Chapter: 11th Nursing : Chapter 2 : Nursing - Health Care Delivery System in India
Health Care Delivery System in India
Health Care Delivery System in India
India is a union of 29 states and
7 union territories. States are largely independent in matters relating to the
delivery of health care to the people. Each state has developed its own system
of health care delivery independent of the Central Government.
The Central Government
responsibility consists mainly of policy making, planning, guiding, assisting,
evaluating and coordinating the work of the State Health Ministries.
The health system in India has 3
main links
A.
Central
B.
State
and
C.
Local
or peripheral
At the Central Level
·
The
official “organs” of health system at national level are
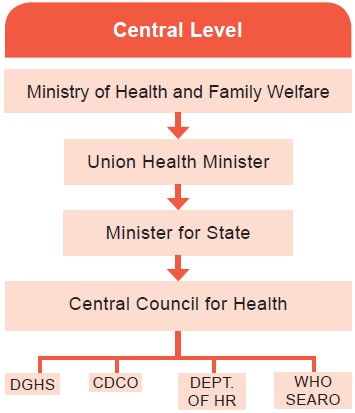
DGHS - Director General of Health
Services
CDCO - Central Drugs Control
Organisation
HR - Health Research
WHO – World Health Organization
SEARO – South East Asia Regional
Office
I. Ministry of Health and Family Welfare
Functions
The functions of the Union
Ministry of Health and Family Welfare are set out in the seventh schedule of
Article 246 of the constitution of India under
1.
Union list and
2.
Concurrent list
1. Union list
1.
International
health relations and administration of port quarantine.
2.
Administration of Central Institutes such as All India Institute
of Hygiene and Public Health, Kolkata.
3.
Promotion of research through research centres
4.
Regulation and development of medical, pharmaceutical, dental
and nursing professions
5.
Establishment and maintenance of drug standards
6.
Census and collection and publication of other statistical data
7.
Immigration and emigration
8.
Regulation of labour in the working of mines and oil fields
9.
Coordination with states and with other ministries for promotion
of health
2. Concurrent list
The functions listed
under the concurrent list are the responsibility of both the union and state
governments
1.
Prevention and extension of communicable diseases
2.
Prevention of adulteration of food stuffs
3.
Control of drugs and poisons
4.
Vital statistics
5.
Labour welfare
6.
Ports other than major
7.
Economic and social planning
8.
Population control and Family Planning
II. Directorate General of Health Services
Functions
1.
International health relations and quarantine of all major ports
in country and international airport
2.
Control of drug standards
3.
Maintain medical store depots
4.
Administration of post graduate training programmes
5.
Administration of certain medical colleges in India
6.
Conducting medical research through Indian Council of Medical
Research (ICMR)
7.
Central Government Health Schemes.
8.
Implementation of National Health Programmes
9.
Preparation of health education material for creating health
awareness through Central Health Education Bureau.
10. Collection, compilation, analysis,
evaluation and dissemination of information through the Central Bureau of
Health Intelligence
11.
National Medical Library
III. Central Council of Health
Functions
1.
To consider and recommend broad outlines of policy with regard
to matters concerning health like environment hygiene, nutrition and health
education.
2.
To make proposals for legislation relating to medical and public
health matters.
3.
To make recommendations to the Central Government regarding
distribution of grants-in-aid.
4.
To establish any organization or organizations invested with
appropriate functions for promoting and maintaining cooperation between the
central and state health administration
At the State Level
The health subjects
are divided into three groups: federal, concurrent and state. The state list is
the responsibility of the state, including provision of medical care,
preventive health services and pilgrimage within the state.
