Chapter: 11th Chemistry : UNIT 10 : Chemical bonding
Kossel - Lewis approach to chemical bonding
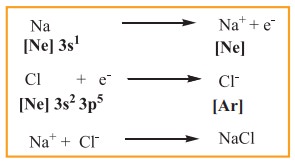
A logical explanation for chemical bonding was provided by Kossel and Lewis in 1916. Their approach to chemical bonding is based on the inertness of the noble gases which have little or no tendency to combine with other atoms. They proposed that the noble gases are stable due to their completely filled outer shell electronic configuration. Elements other than noble gases, try to attain the completely filled electronic configurations by losing, gaining or sharing one or more electrons from their outer shell. For example, sodium loses one electron to form Na+ ion and chlorine accepts that electron to give chloride ion (Cl–), enabling both atoms to attain the nearest noble gas configuration. The resultant ions, Na+ and Cl- are held together by electrostatic attractive forces and the attractive force is called a chemical bond, more specifically an electrovalent bond.
G. N. Lewis proposed that the attainment of stable electronic configuration in molecules such as diatomic nitrogen, oxygen etc… is achieved by mutual sharing of the electrons. He introduced a simple scheme to represent the chemical bond and the electrons present in the outer shell of an atom, called Lewis dot structure. In this scheme, the valence electrons (outer shell electrons) of an element are represented as small dots around the symbol of the element. The first four valence electrons are denoted as single dots around the four sides of the atomic symbol and then the fifth onwards, the electrons are denoted as pairs. For example, the electronic configuration of nitrogen is 1s2, 2s2, 2p3. It has 5 electrons in its outer shell (valence shell). The Lewis structure of nitrogen is as follows.

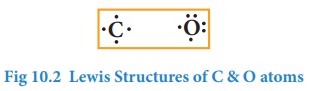
Similarly, Lewis dot structure of carbon, oxygen can be drawn as shown below.
Only exception to this is helium which has only two electrons in its valence shell which is represented as a pair of dots (duet).

Related Topics