Chapter: Modern Analytical Chemistry: Chromatographic and Electrophoretic Methods
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC): Quantitative Applications and Representative Method
Quantitative Applications
HPLC is routinely used for both
qualitative and quantitative analyses of environ- mental, pharmaceutical, industrial, forensic,
clinical, and consumer
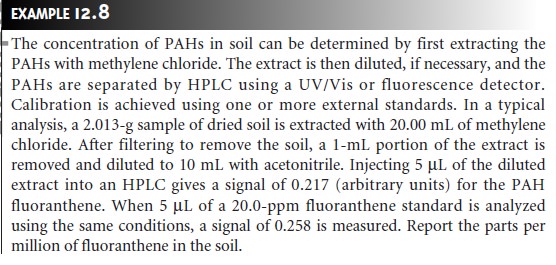
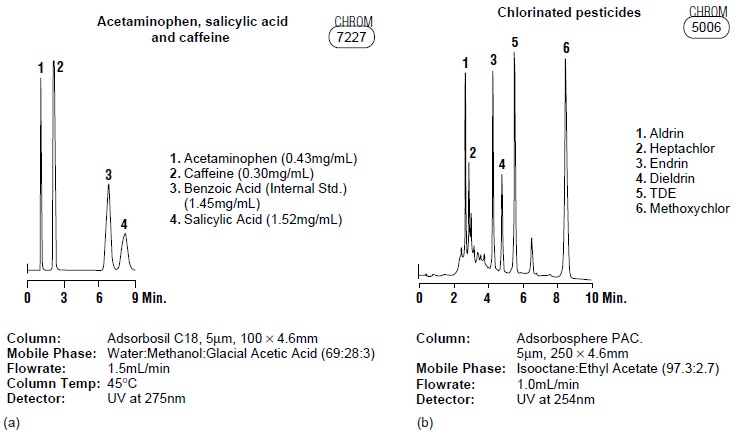
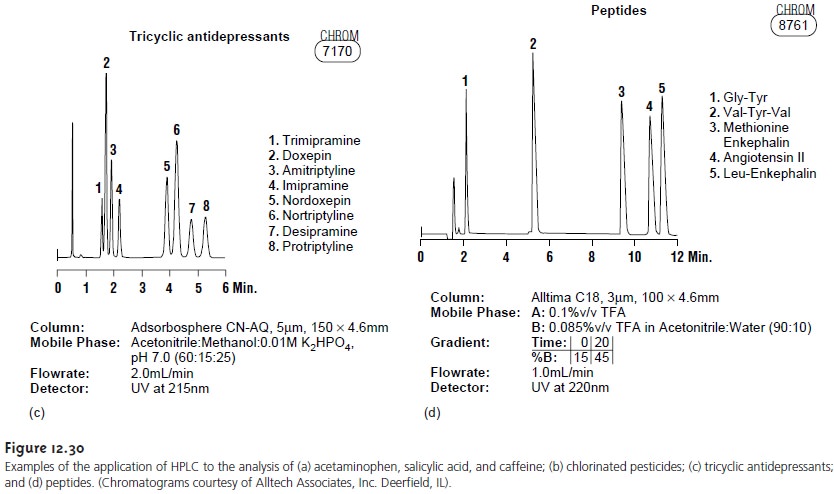
product samples. Figure
12.30 shows several
representative examples.
Preparing Samples for Analysis
Samples
in
liquid
form
can
be
analyzed
di- rectly, after a suitable clean-up to remove any particulate materials or after a
suitable extraction to remove matrix
interferents. In determining polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) in wastewater, for example, an initial extraction with CH2Cl2 serves
the dual purpose
of concentrating the analytes and isolating them from matrix interferents. Solid
samples must first
be dissolved in a suitable sol- vent, or the analytes of interest must be brought
into solution by extraction. For example, an HPLC analysis
for the active
ingredients and degradation products in a pharmaceutical tablet often begins
by extracting the
powdered tablet with
a portion of mobile
phase. Gases are collected by bubbling through
a trap contain- ing a suitable solvent. Organic isocyanates in industrial atmospheres can be de- termined
in this manner by bubbling the air through a solution
of 1-(2- methoxyphenyl)piperazine in toluene. Reacting the isocyanates with 1-(2-methoxyphenyl)piperazine serves the dual purposes of stabilizing them against
degradation before the HPLC analysis while also forming a derivative that can be monitored
by UV absorption.
Quantitative Calculations
Quantitative analyses are often easier to conduct with HPLC than GC because injections are made with a fixed-volume injection loop in- stead of a syringe. As a result, variations in the amount of injected sample are mini- mized, and quantitative measurements can be made using external standards and a normal calibration curve.
Representative Method
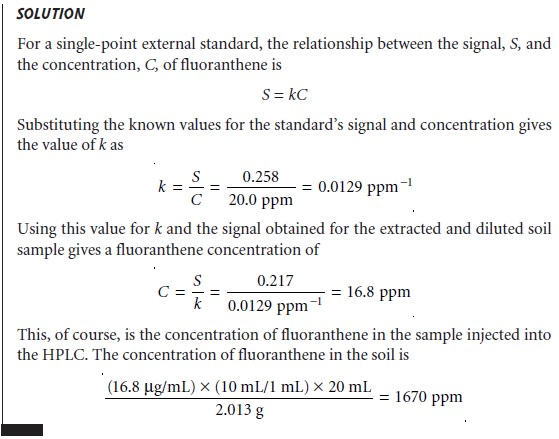
Although each HPLC method has its own unique considerations, the following de- scription of the determination of the fluoxetine in serum provides an instructive ex- ample of a typical procedure.
Related Topics