Chapter: Civil : Railway Airport Harbour Engineering : Railway Engineering : Points and Crossings
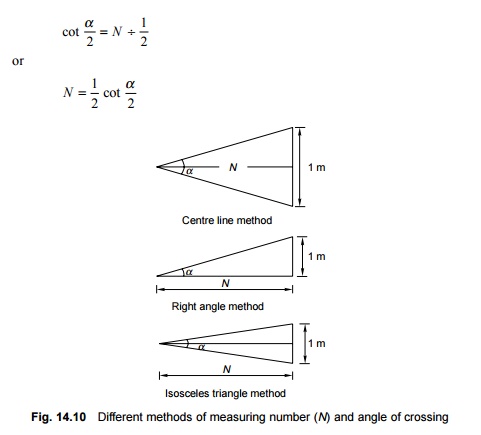
Number and Angle of Railway Crossing
Number and Angle of Crossing
A crossing is designated either
by the angle the gauge faces make with each other or, more commonly, by the
number of the crossing, represented by N. There are three methods of
measuring the number of a crossing, and the value of N also depends upon
the method adopted. All these methods are illustrated in Fig. 14.10.
Centre
line method
This
method is used in Britain and the USA. In this method, N is measured
along the centre line of the crossing.
Fig.
14.10 Different
methods of measuring number (N) and angle of crossing
Right angle method
This
method is used on Indian Railways. In this method, N is measured along
the base of a right-angled triangle. This method is also called Coles method.

Isosceles triangle method
In this
method, N is taken as one of the equal sides of an isosceles triangle.
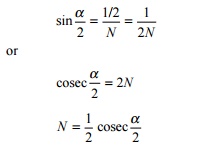
The right angle method used by
Indian Railways, in which N is the cotangent of the angle formed by two
gauge faces, gives the smallest angle for the same value of N.
To determine the number of a
crossing (N) on site, the point where the offset gauge face of the
turnout track is 1 m is marked. The distance of this point (in metres) from the
theoretical nose of crossing gives N.
Related Topics