Chapter: Microbiology and Immunology: Bacteriology: Treponema, Borrelia and Leptospira
Laboratory Diagnosis - Leptospira interrogans Complex Infections
Laboratory Diagnosis
◗ Specimens
Blood, urine, and CSF are used most commonly for demonstration of leptospires by microscopy or culture.
◗ Microscopy
Dark-field microscopy is employed for direct demonstration of motile leptospires in wet mount preparation of blood speci-men. The method is useful for detection of leptospires in the blood specimens early in the disease, but not in the late stage. The dark-field microscopy, however, is relatively insensitive and also shows false positive results. Protein filaments from eryth-rocytes and other blood artifacts can be easily mistaken for Leptospira. Gram stain or silver impregnation staining methodsare not useful to detect leptospires.
◗ Antigen detection
Direct fluorescent antibody assay is available for detection of leptospira antigen directly in blood or CSF. The method, how-ever, is not widely used due to difficulty in availability of this test.
◗ Culture
Isolation of the organism in culture of blood, CSF, and urine establishes the specific diagnosis of leptospirosis. The positiv-ity of the culture depends upon the time of collection of blood:
Blood culture may be negative if collected too early or too late. Positivity is possible if the specimen is collected 4 days after the onset of symptoms.
CSF culture is positive when specimen is collected within first 10 days, and urine culture remains positive for several weeks after the initial infection.
The specimens are cultured on Fetcher’s, Stuart’s, or EMJH media supplemented with neomycin and 5-fluorouracil. The culture bottles are incubated at 37°C for 2 days and thereafter in the dark, at room temperature for 2 weeks. The cultures are examined every third day for leptospires by examining in dark ground microscope. Primary isolation requires a longer period of incubation for many weeks to months.
The identification of leptospira isolates is made by agglu-tination tests using type-specific sera. The identification of isolates in particular serogroups, serovars, etc., is cumbersome, hence is not carried out in routine laboratories, but at reference laboratories.
◗ Animal inoculation
Leptospires can be isolated by animal inoculation. Blood is the usual specimen, which is inoculated intraperitoneally into young guinea pigs. If blood contains virulent L. interrogans, the guinea pig develops fever, jaundice, and dies within 8–12 days with hemorrhages into the veins and serous cavities.
◗ Serodiagnosis
Serological tests are increasingly used for diagnosis of leptospi-rosis. Microscopic agglutination test (MAT) is the traditional gold standard, available only at reference laboratories, for serodiagnosis of leptospirosis.
MAT: This test depends on the ability of the patient’s serumto agglutinate live leptospires obtained by culture. The MAT test uses a battery of live leptospires serovars commonly prevalent in the area endemic for the disease. The MAT uses a battery of antigens taken from common (frequently locally endemic) leptospire serovars prepared from the leptospire strains cultured on the media. The test is performed by mixing the leptospira antigen with serial dilutions of patient’s sera and examining microscopically for agglutination of leptospira antigens. A single titer exceeding 1:200 or serial dilutions exceeding 1:100 are suggestive of leptospirosis. A fourfold rise in convalescent serum is also considered positive. The MAT is highly sensitive (92%) and specific (95%).
· The MAT shows false negative reaction with serum speci-mens collected in immune phase of the disease and in patients treated with antibiotics.
· The MAT may show false positive reactions with serum from the cases of Lyme disease, Legionella infection, and syphilis.
Other serological tests: There is another group of sero-logical tests, which detect serum-specific antibodies without the exact infective serovars. Nonpathogenic L. biflexa Patoc I strain is employed as antigen in these tests. Examples of such tests are the microscopic slide agglutination test, indirect hemagglutination assay (IHA), the leptospirosis immuno-globulin M (IgM) dipstick test, latex agglutination test, and the Leptospira immunoglobulin G (IgG) ELISA. IgM ELISA is of value for diagnosing new infections within 3–5 days. IHA is also rapid and simple method for diagnosis of the condition.
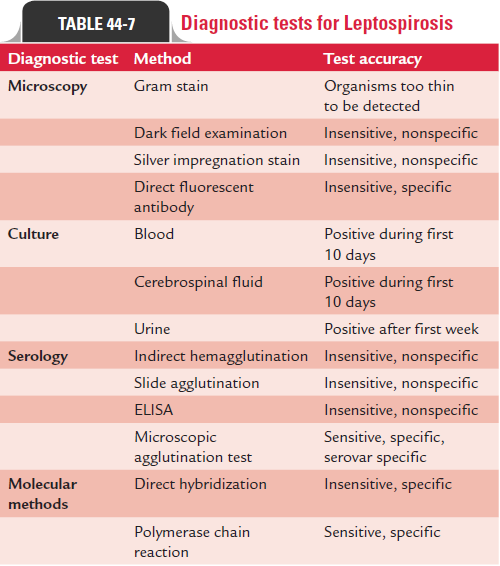
Diagnostic tests for leptospirosis are summarized in Table 44-7.
Related Topics