Chapter: Pathology: Joint Pathology
Infectious Arthritis
INFECTIOUS ARTHRITIS
Suppurative arthritis may result from seeding of
the joint during bacteremia. Other routes include spread from an
adjacent site of infection and direct inoculation. Infecting organisms include
gonococci, Staphylococcus, Streptococcus,
H. influen-zae, and gram-negative
bacilli.
Suppurative arthritis causes
a tender, painful, swollen, and erythematous joint. Large joints (knee, hip,
shoulder) are most often infected, and the arthritis is usually monoarticular.
Joint aspiration shows cloudy synovial fluid that clots readily and has a high
neutrophil count. Gram stain and culture are positive in 50–70% of cases.
Treatment is rapid intervention with antibiotics to prevent permanent joint
damage.
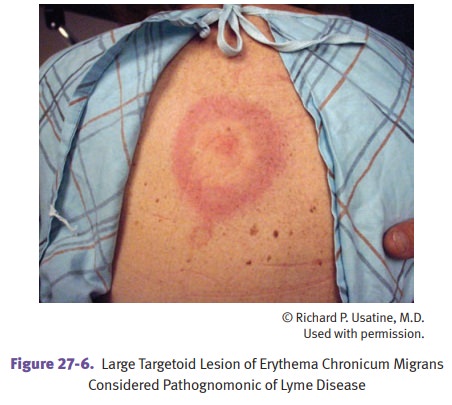
Lyme disease is caused by the spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi. The disease is
arthro-pod-borne, spread by deer ticks (Ixodes
dammini). Symptoms are skin rash (ery-thema chronicum migrans), and
migratory arthritis involving the knees, shoulders, and elbows. The histology
of the arthritic joint is similar to RA. Lyme disease can also have CNS and
cardiac involvement. Serologic tests may remain negative until infection has
been present for several weeks.
Related Topics