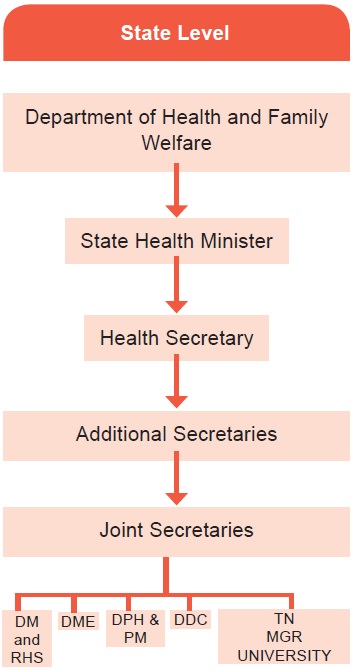
DM & RHS -
Directorate of Medical and Health Services
DME - Directorate of
Medical Education DPH & PM - Directorate of Public Health and Preventive
Medicine
DDC – Directorate of
Drugs control
State Health Administration
At present there are 29 states in
India, each state having its own health administration. In all the states, the
management sector comprises the state ministry of health and a directorate of
health
1. Department of Health & Family Welfare
State Department of
Health and Family Welfare headed by the state minister of Health and Family
Welfare.
1.
State health Directorate
There are three separate major departments in
Health and Family Welfare.
·
The Directorate of medical and Rural Health Services,
Directorate of Medical Education and Directorate of Public Health and
preventive Medicine are the chief Technical directorates to the statte
government on all matters related to public health.
·
There are other directorates such as Directorate of Health and
Family Welfare, Directorate of Drugs control, Directorate of health Transport,
Tamilnadu AIDS control society, State health mission etc.
At the District Level
There are 614 (year
2007) districts in India. Within each district, there are 6 types of
administrative areas.
1.
Sub-division
2.
Thasils (Taluks)
3.
Community Development Blocks
4.
Municipalities and Corporations
5.
Villages and
6.
Panchayats
Most district in India
are divided into two or more subdivision, each incharge of an Assistant
Collector or Sub Collector. Each division is again divided into taluks,
incharge of a Thasildhar. A taluk usually comprises between 200 to 600
villages. The community development block comprises approximately 100 villages
and about 80000 to 1,20,000 population, in charge of a Block Development
Officer. Finally, there are the village panchayats which are institutions of
rural local self-government.
The urban areas of the
district are organized into the following institutions of local
self-government:
1.
Town Area Committees (in areas with population ranging between
5,000 to 10,000)
2.
Municipal Boards (in areas with population ranging between
10,000 and 2,00,000)
3.
Corporations (with population above 2,00,000)
The Town Area
Committees are like panchayats. They provide sanitary services. The Municipal
Boards are headed by Chairman / President, elected by members.
The functions of Municipal Board & Corporations
1.
Construction and maintenance of roads
2.
Sanitation and drainage
3.
Street lighting
4.
Water supply
5.
Maintenance of hospitals and dispensaries
6.
Education and
7.
Registration of births and deaths etc.
The Corporations are
headed by Mayors, elected by councillors, who are elected from different wards
of the city. The executive agency includes the commissioner, the secretary, the
engineer and the health officer.
The activities are
similar to those of municipalities on a much wider scale.
Panchayat Raj
The Panchayat Raj is a
3-tier structure of rural local self-government in India linking the village to
the district
The three institutions
are:
1)
Panchayat (at the village level)
2)
Panchayat Samiti (at the block level)
3)
Zila Parishad (at the district level)
1) Panchayat (at the village level)
The Panchayat Raj at
the village level consists of
·
The Gram Sabha
·
The Gram Panchayat
·
The Nyaya panchayat
The Gram Sabha
considers proposals for taxation and elects members of the gram panchayat.
The Gram Panchayat
covers the civic administration including sanitation and public health and work
for the social and economic development of the village.
2) Panchayat Samiti (at the block level):
The Panchayat Samiti
execute the community development programme in the block. The Block Development
Officer and his staff give technical assistance and guidance in development
work.
3) Zila Parishad (at the district level):
The Zila Parishad is
primarily supervisory and coordinating body. This is the agency of rural local
self-government at the district level. Its functions and powers vary from state
to state.
Related Topics