Chapter: Biotechnology Applying the Genetic Revolution: Pathway Engineering
Ice Forming Bacteria and Frost
ICE-FORMING
BACTERIA AND FROST
Perhaps the simplest
“pathway” of all is the conversion of water to ice. This process may be
“catalyzed” by proteins known as ice
nucleation factors. On a microscopic scale, solidifying water forms crystals
of ice. However, ice crystals need a microscopic nucleus or “seed” to form
around. In the absence of structures allowing nucleation, water will supercool
down to –8 °C without solidifying. Thus, ice nucleation factors are specialized
proteins, mostly found in certain bacteria, which provide nuclei for
crystallization.
Each year, frost causes more
than a billion dollars in damage to crops in the United States alone. It is not
the low temperature itself that does the damage. When water freezes to form ice,
it expands, damaging plant tissues. The seeding of ice crystals on and within
plants is mostly due to proteins on the surface of bacteria, especially Pseudomonas syringae and related
species, which live on plants. The ice crystals that form damage the plant
tissues and disrupt the vessels (xylem and phloem) that carry water and
nutrients throughout the plant. If ice-nucleating bacteria are absent, ice
fails to form and instead the water supercools, leaving the plants unharmed.
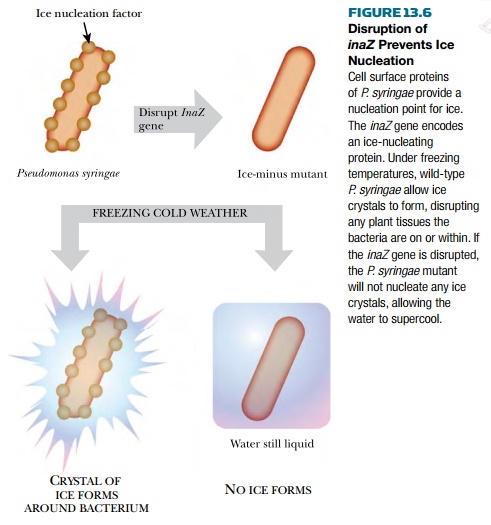
The best known ice-nucleation
protein is encoded by the inaZ gene of Pseudomonas syringae.
Like most bacteria, E. coli does not
normally promote ice formation, although if it expresses a cloned inaZ gene it will gain ice-nucleating
ability. Conversely, when the inaZ
gene of Pseudomonas syringae is
disrupted, ice-nucleating ability is lost (Fig. 13.6). The wild, “ice-plus”
strains of Pseudomonas syringae can
be displaced by spraying the “ice-minus” mutants onto crops that are at risk
from frost damage. Subsequently, even if the temperature falls below freezing,
very few ice crystals form and most of the plants are unharmed.
Related Topics