Chapter: Modern Medical Toxicology: Chemical Poisons: Non-Metallic Chemical Poisons
Fluorine - Chemical Poisons
Fluorine
Physical Appearance
·
Fluorine is a diatomic halogen gas.
It is a very corrosive and toxic gas, and is found in the soil in combination
with calcium. It is released into the atmosphere by the burning of soft coal,
and during manufacturing processes involving superphosphate, aluminium, steel,
lead, copper, etc.
·
Salts (referred to as fluorides)
include sodium fluoride and sodium fluoroacetate. Both are crystalline, white,
odourless, tasteless, and strongly alkaline.
Uses
Sodium
fluoride and sodium fluoroacetate are widely used as cockroach and rat killers.
In
dentistry, fluorides are used in toothpastes, topical gels, and mouthwashes.
Usual Fatal Dose
·
70 to 140 mg/kg of fluoride ion. In
general, 2.2 sodium fluoride contains 1 mg of fluoride ion.
·
Fatal blood fluoride level: more
than 0.2 mg/100 ml.
·
Urinary fluorine output of less than
5 mg/L is used as an index of safe working level for long-term exposure.
·
The safe upper limit for fluorine
gas is 1 ppm.
Mode of Action
·
Fluorine and fluorides act as direct cellular poisons by
inter-fering with calcium metabolism and enzyme mechanisms. Fluoride combines
with hydrochloric acid in the stomach to form hydrofluoric acid which is a
powerful corrosive. After absorption, fluoride ions combine with cations in the
serum, particulaly calcium and magnesium leading to hypocalcaemia and
hypomagnesaemia. Hyperkalaemia is often an added hazard.![]()
·
Dermal cutaneous burns are caused by the violent reaction
between the skin and fluorine producing a thermal burn.
Clinical Features
Acute Poisoning—
·
Fluorine is an extremely strong
tissue irritant, causing caustic irritation of eyes, skin, and mucous
membranes. Thermal burns or frostbite may occur.
·
Inhalation of fluorine gas leads to
headache, respiratory distress, polydipsia, and polyuria.
o Ingestion
of fluorides in large amounts can cause the following manifestations:
o Metallic
taste, salivation, vomiting, diarrhoea, abdominal pain.
o Paraesthesias,
paresis, tetany, convulsions.
o Ventricular
arrhythmias, cardiovascular collapse, coagulopathies.
Chronic Poisoning—
·
Leads to a condition called fluorosis:
o
This is usually the result of high fluoride content in water
supply. Fluoridation of water is done to prevent caries. When the water
fluoride content is more than 3 to 5 ppm, chronic exposure leads to mottling of
teeth (Fig 8.8). The enamel loses
its lustre and becomes rough, pigmented, and pitted.
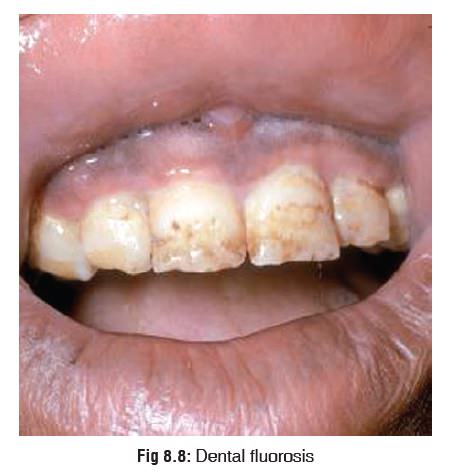
o
Skeletal fluorosis is a different entity which is also
associated with high fluoride concentration in water and soil. In non-endemic
areas it may occur as a result of occupational exposure (aluminium ![]() production, magnesium foundries, superphosphate manufacture,
etc.) . The effects are usually more severe in children.
production, magnesium foundries, superphosphate manufacture,
etc.) . The effects are usually more severe in children.
Main
features include genu valgus or varum (bow legs or knock knees) (Fig 8.9), lateral bowing of femora,
sabre shins, and deformities of thorax, vertebrae, pelvis, and joints. There
may also be mottling of teeth.
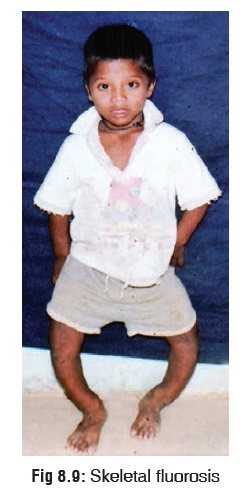
In
adults there may be thickening of long bones, development of exostoses and
osteophytes, calcification of ligaments and tendons, polyar-thralgia, and
contractures of hips and knees.
Treatment
Acute Poisoning—
a.Insecticide fluoride ingestion—
·
Stomach wash with magnesium sulfate,
followed by activated charcoal and sorbitol.
·
Treat convulsions with
anticonvulsants.
·
Supportive measures, including the
use of haemo-dialysis.
b.Non-insecticide fluoride ingestion –
Mild:
·
Administer milk.
·
Watch the progress for at least 12 hours. If symptoms such
as vomiting, diarrhoea or abdominal pain occur, treat as mentioned below.
Moderate to Severe:
·
Stomach wash (if vomiting has not occurred). -- Administer
milk, oral calcium salts, or aluminium (or magnesium) based antacids to bind
fluoride.
·
Treat hypocalcaemia, hypomagnesaemia, and
hyper/hypokalaemia.
·
Consider haemodialysis for severe poisoning.
c.Frostbite—
Rewarming:
·
Place affected area in a water bath
with a temperature of 40 to 420C for 15
to 30 minutes until thawing is complete. The bath should be large enough to
permit complete immersion of the injured part, avoiding contact with the sides
of the bath.
·
Correct systemic hypothermia.
·
Rewarming may be associated with
increasing pain, requiring narcotic analgesics.
Wound Care:
·
Digits should be separated by
sterile absorbent cotton; no constrictive dressings should be used. Protective
dressings should be changed twice per day.
·
The injured extremities should be
elevated and should not be allowed to bear weight.
·
Prophylactic antibiotics may be administered. -- Clear
blisters should be debrided but haemor- rhagic blisters left intact.
·
Further surgical debridement should be delayed until mummification
demarcation has occurred (60 to 90 days). Spontaneous amputation may occur.
·
Tetanus prophylaxis is advisable.
·
Topical aloe vera may decrease tissue destruc-tion and can
be applied every 6 hours.
·
Ibuprofen is a thromboxane inhibitor and may help reduce
tissue loss. Adult dose of 200 milli-grams every 12 hours is recommended.
Forensic Issues
Most
cases of poisoning (acute or chronic) are accidental. Suicidal poisonings have
been reported with fluoride-based rodenticides and cockroach killers.
Related Topics