Chapter: 11th Commerce : Chapter 3 : Classification of Business Activities
Kinds of Industries
Industry
Industry refers to economic activities,
which are connected with conversion of resources into useful goods. The
production side of business activity is referred as industry. Generally the
term industry is used for activities in which mechanical appliances and
technical skills are involved. These include activities relating to producing
or processing of goods as well as breeding and rising of animals.
The term industry is also used to mean
group of firms producing similar or related goods. For example, cotton textile
industry refers to all manufacturing units producing textile goods from cotton.
Similarly, electronic industry would include all firms producing electronic
goods, and so on. Further, in common parlance, certain services like banking
and insurance are also referred to as industry, say banking industry, insurance
industry etc.
Kinds of Industries
Industries may be classified into two
broad categories,
A. On the Basis of Activities and
B. On the Basis of Size
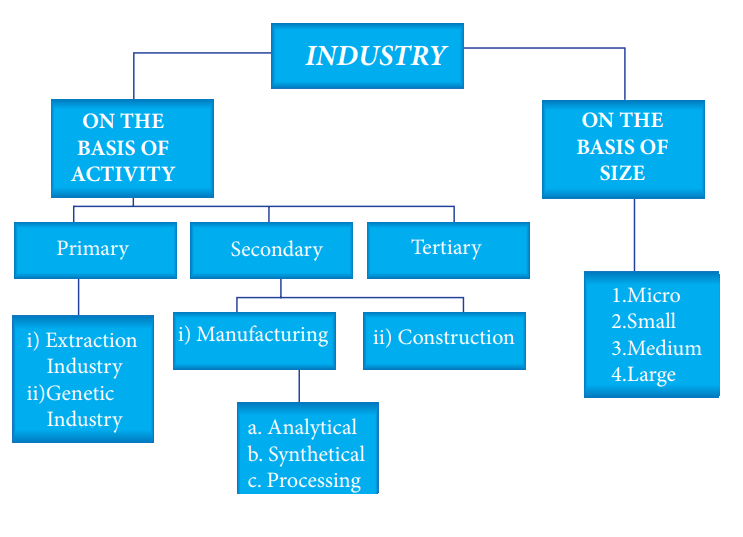
A. On the Basis of Activities
Industries may be divided into three
wide categories namely 1. primary industries,
2. secondary industries and 3.tertiary
industries.
1.
Primary Industries
Primary industry is concerned with
production of goods with the help of nature. It is a nature-oriented industry,
which requires very little human effort,
For example Agriculture, farming, forestry, fishing, horticulture, etc.
These industries may be further sub divided as follows:
(i) Extractive Industries
These industries extract or draw
outproducts from natural sources. Extractive industries

Products of these
industries are usually transformed into many other useful goods by
manufacturing industries. Important extractive industries include farming,
mining, oil drilling, hunting and fishing operations.
(ii) Genetic Industries
These industries remain engaged in breeding plants and animals for their use in further reproduction. The seeds, nursery companies, poultry, diary, piggery, hatcheries, nursery, fisheries, apiary etc are classic examples of genetic industries.

2. Secondary Industries
These are concerned with using the
materials which have already been extracted at the primary stage. These
industries process such materials to produce goods for final consumption or for
further processing by other industrial units. For example mining of an iron ore
is a primary industry, but manufacturing of steel by way of further processing
of raw irons is a secondary industry. Secondary industries may be further
divided as follows:
(i) Manufacturing Industries
These industries are engaged in
producing goods through processing of raw materials and thus creating form
utilities. They bring out diverse finished products, which we consume or use,
through the conversion of raw materials or partly finished materials in their
manufacturing operations. Manufacturing industries may be further divided into
four categories on the basis of method of operation for production.
a.
Analytical Industry which analyses and separates different
elements from the same materials, as in the case of oil refinery.
b.
Synthetic Industry which combines various ingredients into
a new product, as in the case of cement.
c.
Processing Industry which involves successive stages for
manufacturing finished products, as in the case of sugar and paper.
d.
Assembling Industry which assembles different component
parts to make a new product, as in the case of television, car, computer, etc.
(ii)
Construction Industries
These industries are involved in the
construction of building, dams, bridges, roads, as well as tunnels and canals.
3. Tertiary industries or Service industries
They do not produce goods. These
industries produce utility services and sell them at a profit. They help trade,
industry and commerce. This term also includes auxiliaries to trade like
banking, insurance, warehouse, advertisement etc.
Classification of Tertiary Industries
i.
Personalised service: Individuals and private institutions
selling their services to others. E.g. plumber, servant maid, etc.
ii.
Public Service: Government hospitals, schools, police,
Government offices, etc. provide services to the people on behalf of the
Government without profit motive.
iii.
Distributive Service: Transportation, warehousing,
logistics, salesmanship, etc. come under this type of service.
iv.
Financial Service: Banking, factoring, accounting, and
insurance, etc. are grouped under this type of service.
v.
Quaternary Service: Professional or specialised skills and
high technology are used to provide this type of service. E.g. Software
development, Auditing, Research and Development, etc.
vi.
Quinary Service: New ideas are generated, new
technologies are evolved, new policies are implemented by selected individual
experts. Their decisions influence nations, international institutions, etc.
i.e., Inventors.
B. On the basis of Size
On the basis of size or scale of
operations industries may be classified as follows
1.
Micro Industries
2.
Small Industries
3.
Medium Industries and
4.
Large Industries
Related Topics