Chapter: Mathematics (maths) : Initial Value Problems for Ordinary Differential Equations
Initial Value Problems for Ordinary Differential Equations
Numerical Solution of ordinary Differential equations
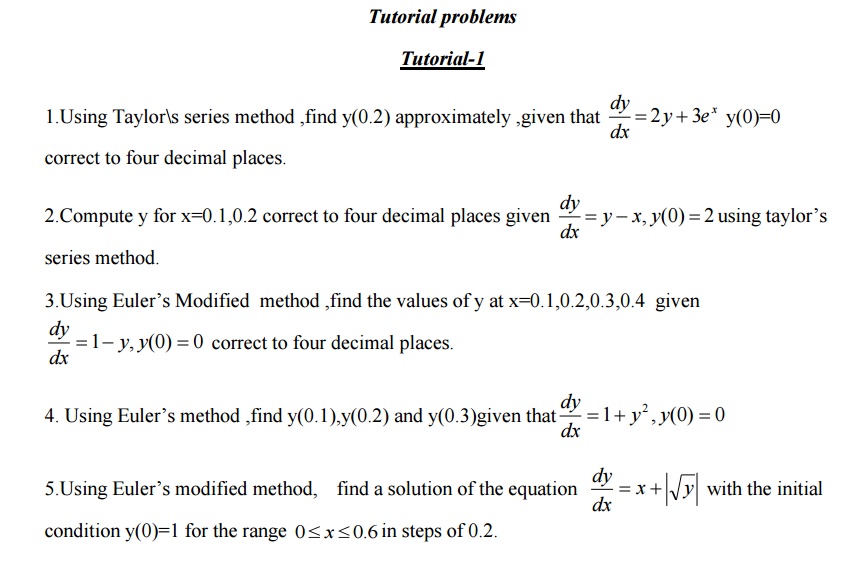
1 Taylor`s Series Method
Power Series Solution
Pointwise Solution
Taylor series method for Simultaneous first order
2 Euler Methods
Euler Method
Modified Euler Method
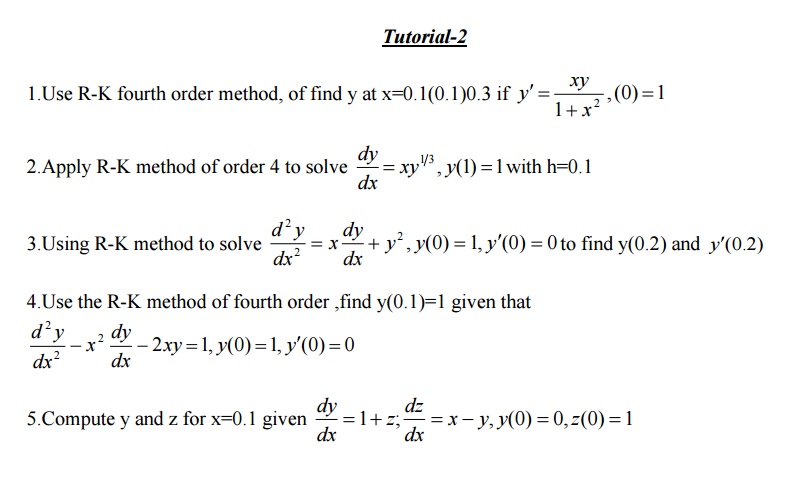
3 Runge – Kutta Method
Fourth order Runge-kutta Method
Runge-Kutta Method for second order differential equations
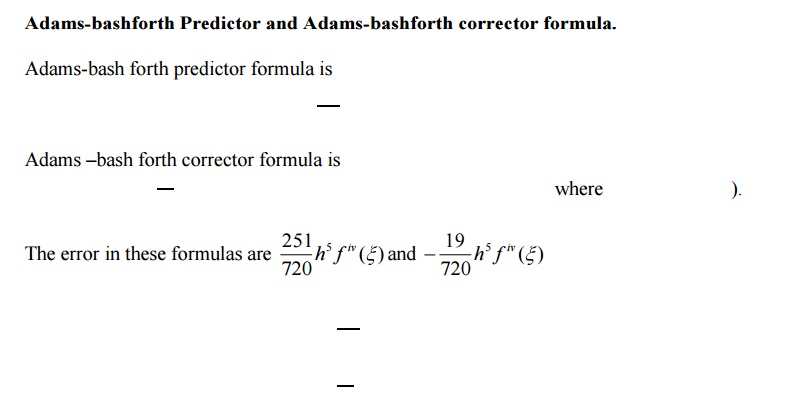
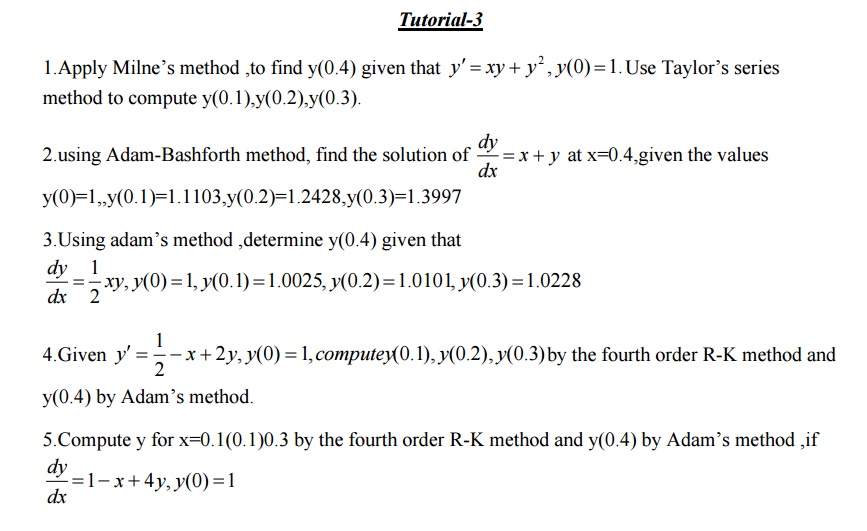
4 Multi-step Methods (Predictor-Corrector Methods)
Milne`s Method
Adam`s Method
Introduction
An ordinary differential equation of order n is a relation of the form
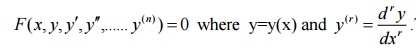
The solution of this differential equation involves n constants and these constants are determined with help of n conditions.
Single step methods
In these methods we use information about the curve at one point and we do not iterate the solution. The method involves more evaluation of the function. We will discuss the Numerical solution by Taylor series method, Euler methods and Runge - Kutta methods all require the information at a single point x=x0.
Multi step methods
These methods required fewer evaluations of the functions to estimate the solution at a point and iteration are performed till sufficient accuracy is achieved. Estimation of error is possible and the methods are called Predictor-corrector methods. In this type we mainly discuss Milne’s –and Bashforth Adams method.
In the multi step method , to compute yn+1,we need the functional values yn,yn-1, yn-2 and yn-3.
1 Taylor Series method
Consider the first order differential equation
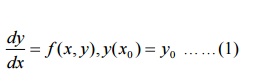
The solution of the above initial value problem is obtained in two types
Ø Power series solution
Ø Point wise solution
Power series solution
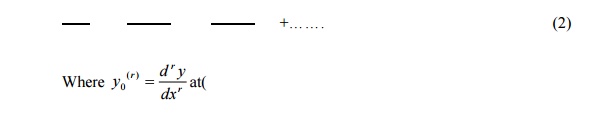
Using equation (1) the derivatives can be found by means of successive differentiations .Expressions (2) gives the value for every value of x for which (2) converges.
(ii)Point wise solution

