Chapter: 10th Science : Chapter 12 : Anatomy and Plant Physiology
Internal Structure of Monocot Stem (Maize)
Internal
Structure of Monocot Stem (Maize)
A transverse section of
monocot stem reveals the following structures.
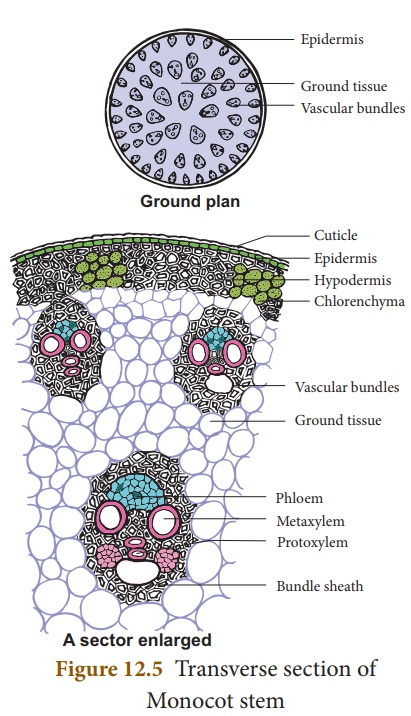
1. Epidermis: It is the outermost
layer. It is made up of single layer of parenchyma cells. It is covered
with thick cuticle. Multicellular hairs are absent and stomata are also less in
number.
2. Hypodermis: It is made up of few layers of
sclerenchyma cells interrupted by chlorenchyma. Sclerenchyma provides
mechanical support to plant.
3. Ground tissue: The entire mass of parenchyma cells next to hypodermis and extending to the centre is called ground tissue. It is not differentiated into endodermis, cortex, pericycle and pith.
4.
Vascular Bundle:
Vascular bundles are skull shaped and scattered in the ground tissue. Vascular
bundles are conjoint, collateral, endarch and closed. Each vascular bundle is
surrounded by few layer of sclerenchyma cells called bundle sheath.
(a)
Xylem: It
consists of metaxylem and protoxylem. Xylem vessels are arranged in V or Y
shape. In mature vascular bundle, the lower most protoxylem disintegrates and
form a cavity. This is called protoxylem
lacuna.
(b)
Phloem: It
consists of sieve tube elements and companion cells. Phloem parenchyma, and
phloem fibers are absent.
5.
Pith: Pith is
not differentiated in monocot stems.
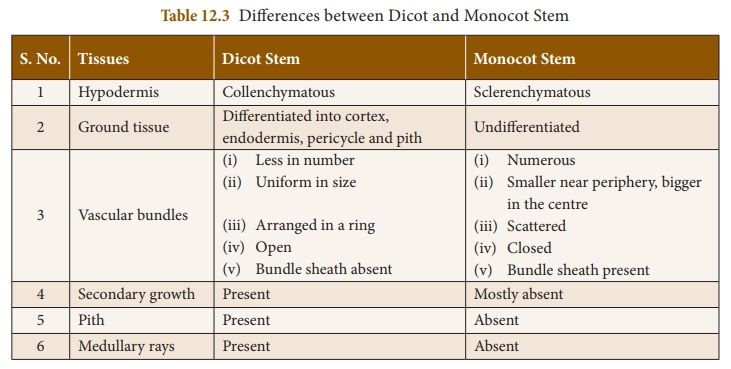
Differences between Dicot and Monocot Stem
Related Topics