Chapter: Medical Surgical Nursing: Musculoskeletal Care Modalities
Managing the Patient Undergoing Orthopedic Surgery
Managing
the Patient Undergoing Orthopedic Surgery
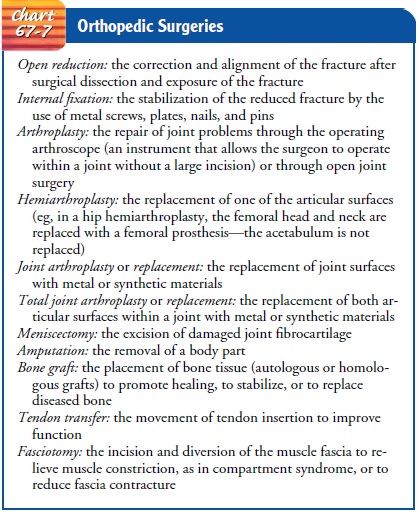
Many patients with
musculoskeletal dysfunction undergo surgery to correct the problem. Problems
that may be corrected by surgery include unstabilized fracture, deformity,
joint disease, necrotic or infected tissue, and tumors. Frequent surgical
procedures include open reduction with
internal fixation (ORIF) and closed re-duction with internal fixation
(fracture fragments are not surgi-cally exposed) for fractures; arthroplasty,
meniscectomy, and joint replacement for joint problems; amputation for severe
extremity problems (eg, gangrene, massive trauma); bone graft for joint
sta-bilization, defect-filling, or stimulation of bone healing; and ten-don
transfer for improving motion. The goals include improving function by
restoring motion and stability and relieving pain and disability. See Chart
67-7 for descriptions of orthopedic surgeries.
Joint surgery is one the most frequently performed
orthopedic surgeries. Joint disease or deformity may necessitate surgical
inter-vention to relieve pain, improve stability, and improve function.
Surgical procedures include excision of damaged and diseased tis-sue, repair of
damaged structures (eg, ruptured tendon), removal of loose bodies
(débridement), arthroplasty
(replacement of all or part of the joint surfaces), and arthrodesis (immobilizing fusion of a joint).
The procedure is based on the patient’s underlying orthope-dic condition, general physical health, impact of joint disability on daily activities, and age. Timing of these procedures is impor-tant to ensure maximum function. Surgery should be performed before surrounding muscles become contracted and atrophied and serious structural abnormalities occur. The physician care-fully evaluates the patient so that the most appropriate procedure is performed.
Because these are
elective procedures, many patients donate their own blood during the weeks
preceding their surgery. This blood is used to replace blood lost during
surgery. Autologous blood trans-fusions eliminate many of the risks of
transfusion therapy.
Also, during surgery blood is conserved to minimize loss.
A pneumatic tourniquet may be applied after exsanguination of the limb with
bandages to produce a “bloodless field.” Intraoperative blood salvage with
reinfusion is used when a large volume of blood loss is anticipated.
Postoperative blood salvage with intermittent autotransfusion also reduces the
need for blood transfusion.
Related Topics