2. Find the Taylor series solution with three terms for the initial value problem. = +y,y(1)=1.

2 EULER’S METHOD:
In Taylor’s series method, we obtain approximate solutions of the initial value problem
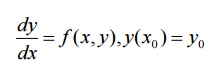
as a power series in x , and the solution can be used to compare y numerically specified value x near x0.

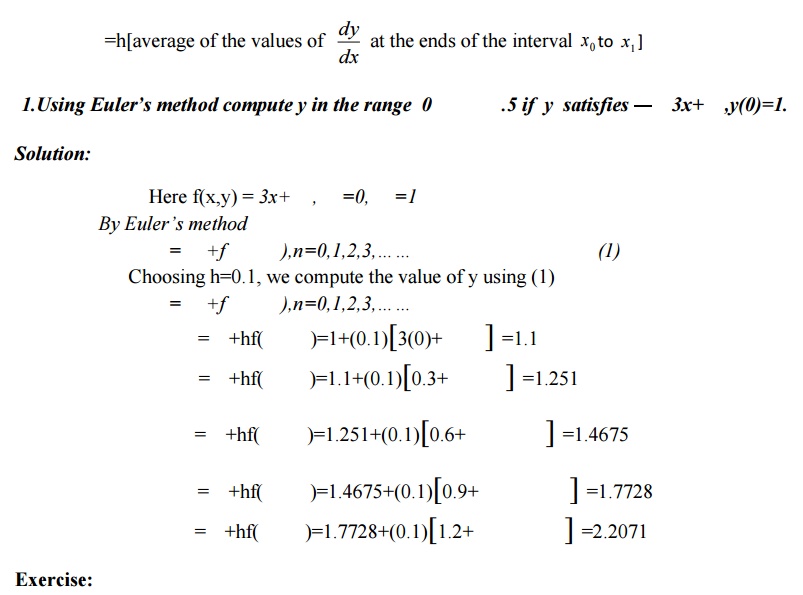
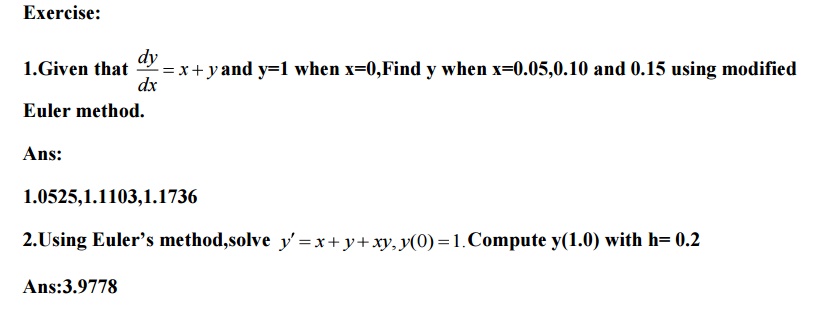
MODIFIED EULER’S METHOD:
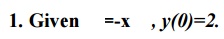
Using Euler’s modified method, find y(0.2)in two steps of 0.1 each.

=2+0.05[0+(-0.1)(4)]
![]() 1.98
1.98
Y(0.1)=1.98
To find y(0.2)
=1.98 –(0.1)(0.1)(1.98)=1.9602 + f( f( ]
![]()
=1.9602-(0.05)[(0.198)+(0.39204)]
Hence y(0.2)=1.9307
3 Runge-kutta method
The Taylor’s series method of solving diff because of the evaluation of the higher order derivatives. Runge-kutta methods of solving intial value problems do not require the calculations of higher order derivatives and give greater accuracy.The Runge-Kutta formula posses the advantage of requiring only the function values at some selected points.These methods agree with Taylor series solutions upto the term in hr where r is called the order of that method.
Fourth-order Runge-Kutta method
This only is commonly used for solving initial values problem

Choosing h=0.1,x1=0.1
Then by R-K fourth order method,
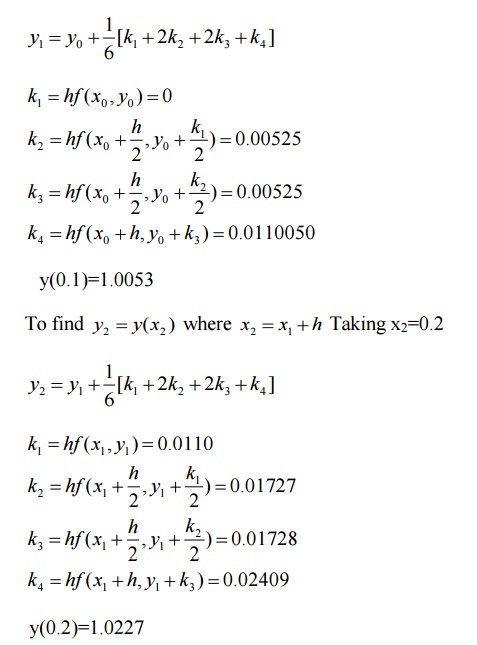
y(0.2)=1.0227
2.Apply Runge –kutta method to find an approximate value of y for x=0.2 in steps of 0.1 if

Here f(x,y)=x+y2,x0=0,y(0)=1
Then by R-K fourth order method,
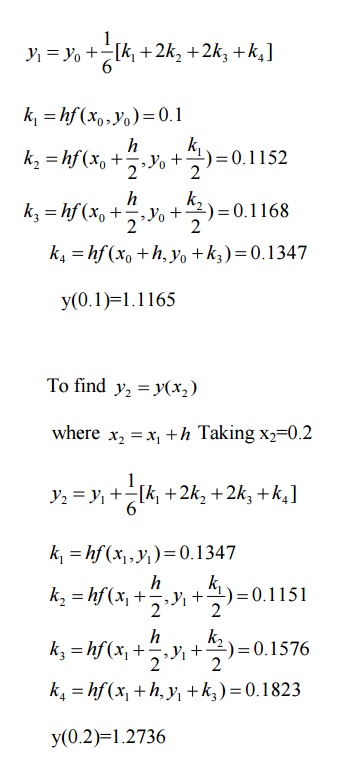
4 Multi step methods(Predictor-Corrector Methods)
Introduction
Predictor-Corrector Methods are methods which require function values at
xn , xn - 1 , xn- 2 , xn -3 for the compulation of the function value at xn+1.A predictor is used to find the value of y at xn+1 and then a corrector formula to improve the value of yn+1.
The following two methods are discussed in this session.
Milne’s method
Adam’s method.
Milne’s -Corrector Predictor method
Milne’s predictor formula is

