Chapter: 9th Science : Measurement and Measuring Instruments
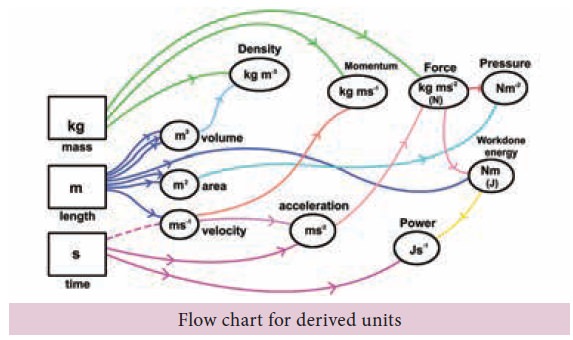
Fundamental Units of SI System
Fundamental
Units of SI System
1. Length
Length is de ned as the distance between two points.
The SI unit of length is metre. One metre is the distance travelled by light
through vacuum in 1/29,97,92,458 second.
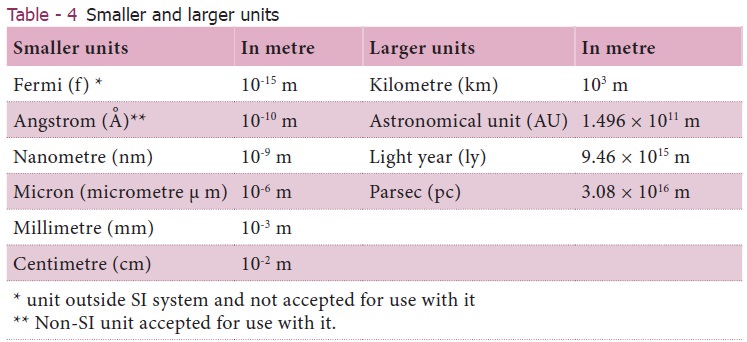
In order to measure very large distance (distance
of astronomical objects) we use the following units.
·
Light year
·
Astronomical unit
·
Parsec
Light year: It is the distance travelled by light
in one year in vacuum and it is equal to 9.46 × 1015m.
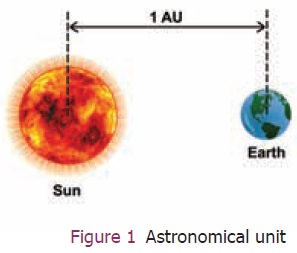
Astronomical unit (AU): It is the mean distance of
the centre of the Sun from the centre of the earth. 1 AU = 1.496 × 1011
m Figure 1.
Parsec: Parsec is the unit of distance used to
measure astronomical objects outside the solar system.
1 parsec = 3.26 light year.
To measure small distances such as distance between
two atoms in a molecule, the size of the nucleus and the wavelength, we use
submultiples of ten. These quantities are measured in Angstrom unit (Table 4).
2. Mass
Mass is the quantity of matter contained in a body. The SI unit of mass is kilogram. One kilogram is the mass of a particular international prototype cylinder made of platinum-iridium alloy, kept at the International Bureau of Weights and Measures at Sevres, France.
The related units in submultiples of 10 (1/10) are
gram and milligram and in multiples of 10 are quintal and metric tonne.
1 quintal = 100 kg
1 metric tonne = 1000 kg = 10 quintal
1 solar mass = 2 × 1030 kg
Atomic mass unit (amu):
Mass of a proton, neutron and electron can be
determined using atomic mass unit.
1 amu = 1/12th of the mass of carbon-12 atom.

3. Time
Time is a measure of duration of events and the
intervals between them. The SI unit of time is second. One second is the time
required for the light to propagate 29,97,92,458 metres through vacuum. It is
also defined as 1/86, 400th part of a mean solar day. Larger unit for measuring
time is millennium. 1 millenium = 3.16 × 109 s.
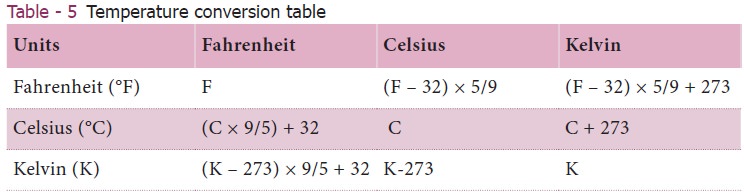
4. Temperature
Temperature is the measure of hotness. SI unit of
temperature is kelvin(K). One kelvin is the fraction of 1/273.16 of the
thermodynamic temperature of the triple point of water ( e temperature at which
saturated water vapour, pure water and melting ice are in equilibrium). Zero
kelvin (0 K) is commonly known as absolute zero. The other units for measuring
temperature are degree Celsius and Fahrenheit (Table 5). To convert temperature
from one scale to another we use
C/100 =
(F – 32)/180 = (K-273) /100
Example:
Convert (a) 300 K in to Celsius scale, (b) 104°F in
to Celsius scale.
Solution
(a)
Celsius = K-273 = 300-273 = 27°C
(b)
Celsius = (F – 32) × 5/9 = (104-32) × 5/9 =72 × 5/9 = 40°C
Related Topics