Chapter: Security Investigation : Security Investigation
Legal, Ethical, and Professional Issues in Information Security
LEGAL, ETHICAL, AND PROFESSIONAL ISSUES IN
INFORMATION SECURITY
ü
Law and
Ethics in Information Security
Laws are rules that mandate or
prohibit certain behavior in society; they are drawn from ethics, which define socially acceptable behaviors. The key
difference between laws and ethics
is that laws carry the sanctions of a governing authority and ethics do not.
Ethics in turn are based on Cultural
mores.
Types of Law
Civil law
Criminal law
Tort law
Private law
Public law
ü
Relevant
U.S. Laws – General
Computer
Fraud and Abuse Act of 1986
National
Information Infrastructure Protection Act of 1996
USA
Patriot Act of 2001
Telecommunications
Deregulation and Competition Act of 1996
Communications
Decency Act (CDA)
Computer
Security Act of 1987
Privacy
ü The issue
of privacy has become one of the hottest topics in information
ü The
ability to collect information on an individual, combine facts from separate
sources, and merge it with other information has resulted in databases of
information that were previously impossible to set up
ü The
aggregation of data from multiple sources permits unethical organizations to
build databases of facts with frightening capabilities
Privacy of Customer Information
· Privacy
of Customer Information Section of Common Carrier Regulations
· Federal
Privacy Act of 1974
· The
Electronic Communications Privacy Act of 1986
· The
Health Insurance Portability & Accountability Act Of 1996 (HIPAA) also
known as the Kennedy-Kassebaum Act
· The
Financial Services Modernization Act or Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act of 1999
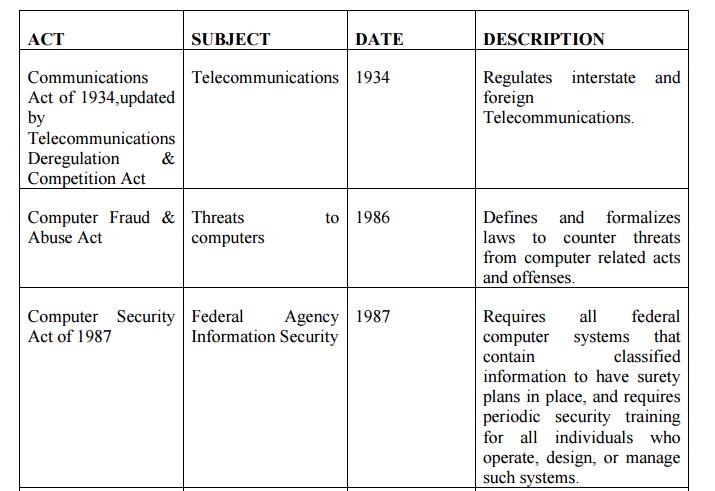
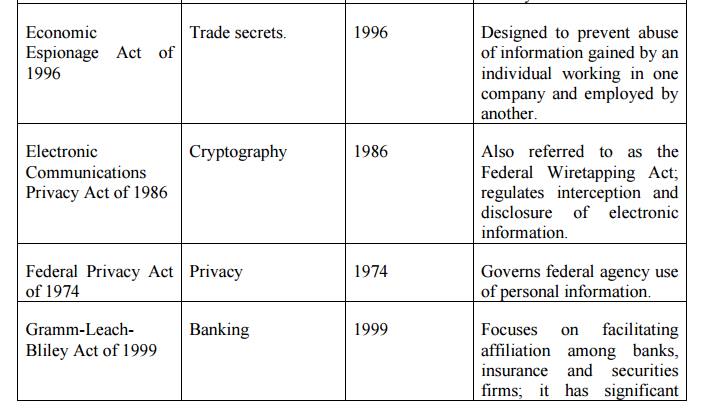
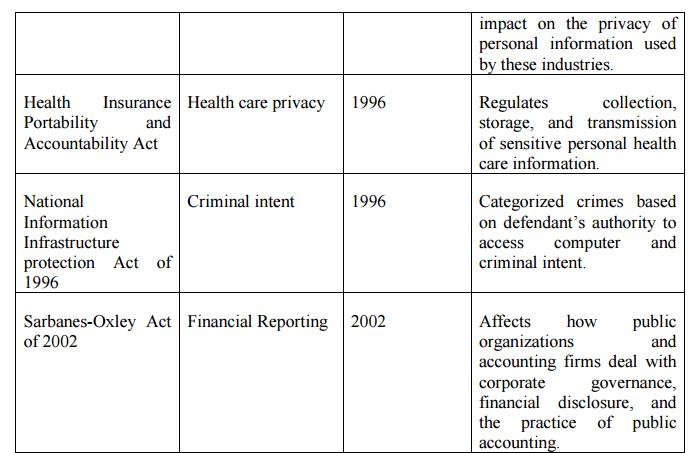
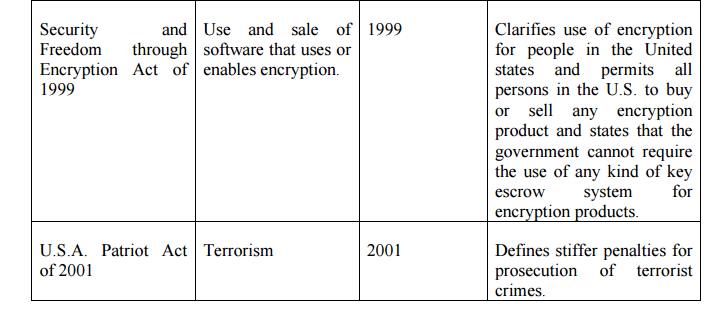
Table 2.5.2.1 Key U.S Laws of Interest to
Information Security Professionals
Export and Espionage Laws
· Economic Espionage Act (EEA) of
1996
· Security and Freedom Through Encryption Act of 1997
(SAFE)
US Copyright Law
ü Intellectual
property is recognized as a protected asset in the US
ü US
copyright law extends this right to the published word, including electronic
formats
ü Fair use
of copyrighted materials includes
the use to support news reporting, teaching,
scholarship, and a number of other related permissions
the purpose of the use has to be for educational or
library purposes, not for profit, and should not be excessive
Freedom of Information Act of 1966 (FOIA)
ü The Freedom of Information Act provides any
person with the right to request access to federal agency records or
information, not determined to be of national security
US Government agencies are required to disclose any
requested information on receipt of a written request
ü There are
exceptions for information that is protected from disclosure, and the Act does
not apply to state or local government agencies or to private businesses or
individuals, although many states have their own version of the FOIA
State & Local Regulations
ü In
addition to the national and international restrictions placed on an
organization in the use of computer technology, each state or locality may have
a number of laws and regulations that impact operations
It is the
responsibility of the information security professional to understand state
laws and regulations and insure the organization’s security policies and
procedures comply with those
