Chapter: Mechanical : Dynamics of Machines : Single Degree Free Vibration
Important Short Questions and Answers: Single Degree Free Vibration
SINGLE DEGREE FREE VIBRATION
1. How will
you classify vibration? (Or) what are the different type f vibratory motions?
• Free vibrations
• Longitudinal vibration,
• Transverse vibration, and
• Torsional vibration.
• Forced vibrations, and
• Damped vibration.
2. What are
the causes and effect of vibration?
The
causes of vibration are unbalanced forces, elastic nature of the system, self
excitation, wind and earthquakes.
The
existence of vibration elements in any mechanical system produces unwanted
noise, high stress, poor reliability and premature failure of one or more of
the parts.
3. What do
you mean by a degree of freedom or movability?
The
number of independent coordinates required to completely define the motion of a
system is known as degree of freedom of the system.
4. What is
the limit beyond which damping is detrimental and why?
When
damping factor x > 1, the aperiodic motion is resulted.
That is, aperiodic motion means the system cannot vibrate due to over damping.
Once the system is disturbed, it will take infinite time to come back to
equilibrium position.
5. What is
meant by critical damping?
The
system is said to be critically damped when the damping factor Ϛ = 1. If the
system is critically damped, the mass moves back very quickly to its
equilibrium position within no time.
6. Define
critical or whirling or whipping speed of a shaft? Give one application of
critical damping.
The speed
at which resonance occurs is called critical speed of the shaft . In other
words, the speed at which the shaft runs so that the additional deflection of
the shaft from the axis of rotation becomes infinite is known as critical
speed.
The
property of critical damping is used in designing elecrical instruments,
hydraulic door closers and large guns.
7. What are
the factors that affect the critical speed of a shaft?
The
critical speed essentially depends on:
• The eccentricity of the C.G of the
rotating masses from the axis of rotation of the shaft,
• Diameter of the disc,
• Span of the shaft, and
• Type of supports connections at its ends.
8. What is
the effect of inertia on the shaft in longitudinal and transverse vibrations?
In
longitudinal vibrations, he inertia effect of the shaft is equal to the that of
a mass one third of the mass of the shaft concentrated at its free end.
9. Define
logarithmic decrement.
Logarithmic
decrement is defined as the natural logarithm of the amplitude reduction
factor. The amplitude reduction factor is the ratio of any two successive
amplitudes on the same side of the mean position.
10. Define
damping factor and damping co-efficient.
• The
damping factor or damping ratio is defined as the ratio of actual damping
coefficient (c) to the critical damping co-efficient(cc).
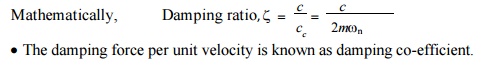
11. Define
node in torsional vibration. (or) what is nodal section in two rotor system.
Node is
the point or the section of the shaft at which amplitude of the torsional
vibration is zero. At nodes, the shaft remains unaffected by the vibration.
12. What is
difference between damping, viscous damping and Coloumb damping?
• Damping: The resistance against the
vibration is called damping.
• Viscous Damping is the damping provided by
fluid resistance.
• Coloumb damping is the dampin results from
two dry or unlubricated surfaces rubbing together.
13. Define
torsional equivalent shaft?
A shaft
having diameter for different lengths can be theoretically replaced by an
equivalent shaft of uniform diameter such that they have the same total angle
of twist when equal opposing torques are applied at their ends. Such a
theoretically replaced shaft is known as torsion ally equivalent shaft.
14. Determine
the natural frequency of mass of 10kgsuspended at the bottom of two springs of
stiffness: 5 N/mm and 8 N/mm in series.
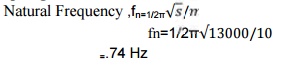
15. State
natural frequency of torsional vibration of a simple system?
Natural
frequency of torsional vibration,
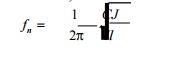
Where C =
Rigidity modulus of shaft, I = Mass M.I. of rotor, J = polar M.I of shaft, and
l =
Length of node from rotor.
Related Topics