Chapter: Genetics and Molecular Biology: Biological Assembly, Ribosomes and Lambda Phage
Head Assembly Sequence and Host Proteins
The Head Assembly Sequence and Host Proteins
Head precursors of lambda can be isolated by
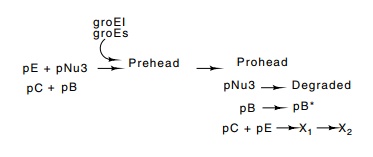
centrifugation and can thereby be studied. The first consists of pE, pNu3, pB
and pC (Fig. 21.16). Without pE, nothing forms, and without pNu3, only large
amorphous shapes appear. The formation of this structure also requires that
about 12 molecules of the pB protein be polymerized. This is done with the
assistance of the host proteins GroEL and GroES. The pB protein ultimately
forms the connector between head and tail.
In the head maturation process there is both
cleavage of polypeptide chains and fusion of chains. For example, some
molecules of pB are cleaved and some molecules of pE are fused to protein pC.
The final head is formed by the addition of lambda DNA, its cleavage to
unit-length molecules containing the 12-base single-stranded cos ends, and the addition of pD on an
equimolar basis to pE. Proteins pW and pFII prepare the head for attachment
of the tail. One of the functions of such a protein is to act as an adapter
between the hexagonal tail and the pentagonal vertex to which the tail is
attached.
The protein pNu3 occupies a role predicted for many
other proteins but thus far found rather infrequently. It appears to be a
structural protein and is used during the assembly of the phage particle but is
not present in the assembled phage particle. It is synthesized in high
quantities and forms a part of the scaffolding during formation of the
particle. In the case of lambda, this protein is cleaved after a single use,
but in some other phage the analogous protein is used more than once.
The GroEL-GroES protein complex is a member of the
class of proteins that assists the formation of complex protein structures.
Often these proteins possess ATPase activities. Some disaggregate oligomers
that have formed from hydrophobic interactions or prevent their for-mation. Others
assist the molten globule state to perform final rear-rangements of secondary
structure elements. The protein DnaK that functions in assembling the
replication complex of lambda along with the phage P protein and the host DnaB
protein, also participates in the lambda capsid maturation reactions. Mutants
with altered GroE protein
Figure
21.16 Maturation scheme of lambda
heads.
frequently fail to support the growth of not only
phage lambda but also related phage and even phage T4. In addition to failing
to cleave pB, they do not package DNA. Mutants of lambda that overcome the groE defect can be isolated. These are
usually found to be altered in the lambda E
gene. Some of the rarer groE
mutations can be overcome by compensating mutations in the lambda B gene. These results strongly suggest
that GroE protein touches the pE and pB proteins during the maturation of the
phage.
The groE
mutation joins the list of other cellular mutations that may block maturation
of the phage. In addition to groE,
there are also the groP mutations in
the host cell, which block DNA replication of thephage, and groN mutations which make the phage
appear to be N defective. The groP
mutations lie within a subunit of DNA polymerase. Some groN mutations lie in the RNA polymerase and can be overcome by a
compensating mutation in the phage N gene.
Related Topics