Chapter: Biochemistry: Lipid Metabolism
Lipid Metabolism
Lipid
Metabolism
Introduction
Lipids are organic compounds of biological
nature that includes fats, oils and waxes. They are insoluble in water but
soluble in nonpolar solvents such as ether, chloroform and benzene. Lipids are
utilizable by living organisms.
In the normal mammal at least 10 to 20 percent
of the body weight is lipid. They form important dietary constituent on account
of their high calorific value and fat soluble vitamins (vitamins A, D, E and K)
along with the essential fatty acids. Lipids are distributed in all organs,
particularly in adipose tissues in which lipids represent more than 90 percent
of the cytoplasm of a cell.
Biological functions of Lipids
Lipids are stored in a relatively water - free
state in the tissues in contrast to carbohydrates which are heavily hydrated to
perform a wide variety of functions.
1.
Body
lipids are reservoir of potential chemical energy. Lipids can be stored in the
body in almost unlimited amount in contrast to carbohydrates. Furthermore,
lipids have a high calorific value (9.3 calories per gram) which is twice as
great as carbohydrate. Large amount of energy is stored as lipid than as
carbohydrates.
2.
Lipids
which forms the major constituent of biomembranes are responsible for membrane
integrity and regulation of membrane permeability.
3.
The
subcutaneous lipids serve as insulating materials against atmospheric heat and
cold and protect internal organs.
4.
They
serve as a source of fat soluble vitamins (Vitamin A, D, E and K) and essential
fatty acids. (Linoleic, Linolenic and Arachidonic acid).
5.
Lipids
serve as metabolic regulators of steroid hormones and prostaglandins.
6.
Lipids
present in inner mitochondrial membrane actively participate in electron
transport chain.
7.
Polyunsaturated
fatty acids help in lowering blood cholesterol.
8.
Squalamine,
a steroid, is an potential antibiotic and antifungal agent.
Fatty acids
The fatty acids are the basic units of lipid
molecules. Fatty acids are derivatives of aliphatic hydrocarbon chain that
contains a carboxylic acid group. Over 200 fatty acids have been isolated from
various lipids. They differ among themselves in hydrocarbon chain length,
number and position of double bonds as well as in the nature of substituents
such as oxy-, keto-, epoxy groups and cyclic structure. Depending on the
absence, or presence of double bonds, they are classified into saturated and
unsaturated fatty acids.
Saturated fatty acids, do not contain double
bonds. The hydrocarbon chain may contain 12 to 18 carbon atoms. eg. palmitic
and stearic acids
CH3 (CH2)14 COOH - Palmitic acid (C-16)
CH3 (CH2)16 COOH -
Stearic acid (C-18)
Unsaturated fatty acids are classified into
different types depending on the number of double bonds present in the
hydrocarbon chain. These fatty acids are mainly found in plant lipids.
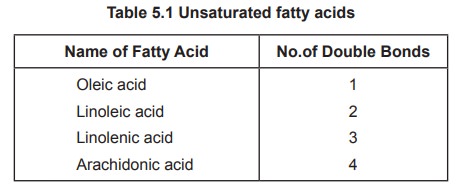
Name of Fatty Acid No.of Double Bonds
Oleic acid
1
Linoleic acid 2
Linolenic acid
3
Arachidonic acid
4
Essential fatty acids
Fatty acids required in the diet are called
essential fatty acids (EFA). They are not synthesized by the body and are
mainly polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA).
eg. Linoleic
acid
Linolenic acid
Arachidonic acid
Functions of essential fatty acids
They are required for membrane structure and
function, transport of cholesterol, formation of lipoproteins and prevention of
fatty liver.
Deficiency of essential fatty acids
The deficiency of essential fatty acid results
in phrynoderma or toad skin.
Related Topics