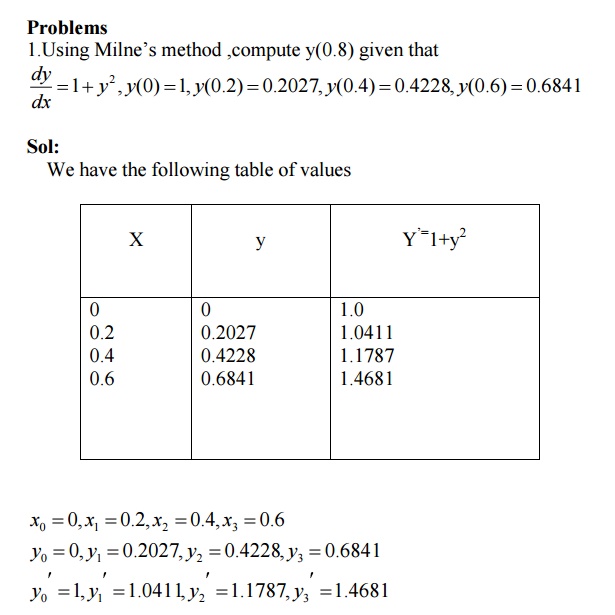


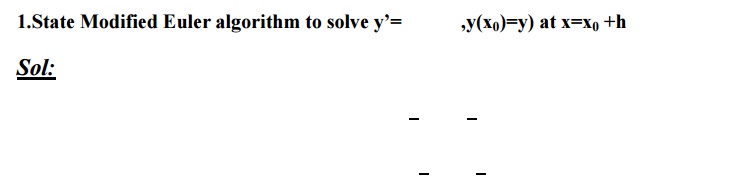
2. State the disadvantage of Taylor series method.
Sol:
In the differential equation f (x, y), = f (x, y), the function f (x, y),may have a complicated algebraical structure. Then the evaluation of higher order derivatives may become tedious. This is the demerit of this method.
3. Write the merits and demerits of the Taylor method of solution.
Sol:
The method gives a straight forward adaptation of classic to develop the solution as an infinite series. It is a powerful single step method if we are able to find the successive derivatives easily. If f (x.y) involves some complicated algebraic structures then the calculation of higher derivatives becomes tedious and the method fails.This is the major drawback of this method. However the method will be very useful for finding
the starting values for powerful methods like Runge - Kutta method, Milne’s me
4.Which is better Taylor’s method or R. K. Method?(or) State the special advantage of Runge-Kutta method over taylor series method
Sol:
R.K Methods do not require prior calculation of higher derivatives of y(x) ,as the Taylor method does. Since the differential equations using in applications are often complicated, the calculation of derivatives may be difficult.
Also the R.K formulas involve the computation of f (x, y) at various positions, instead of derivatives and this function occurs in the given equation.
5.Compare Runge-Kutta methods and predictor –corrector methods for solution of initial value problem.
Sol:Runge-Kutta methods
1.Runge-methods are self starting,since they do not use information from previously calculated points.
2.As mesne are self starting,an easy change in the step size can be made at any stage. 3.Since these methods require several evaluations of the function f (x, y), they are time consuming.
4.In these methods,it is not possible to get any information about truncation error. Predictor Corrector methods:
1.These methods require information about prior points and so they are not self starting. 2.In these methods it is not possible to get easily a good estimate of the truncation error.
6. What is a Predictor-collector method of solving a differential equation?
Sol:
Predictor-collector methods are methods which require the values of y at xn,xn-1,xn-2,… for computing the value of y at . x n+1We first use a formula to find the
value of y at . x n+1 and this is known as a predictor formula.The value of y so got is improved or corrected by another formula known as corrector formula.
7. State the third order R.K method algorithm to find the numerical solution of the first order differential equation.
Sol:
To solve the differential equation y′ f (=x, y) by the third order R.K method, we use the following algorithm.



Related Topics