Chapter: Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology: Tissues
Muscle tissue
Muscle tissue
Discuss the three types of muscle tissue by describingtheir general structures, their locations in the body, and their functions.
The main characteristic of muscle tissue is its ability to contract, or shorten, making movement possible. Muscle contraction results from contractile proteins located within the muscle cells. The length of muscle cells is greater than the \diameter. Muscle cells are sometimes called muscle fibers because they often resemble tiny threads.
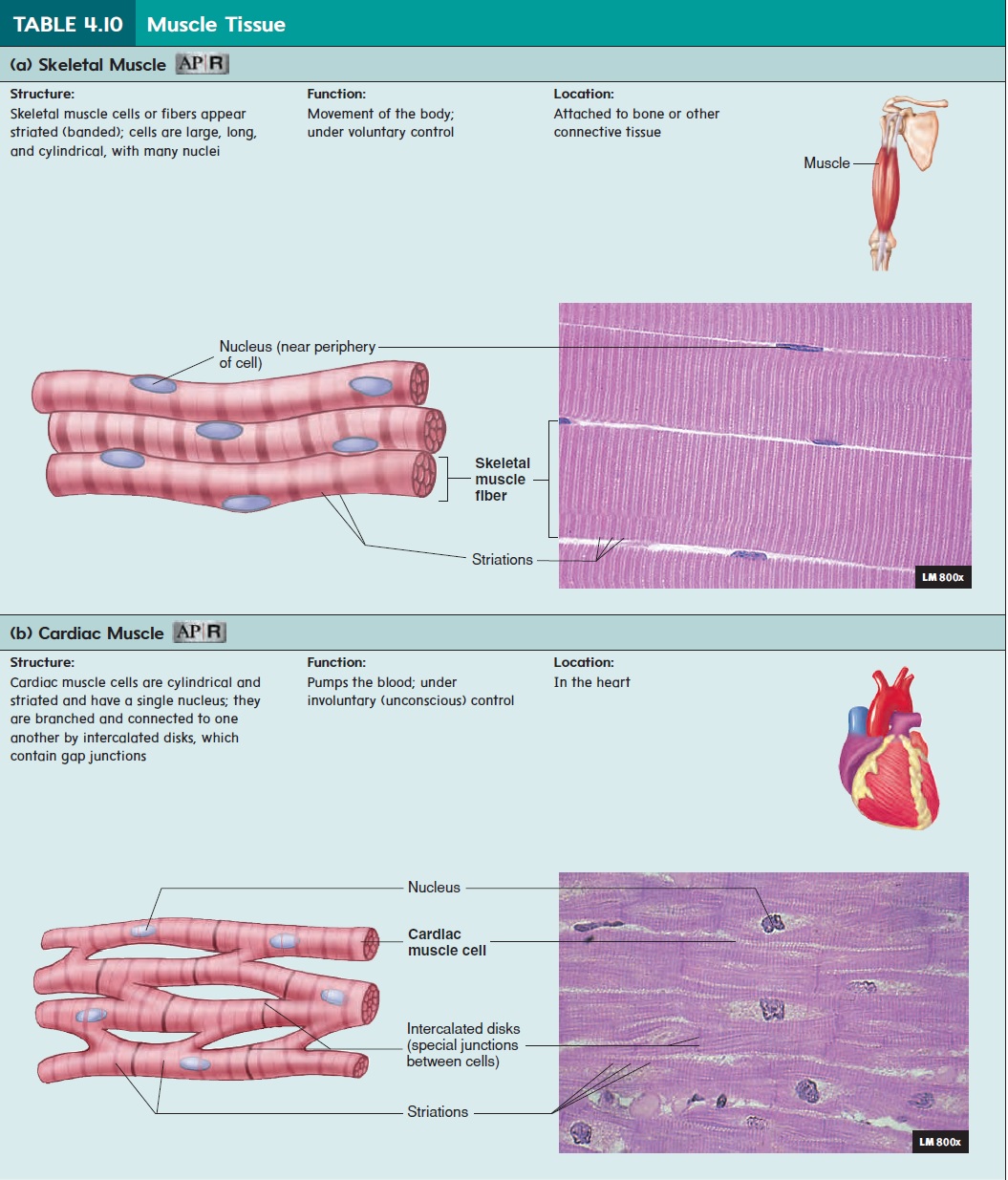
The three types of muscle tissue are skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. Skeletal muscle is what we normally think of as “muscle” (table 4.10a). It is the meat of animals and constitutes about 40% of a person’s body weight. As the name implies, skeletal muscle attaches to the skeleton and enables the body to move. Skeletal muscle is described as voluntary (under conscious \control) because a person can purposefully cause skeletal \muscle contraction to achieve specific body movements. However, the nervous system can cause skeletal muscles to contract without conscious involvement, as occurs during reflex movements and the maintenance of muscle tone. Skeletal muscle cells tend to be long and cylindrical, with several nuclei per cell. Some skeletal muscle cells extend the length of an entire muscle. Skeletal muscle cells are striated (strı̄′\āt-ed), or banded, because of the arrange-ment of contractile proteins within the cells .
