Alternating Current (AC) - Mean or Average value of AC | 12th Physics : Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current
Chapter: 12th Physics : Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current
Mean or Average value of AC
Mean or Average value of AC
The current and voltage
in a DC system remain constant over a period of time so that there is no
problem in specifying their magnitudes. However, an alternating current or voltage
varies from time to time. Then a question arises how to express the magnitude
of an alternating current or voltage. Though there are many ways of expressing
it, we limit our discussion with two ways, namely mean value and RMS (Root Mean
Square) value of AC.
Mean or Average value of
AC
We have learnt that the
magnitude of an alternating current in a circuit changes from one instant to
other instant and its direction also reverses for every half cycle. During
positive half cycle, current is taken as positive and during negative cycle it
is negative. Therefore mean or average value of symmetrical alternating current
over one complete cycle is zero.
Therefore the average or
mean value is measured over one half of a cycle. These electrical terms,
average current and average voltage can be used in both AC and DC circuit
analysis and calculations.
The average value of
alternating current is defined as the average of all values of current over a
positive half-cycle or negative half-cycle.
The instantaneous value of
sinusoidal alternating current is given by the equation i = I m sin Žē t or i = Im sin╬Ė (where ╬Ė = Žēt)
whose graphical representation is given in Figure 4.41.
The sum of all currents
over a half-cycle is given by area of positive half-cycle (or negative half-cycle).
Therefore,
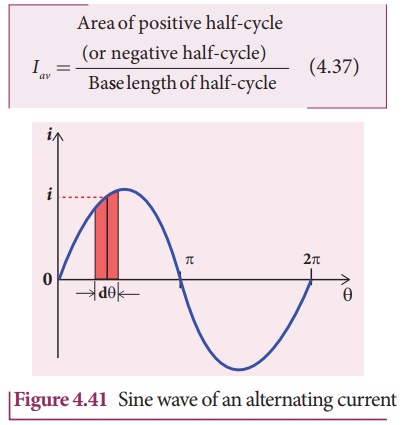
Consider an elementary
strip of thickness d╬Ė in the positive half-cycle of the current wave
(Figure 4.41). Let i be the mid-ordinate of that strip. ![]()
![]()
Area of the elementary
strip = i d╬Ė
Area of positive
half-cycle
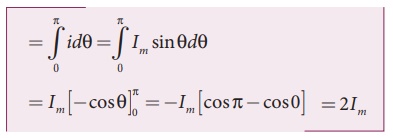
Substituting
this in equation (4.37), we get (The base length of
half-cycle is ŽĆ)
Average value of AC, Iav
= 2Im/ŽĆ
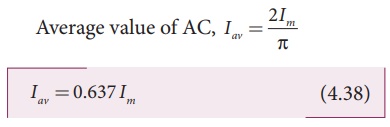
Hence the average value of AC
is 0.637 times the maximum value Im of the alternating
current. For negative half-cycle, av = ŌłÆ0.637 Im .
Related Topics