Chapter: Medical Physiology: Female Physiology Before Pregnancy and Female Hormones
Menopause
Menopause
At age 40 to 50 years, the sexual cycle usually becomes irregular, and ovulation often fails to occur.After a few
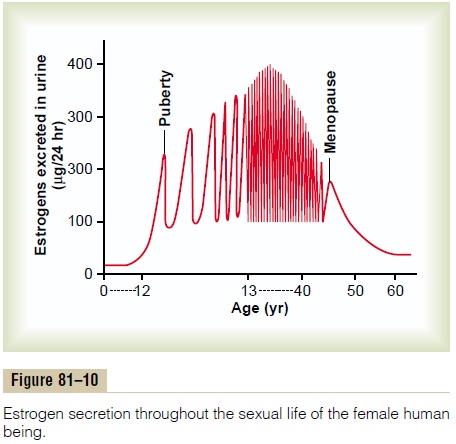
The period during which the cycle ceases and the female sex hormones diminish to almost none is called menopause.
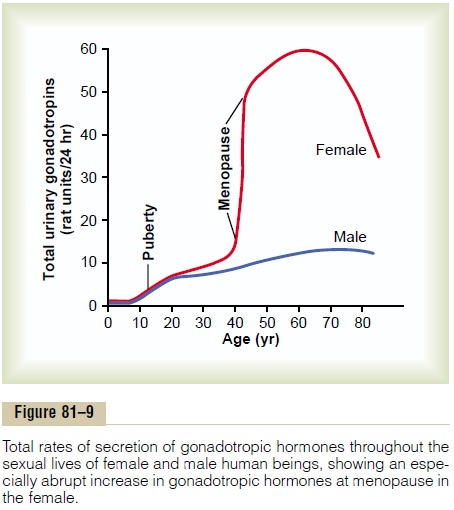
The cause of menopause is “burning out” of the ovaries. Throughout a woman’s reproductive life, about 400 of the primordial follicles grow into mature follicles and ovulate, and hundreds of thousands of ova degenerate. At about age 45 years, only a few primor-dial follicles remain to be stimulated by FSH and LH, and, as shown in Figure 81–10, the production of estrogens by the ovaries decreases as the number of primordial follicles approaches zero. When estrogen production falls below a critical value, the estrogens can no longer inhibit the production of the gonadotropins FSH and LH. Instead, as shown in Figure 81–9, the gonadotropins FSH and LH (mainly FSH) are produced after menopause in large and con-tinuous quantities, but as the remaining primordial fol-licles become atretic, the production of estrogens by the ovaries falls virtually to zero.
At the time of menopause, a woman must readjust her life from one that has been physiologically stimu-lated by estrogen and progesterone production to one devoid of these hormones. The loss of estrogens often causes marked physiological changes in the function of the body, including (1) “hot flushes” characterized by extreme flushing of the skin, (2) psychic sensations of dyspnea, (3) irritability, (4) fatigue, (5) anxiety, (6) occasionally various psychotic states, and (7) decreased strength and calcification of bones through-out the body. These symptoms are of sufficient magni-tude in about 15 per cent of women to warrant treatment. If counseling fails, daily administration of estrogen in small quantities usually reverses the symp-toms, and by gradually decreasing the dose, post-menopausal women can likely avoid severe symptoms.
Related Topics