and humidification. A puréed diet may be given if the
patient has dysphagia.
IMPROVING MOBILITY
Postoperatively, a
cervical collar (neck orthosis) is usually worn, which contributes to limited
neck motion and altered mobility. Patients are instructed to turn the body
instead of the neck when looking from side to side. The neck should be kept in
a neutral(midline) position. Patients are assisted during position
changes, making sure that head, shoulders, and thorax are kept aligned. When
assisting a patient to a sitting position, the nurse supports the patient’s
neck and shoulders. Patients should wear shoes when ambulating to increase
stability.
MONITORING AND MANAGINGPOTENTIAL COMPLICATIONS
The patient is evaluated
for bleeding and hematoma formation by assessing for excessive pressure in the
neck or severe pain in the incision area. The dressing is inspected for serosanguineous
drainage, which suggests a dural leak. In this event, meningitis is a threat. A
complaint of headache requires careful evaluation. Neurologic checks are made
for swallowing deficits and upper and lower extremity weakness because cord
compression may produce rapid or delayed onset of paralysis. The patient who
has had an anterior cervical discectomy is also assessed for a sudden return of
radicular (spinal nerve root) pain, which may indicate instability of the
spine.
Throughout the postoperative
course, the patient is moni-tored frequently to detect any signs of respiratory
difficulty be-cause retractors during surgery may injure the recurrent
laryngeal nerve, resulting in hoarseness and the inability to cough
effec-tively and clear pulmonary secretions. In addition, the blood pres-sure
and pulse are monitored to evaluate cardiovascular status.
Bleeding at the surgical
site and subsequent hematoma for-mation may occur. Severe localized pain not
relieved by analgesic agents should be reported to the surgeon. A change in
neurologic status (motor or sensory function) should be reported promptly
because it suggests hematoma formation that may necessitate surgery to prevent
irreversible motor and sensory deficits.
PROMOTING HOME AND COMMUNITY-BASED CARE
Teaching Patients Self-Care
The patient’s hospital
stay is likely to be short; therefore, the patient and family should understand
the care that is important for a smooth recovery. A cervical collar is usually
worn for about 6 weeks. The patient is instructed in use and care of the
cervical collar. Patients are instructed to alternate tasks in which the body
does not move (eg, reading) with tasks that require greater body movement.
The patient is
instructed about strategies for pain manage-ment and about signs and symptoms
that may indicate compli-cations that should be reported to the physician. The
nurse assesses the patient’s understanding of these management strategies,
lim-itations, and recommendations. Additionally, the nurse assists the patient
in identifying strategies to cope with activities of daily living (ie,
self-care and childcare) and minimize risks to the sur-gical site (Chart 65-6).
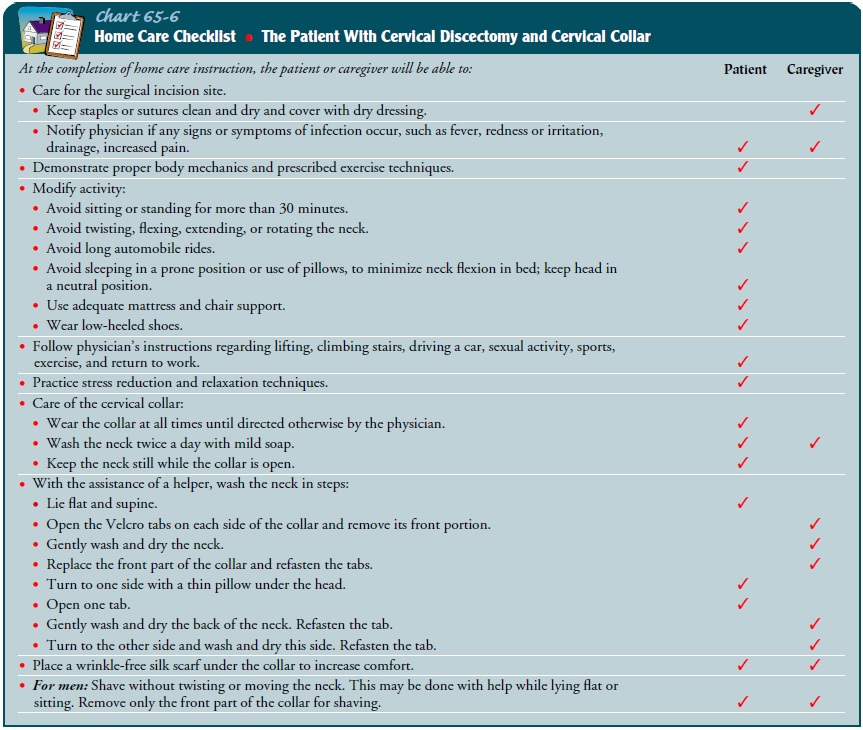
A discharge teaching
plan is developed collaboratively by members of the health care team to
decrease the risk for recurrent disk herniation. Topics include those
previously discussed as well as proper body mechanics, maintenance of optimal
weight, proper exercise techniques, and modifications in activity.
Continuing Care
Patients are instructed to see their physician at prescribed inter-vals to document the disappearance of old symptoms and for as-sessment of range of motion of the neck. Recurrent or persistent pain may occur despite removal of the offending disk or disk fragments.
Patients who
undergo discectomy usually have con-sented to surgery after prolonged pain;
they have often undergone repeated courses of ineffective conservative
management and pre-vious surgeries to relieve the pain. Therefore, the
recurrence or persistence of symptoms postoperatively, including pain and
sen-sory deficits, is often discouraging for the patient and family. The
patient who experiences recurrence of symptoms requires emo-tional support and
understanding. Additionally, the patient is assisted in modifying activities
and in considering options for subsequent treatment.
The patient with degenerative disk disease tends to focus
on obvious needs, issues, and deficits. The nurse needs to remind pa-tients and
family members of the need for participating in health promotion and health
screening practices.
Evaluation
EXPECTED PATIENT OUTCOMES
Expected patient outcomes may include:
1) Reports
decreasing frequency and severity of pain
2) Demonstrates
improved mobility
a) Demonstrates
progressive participation in self-care activities
b) Identifies
prescribed activity limitations and restrictions
c) Demonstrates
proper body mechanics
3)Is
knowledgeable about postoperative course, medications, and home care
management.
a) Lists
the signs and symptoms to be reported post-operatively
b) Identifies
dose, action, and potential side effects of medications
c) Identifies
appropriate home care management activities and any restrictions
4)Absence
of complications
a) Reports
no increase in incision pain or sensory symptoms
b) Demonstrates
normal findings on neurologic assessment
Related Topics