Chapter: Physics : Photonics and fibre Optics
Important Short Questions and Answers: Photonics and fibre Optics
1. Give four applications of fiber optic sensors.
a) Fiber optic sensors are used as optical displacement sensors, which is used to find the displacement of a target along with its position.
b) It is used as fluid level detector.
c) It is used to sense the pressure, temperature at any environment.
d) It is also used to measure the number of rotations of the fiber coil using the instrument called a gyroscope.
2. Explain the basic principle of fiber optic communication.
Total internal reflection is the principle of fiber optic communication.
Principle:
When light travels from a denser to rarer medium, at a particular angle of incidence called the critical angle, the ray emerges along the surface of separation. When the angle of incidence exceeds the critical angle, the incident ray is reflected in the same medium and this phenomenon is called the total internal reflection.
3. Give the application of fiber optical system.
a) It can be used for long distance communication in trunk lines.
b) A large no of telephone signals nearly 15000 can be passed through the optical fibers in a particular time without any interference.
c) It is used in computer networks especially in LAN.
d) It is also used as optical sensor.
4. Mention any four advantages of LED in electronic display.
a) Very small in size.
b) Different colours of display.
c) Works under a wide range of temperature.
d) It is a very wide range of operation.
5. Mention any four advantages of fiber optic sensors.
a) It has no external interference
c) It is used in remote sensing.
d) Safety of data transfer.
e) It is small in size.
6. Mention any two fiber optic sources.
a) Light emitting diode (LED) in LED we have two types 1.planar 2.dome shaped LED.
b) Laser diodes (LD). In laser diodes we have homojunction laser heterojunction laser injection laser diode etc.
7. What is meant by injection luminescence? Give examples.
When the majority careers are injected from P to N and N to P region, they become excess minority carriers. Then this excess minority carrier diffuses away from the junction and recombines with the majority carriers in P and N region and emits light. This phenomenon is known as injection luminescence.
8. What is meant by LED? Give its principle.
An LED is the abbreviation of light emitting diode. It is a semiconductor P N junction diode which converts electrical energy to light energy under forward biasing. 9. What is the principle used in PIN photodiode?
This diode works in reverse bias. Under reverse bias when light is made to fall on the neutral or intrinsic region electron hole pairs are generated. These electrons and holes are accelerated by the external electric field, which results in photo current. Thus light is converted into electrical signal.
10. Give any four examples of intrinsic sensor.
a) Pressure sensor
b) Liquid level sensor
c) Phase and polarization sensor.
d) Optical fiber flow sensor.
11. 10. Give any four examples of extrinsic sensor.
a) Displacement sensor
b) Laser Doppler velocimter sensor
c) Fluor optic temperature sensor
d) Current measurement sensor
12. State the applications of optical fibers in medical field.
a) Fiber optics endoscopes are used in medical diagnosis
b) It is used to visualize the inner organs of the body
c) Fibers as endoscopes are used in various medical fields such as cardioscopy, laparoscopy, cryoscopy etc.
13. What is meant by attenuation?
It is defined as the ratio of the optical power (Pout) from a fiber of length ‘L’ to the power input (Pin).
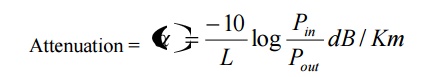
14. Mention the advantages of optical fiber communication over radio wave communication.
a) Optical communication can be made even in the absence of electricity
b) The optical signals are not affected by any electrical signals or lightening
c) Optical fiber communication is free from electromagnetic interference(EMI)
d) This type of communication is suitable to any environmental conditions
e) Easy maintenance, longer life, economical and high quality signal transmission are the additional features of optical fiber communication.
15. What are the losses that occur during optical fiber communication?
During the transmission of light through the optical fiber, three major losses will occur, viz., attenuation, distortion, and dispersion.
Attenuation is mainly caused due to absorption, scattering and radiation of light inside the fibers.
Distortion and dispersion occurs due to spreading of light and also due to manufacturing the defects.
16. What are the conditions of Total Internal reflection?
a) Light should travel from denser medium to rarer medium
b) The angle of incidence(Ф) on core should be greater than critical angle (Фc)
Ф> Фc
c) The refractive index of the core (n1) should be greater than the refractive index of the cladding (n2).
n1 > n2
Related Topics