Cardiac muscle is the muscle of the heart; it is responsible for pumping blood (table 4.10b). Cardiac muscle is under invol-untary (unconscious) control, although a person can learn to influence the heart rate by using techniques such as meditation and biofeedback. Cardiac muscle cells are cylindrical but much shorter than skeletal muscle cells. Cardiac muscle cells are striated and usually have one nucleus per cell. They are often branched and connected to one another by intercalated (in-ter′\kă-lā-ted)disks. The intercalated disks, which contain specialized gap junc-tions, are important in coordinating the contractions of the cardiac muscle cells .
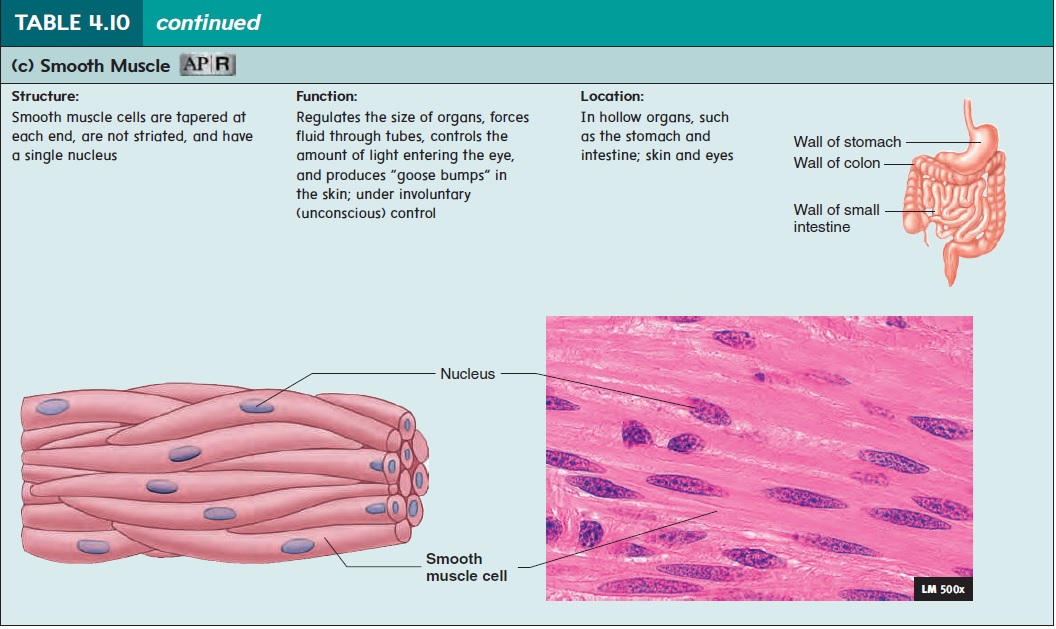
Smooth muscle forms the walls of hollow organs (except the heart); it is also found in the skin and the eyes (table 4.10c). Smooth muscle is responsible for a number of functions, such as moving food through the digestive tract and emptying the urinary bladder. Like cardiac muscle, smooth muscle is controlled invol\ untarily. Smooth muscle cells are tapered at each end, have a single nucleus, and are not striated.
Related Topics