Chapter: Pathology: Skin Pathology
Melanocytic Tumors
MELANOCYTIC TUMORS
Congenital
nevi (birthmarks) are present at birth; giant congenital nevi
haveincreased risk of developing melanoma.
Nevocellular
nevus (mole) is a benign tumor of melanocytes (melanocytic
nevuscells) that is clearly related to sun exposure. Types of nevi include
junctional, compound, and intradermal. Nevi have uniform tan to brown color
with sharp, well-circumscribed borders and tend to be stable in shape and size.
Malignant trans-formation is uncommon.
Dysplastic
nevi (BK moles) are larger and more irregular than common nevi,
andthey may have pigment variation. Microscopically, the nevus exhibits
cytological and architectural atypia. Dysplastic nevus syndrome is autosomal
dominant (CMM1 locus on chromosome
1); patients often have multiple dysplastic nevi; and there is increased risk
of developing melanoma.
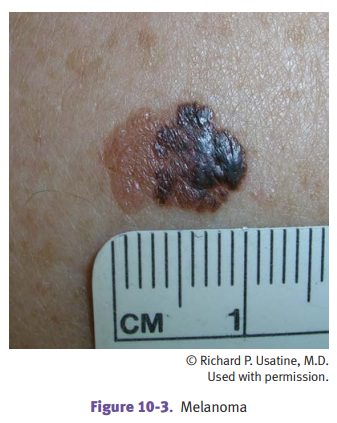
Malignant
melanoma is a malignancy of melanocytes whose incidence is
increasingat a rapid rate, with peak in ages 40–70. Risk factors include
chronic sun exposure, sunburn, fair skin, dysplastic nevus syndrome, and
familial melanoma (associated with loss of function mutation of the p16 tumor
suppressor gene, CDKN2A, on
chromosome 9; somatic mutations of NRAS
and BRAF also occur). Melanomas
characteristically form skin lesions of large diameter with asymmetric and
irregular borders and variegated color; the lesions may be macules, papules, or
nodules. Mela-nomas on males have increased frequency on the upper back;
females have increased frequency on the back and legs.
Several
types of melanomas occur:
·
Lentigo maligna melanoma is usually
located on the face or neck of older indi-viduals and has the best prognosis.
·
Superficial spreading melanoma is
the most common type of melanoma and has a primarily horizontal growth pattern.
·
Acral lentiginous melanoma is the
most common melanoma in dark-skinned individuals; it affects palms, soles, and
subungual area.
·
Nodular melanoma is a nodular tumor
with a vertical growth pattern that has the worst prognosis of the melanomas.
The
prognosis of melanomas is determined
by TNM staging; T status is based on the depth of invasion (Breslow thickness
measured histologically in millimeters).
Local
disease is treated with wide surgical excision and sometimes sentinel node
biopsy. Systemic disease is treated with chemotherapy or immunotherapy.
Metas-tases may occur after years of dormancy.