Definition, Classification, Structure, Functions - Nucleic acids - Biomolecules | 11th Biochemistry : Chapter 2 : Biomolecules
Chapter: 11th Biochemistry : Chapter 2 : Biomolecules
Nucleic acids - Biomolecules
Nucleic acids
Nucleic acids are biopolymers,
essential to all known forms of life.
1. Definition
Nucleic
acids are the polymers of nucleotides. Nucleotides are made of three
components:
·
5-carbon sugar
·
Nitrogenous base
·
Phosphate groups
2. Structure of nucleic acids:
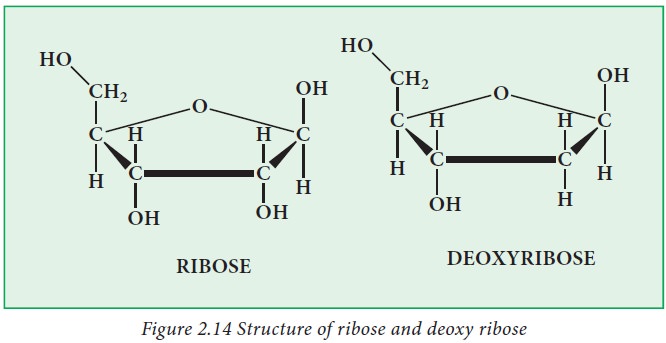
Sugar unit:
If the sugar unit present in the
nucleic acid is a ribose, then the polymer is called ribonucleic acid (RNA) and
if the sugar is deoxyribose, then the polymer is deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA).
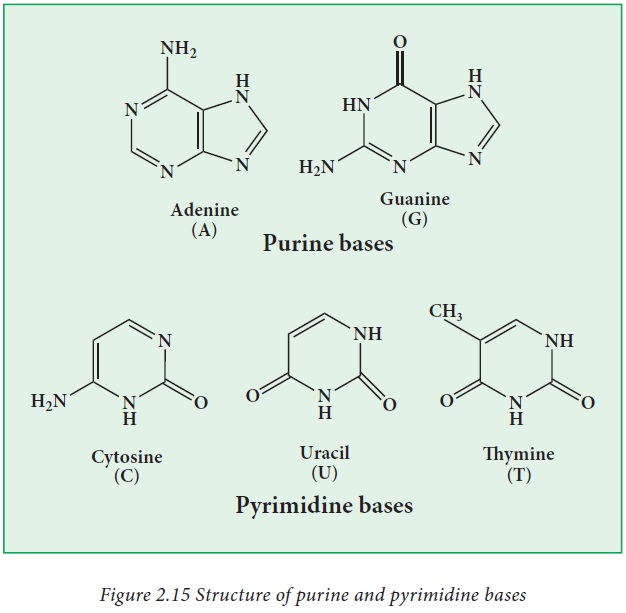
Nitrogen base:
Nucleic
acids contain purine and pyrimidine bases. They are Adenine (A), Guanine (G),
Cytosine(C), Thymine (T) and uracil(U).
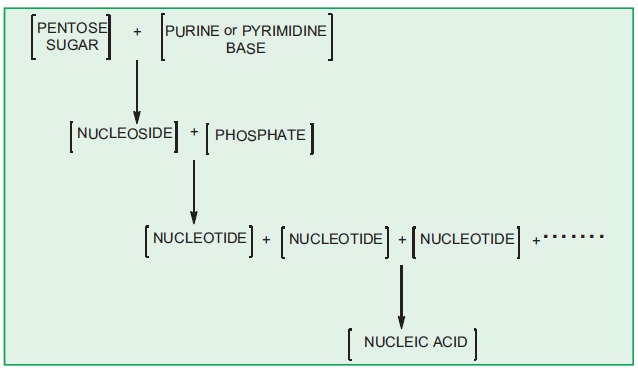
Phosphate group:
In nucleic acids, sugar unit and
nitorgenous base can combine to form a nucleoside, these nucleosides combine
with a phosphate to form a nucleotide, which in turn polymerises to form
nucleic acids.
3. Classification
Nucleic acids are classified into two
types based on the ribose sugar.
a. Deoxyribonucleic acids (DNA)
The most important constituent of
chromosome. DNA is a polymer of nucleotides containing 2-deoxyribose sugar and
nitrogenous bases like Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Thymine (T) andCytosine(C).
b. Ribonucleic acids (RNA)
RNA is a polymer of nucleotides
containing ribose sugar and nitrogenous bases like Adenine (A), Guanine (G),
Uracil(U), and Cytosine(C).
There are three main classes of RNA
molecules, they are
i. Messenger RNA (mRNA). ii. Transfer RNA
(tRNA) iii. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
4. Functions of DNA and RNA:
· The main function of nucleic acids
is to store and transfer genetic information.
· DNA controls the synthesis of RNA
in the cell.
· DNA transmits the genetic
information to mRNA for the synthesis a specific protein.
· RNA directs synthesis of proteins.
· mRNA takes genetic message from
DNA.
· tRNA transfers activated amino
acid, to the site of protein synthesis.
·
rRNA are mostly present in the ribosomes, and responsible
for stability of mRNA.
Related Topics