Chapter: 11th Food Service Management : Chapter 3 : Selection of Foods and Methods of Cooking
Methods of Cooking
Methods
of Cooking
“Cooking is the art of preparing food for consumption
commonly with the appli-cation of heat”
Cooking techniques and
ingredients vary widely across the world, reflecting unique environmental,
economical, cul-tural and traditional trends. Art of skill and training are
needed for effective cooking.
1. Objectives of Cooking
Cooking
kills micro-organisms
Sterilizes
food
Helps to
keep food longer
Softens
the food
Aids
digestion
Improves
palatability and quality of food
Introduces
variety and
Increases
the availability of nutrients.
2. Cooking Methods
Heat is transferred to the food
during cooking by conduction, convection and radiation. The manner in which
heat is applied to the food during cooking deter-mines the type of cooking
method used. The methods developed may be classified under three main heads:
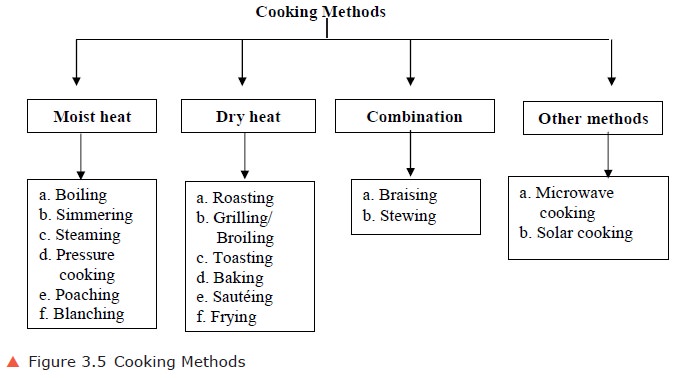
3. Classification of Cooking Methods
I. Moist Heat Methods
a. Boiling:
It is a method of cooking food by just immersing in water at 100°C and
maintaining the water at that temperature till the food becomes tender. Eg:
Rice, egg, dhal, meat, roots and tubers can be cooked by boiling.

b. Simmering: Food is cooked in liquid at a temperature just below the boiling
point.

c. Steaming: It is a method of cook-ing food in steam, generated from vig-orously
boiling water in a pan. Eg: Idli, Idiappam(string hopper) and vegetables are prepared
by steaming.

d. Pressure Cooking: When steam under pressure is used, the method is known as pressure cooking
and the equipment used is pressure cooker. In this meth-od the temperature of
boiling water can be raised above 100°C. Eg: Rice, dhal, meat, roots and tubers can
be pressure cooked.

e. Poaching: This involves cooking in minimum amount of liquid at
temper-atures of 80°C–85°C that is below the boiling point. Eg: Egg and fish can be poached.

f. Blanching: In this method, food is immersed in boiling water for five
seconds to two minutes depending on the texture of the food and put it in cold
water. This helps to remove the skin or peel without softening the food.
Eg: Tomatoes can be blanched.

II. Dry Heat Methods
a.
Roasting: In this method, food is roasted in a heated tawa or frying pan without
covering it. But roasting can be done with or without any medium of cooking.
Eg: Groundnut can be roasted with or without oil.

b.
Grilling/Broiling: Grilling or broiling refers to the cooking of food
by expos-ing it to direct heat. In this method food is placed below or above or
in between a red-hot surface.
Eg: Papads, corn, phulkas, chicken and fish.

c.
Toasting: In this method the food is kept between two heated elements to facilitate
browning on both sides.
Eg: Bread slices can be toasted.

d. Baking: Baking is the method by which food is cooked by hot air. Country
ovens and modern ovens are used for baking. Eg: Bread, cake, biscuits and meat can be baked.

e. Sautéing: It is a method of cooking or browning of food in a pan using a small
quantity of butter, oil or ghee. Eg: Vegetables.

f. Frying: It is the process of cooking food in hot ghee or oil. Food can be cooked
either by shallow frying or by deep frying

·
Shallow
frying means frying in little oil. Eg: Omelette, cutlets.
·
Deep
frying means immersing food fully in hot ghee or oil. Eg: Samosa,
chips, Poori.![]()
III. Combination of Cooking Method
a.
Braising: It is a combined cooking method of frying lightly and stewing it
slowly in a closed container.
Eg: Uppuma –
Roasting and boiling, Cutlet – Boiling and shallow fat frying.
b. Stewing:
It is a combination of sautéing and simmering. Eg: Meat stew.
IV. Other methods
a.
Microwave Cooking: A magnetron tube is a source from where the
electro-magnetic radiation with high frequency wave cooks the food.
Food should be kept in containers made of plastic, glass or chinaware and non-metallic containers. These contain-ers are used because they transmit the microwaves but do not absorb or reflect them.

Eg: Cake can be baked in microwave oven.
b. Solar Cooking: Solar cooking is a very simple technique that makes use of
sun-light or solar energy.
Solar cooker consists of a well-insulated box which is painted black
inside and covered with one or more transparent covers. These covers allow the
radiation from the sun to come inside the box but do not allow the heat from
the hot black absorbing plate to come out of the box.
Because of this, temperature up to 140°C can be obtained which is
adequate for cooking. Solar cooking is free of scorching and oozing of
contents. Eg:
Rice

Related Topics