Chapter: Ophthalmology: Retina
Hemangiomas
Hemangiomas
Definition
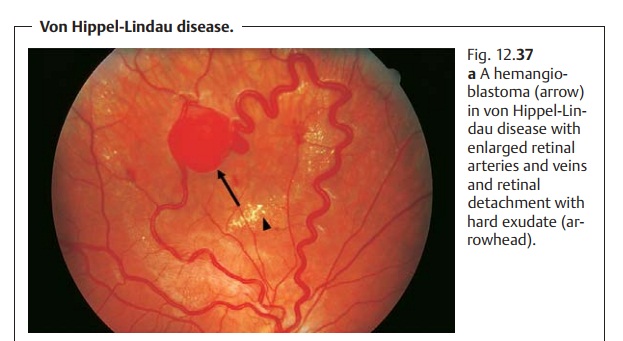
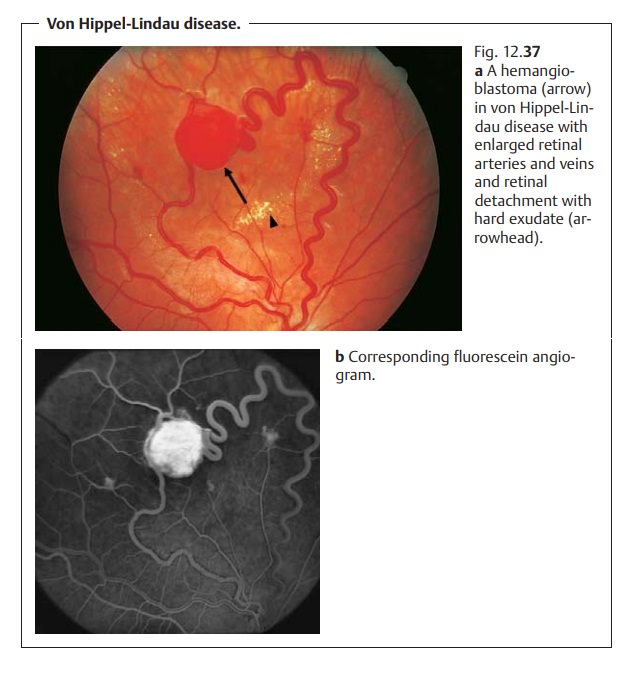
Capillary hemangiomas or hemangioblastomas occur in angiomatosis retinae (von Hippel-Lindau disease).
Epidemiology:
Hemangiomas are rare.
Etiology:
These arebenigncongenital
changes. There may be an autosomaldominant inheritance.
Symptoms:
Loss of visual acuity will result where exudative retinal detach-ment develops.
Findings and diagnostic considerations:
Retinal hemangiomas are charac-terized by
thickened tortuous arteries and veins (Figs. 12.37a and b). Bilateral
changes are present in 50% of all patients.
Differential diagnosis:
Coats’ disease, branching retinal hemangiomas inWyburn-Mason
syndrome, and cavernous hemangiomas should be con-sidered. Cerebral
hemangiomas, renal cysts, hypernephromas, and pheochro-mocytomas should also be
excluded.
Treatment:
Retinal hemangiomas may be treated by laser or
cryocauterytherapy. However, exudative retinal detachment will develop as the treat-ment
increases this risk.
Clinical course and prognosis:
The disorder is gradually progressive. Theprognosis for visual
acuity is poor in the disorder where retinal detachment develops.
Related Topics