Chapter: Biochemistry: Carbohydrate Metabolism
Gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis
The synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate
precursors is known as gluconeogenesis. The major site of gluconeogenesis is
liver. It usually occurs when the carbohydrate in the diet is insufficient to
meet the demand in the body, with the intake of protein rich diet and at the
time of starvation, when tissue proteins are broken down to amino acids.
Gluconeogenesis and glycolysis
Gluconeogenesis and glycolysis are opposing
metabolic pathways and share a number of enzymes. In glycolysis, glucose is
converted to pyruvate and in gluconeogenesis pyruvate is converted to glucose.
However gluconeogenesis is not exact reversal of glycolysis.
There are three essentially irrevesible steps in
glycolysis which are
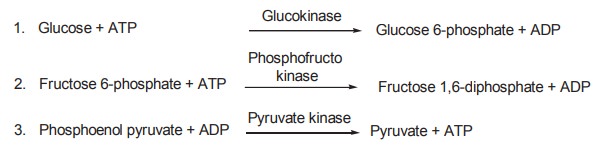
In gluconeogenesis these three reactions are
bypassed or substituted by the following news ones.
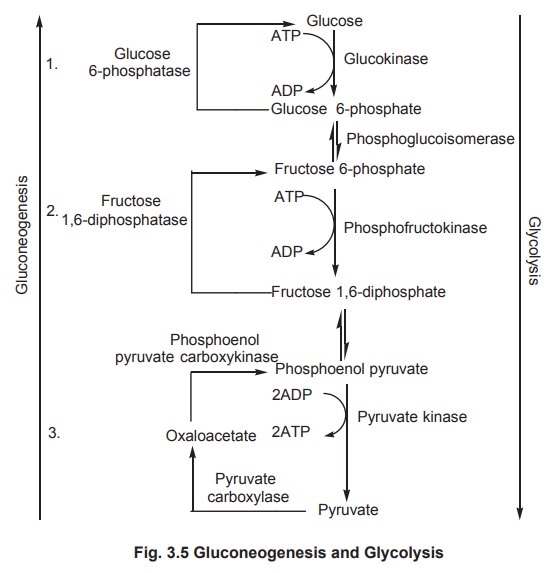
Reactions of gluconeogenesis
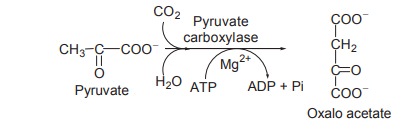
1. The formation of phosphoenol pyruvate begins
with the carboxylation of pyruvate at the expense of ATP to form oxalo acetate.
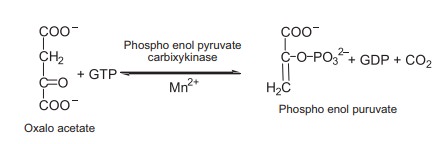
Oxaloacetate is converted to phosphoenolpyruvate by phosphorylation with GTP, accompanied by a simultaneous decarboxylation.
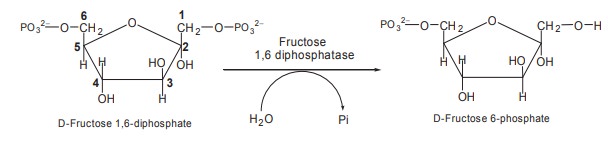
2. Fructose 6-phosphate is formed from fructose
1,6-diphosphate by hydrolysis and the enzyme fructose 1,6-diphosphatase
catalyses this reaction.
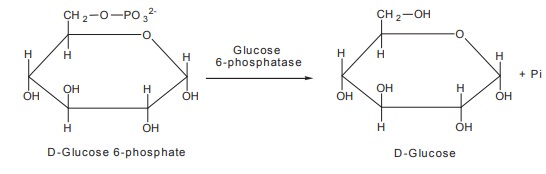
3. Glucose is formed by hydrolysis of glucose
6-phosphate catalysed by glucose 6-phosphatase.
Gluconeogenesis of amino acids
Amino acids which could be converted to glucose
are called glucogenic amino acids. Most of the glucogenic amino acids are
converted to the intermediates of citric acid cycle either by transamination or
deamination.
Gluconeogenesis of Propionate
Propionate is a major source of glucose in
ruminants, and enters the main gluconeogenic pathway via the citric acid cycle
after conversion to succinyl CoA.
Gluconeogenesis of Glycerol
At the time of starvation glycerol can also
undergo gluconeogenesis. When the triglycerides are hydrolysed in the adipose
tissue, glycerol is released. Further metabolism of glycerol does not take
place in the adipose tissue because of the lack of glycerol kinase necessary to
phosphorylate it. Instead, glycerol passes to the liver where it is
phosphorylated to glycerol 3-phosphate by the enzyme glycerol kinase.

This pathway connects the triose phosphate stage of glycolysis, because glycerol 3-phosphate is oxidized to dihydroxy acetone phosphate in the presence of NAD+ and glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
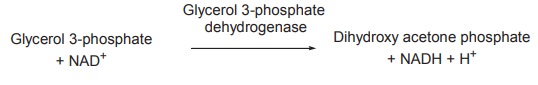
This dihydroxy acetone phosphate enters
gluconeogenesis pathway and gets converted to glucose. Liver and kidney are
able to convert glycerol to blood glucose by making use of the above enzymes.
Gluconeogenesis of lactic acid (Cori cycle)
The liver and skeletal muscles exhibit a special
metabolic cooperation as far as carbohydrates are concerned by the way of a
cycle of conversions known as Cori cycle.
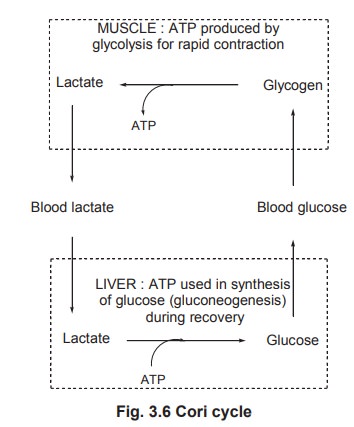
In this cycle liver glycogen may be converted
into muscle glycogen and vice versa and the major raw material of this cycle is
lactate produced by the active skeletal muscles.
At the time of heavy muscular work or strenuous
exercise, O2 supply is inadequate in active muscles but the muscles
keep contracting to the maximum. Hence, glycogen stored up in the muscle is
converted into lactic acid by glycogenolysis followed by anaerobic glycolysis
and thus lactate gets accumulated in the muscle. Muscle tissue lacks the enzyme
glucose 6-phosphatase hence it is incapable of synthesizing glucose from lactic
acid and the conversion take place only in the liver.
Lactate diffuses out of the muscle and enters
the liver through blood. In the liver lactate is oxidised to pyruvate which
undergoes the process of gluconeogenesis resulting in the resynthesis of
glucose. The glycogen may be once again converted to glucose (glycogenolysis)
and may be recycled to the muscle through the blood. The process of
gluconeogenesis completes the cycle by converting glucose once again to muscle
glycogen.
Related Topics