Chapter: Medical Microbiology: An Introduction to Infectious Diseases: Cestodes
Fish Tapeworm: Diphyllobothrium latum : Parasitology
FISH TAPEWORM
Diphyllobothrium latum : PARASITOLOGY
The adult D. latum attaches to the ileal mucosa with the aid of two sucking grooves (both-ria) located in an elongated fusiform scolex (Fig 57 – 2). In lifespan and overall length, it resembles the Taenia species discussed previously. The 3000 to 4000 proglottids, however, are uniformly wider than they are long, accounting for this cestode’s species designation as well as one of its common names, the broad tapeworm. The gravid segments contain a cen-trally positioned, rosette-shaped uterus unique among the tapeworms of humans. Unlike those of the Taenia species, ova are released through the uterine pore. Over 1 million oval (55 by 75 mm) operculate eggs are released daily into the stool (Fig 57 – 2B).
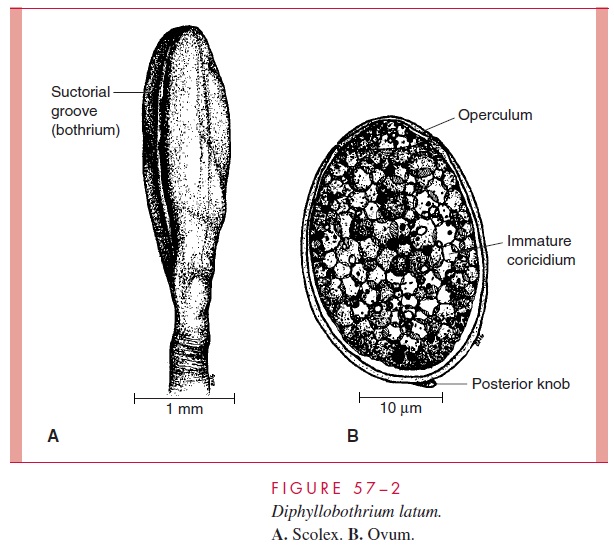
On reaching fresh water they hatch, releasing ciliated, free-swimming larvae or coracidia. If ingested within a few days by small freshwater crustaceans of the genera Cy-clops or Diaptomus, they develop into procercoid larvae. When the crustacean is ingestedby a freshwater or anadromous marine fish, the larvae migrate into the musculature of the fish and develop into infectious plerocercoid larvae. Humans are infected when they eat improperly prepared freshwater fish containing such forms.
Related Topics