laws and
regulations
ü
International
Laws and Legal Bodies
Recently
the Council of Europe drafted the European
Council Cyber-Crime Convention, designed
to create an international task force to oversee a
range of security functions associated with Internet activities,
to standardize technology laws across international
borders
It also
attempts to improve the effectiveness of international investigations into
breaches of technology law
This
convention is well received by advocates of intellectual property rights with
its emphasis on copyright infringement prosecution
Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) Digital
Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA)
ü The
Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) is the US version of an international
effort to reduce the impact of copyright, trademark, and privacy infringement
ü The
European Union Directive 95/46/EC increases protection of individuals with
regard to the processing of personal data and limits the free movement of such
data
ü The
United Kingdom has already implemented a version of this directive called the
Database Right
United Nations Charter
ü To some
degree the United Nations Charter
provides provisions for information security during Information Warfare
ü Information
Warfare (IW) involves the use of information technology to conduct offensive
operations as part of an organized and lawful military operation by a sovereign
state
ü IW is a
relatively new application of warfare, although the military has been
conducting electronic warfare and counter-warfare operations for decades,
jamming, intercepting, and spoofing enemy communications
Policy Versus Law
o
Most organizations develop and formalize a body of
expectations called policy
o
Policies function in an organization like laws
o
For a policy to become enforceable, it must be:
§ Distributed
to all individuals who are expected to comply with it
§ Readily
available for employee reference
§ Easily
understood with multi-language translations and translations for visually
impaired, or literacy-impaired employees
§ Acknowledged
by the employee, usually by means of a signed consent form
o
Only when all conditions are met, does the
organization have a reasonable expectation of effective policy
Ethical Concepts in Information Security
Cultural Differences in Ethical Concepts
· Differences
in cultures cause problems in determining what is ethical and what is not
ethical
· Studies
of ethical sensitivity to computer use reveal different nationalities have
different perspectives
· Difficulties
arise when one nationality’s ethical behavior contradicts that of another
national group
Ethics and Education
Employees
must be trained and kept aware of a number of topics related to information
security, not the least of which is the expected behaviors of an ethical
employee
ü This is especially important in areas of information security, as many employees may not have the formal technical training to understand that their behavior is unethical or even illegal
ü Proper
ethical and legal training is vital to creating an informed, well prepared, and
low-risk system user
Deterrence to Unethical and Illegal Behavior
ü Deterrence
- preventing an illegal or unethical activity
ü Laws,
policies, and technical controls are all examples of deterrents
ü Laws and
policies only deter if three conditions are present:
Fear of penalty
Probability of being caught
Probability
of penalty being administered
Related Topics