Chapter: Business Science : Enterpreneurship Development : Launching of Small Business
Financial Planning - Launching of Small Business
Financial Planning
Working Capital Management
•
Working capital management is concerned with making
sure we have exactly the right amount of money and lines of credit available to
the business at all times
•
Working Capital is the money used to make goods and
attract sales
•
The less Working Capital used to attract sales, the
higher is likely to be the return on investment
•
Working Capital = Current Assets − Current
Liabilities
Working Capital Management
•
Cash Management
•
Receivables Management
•
Inventory Management
Cash Management
•
Identify the cash balance which allows for the
business to meet day to day expenses reduces cash holding costs
Receivables Management
•
Money which is owed to a company by a customer for
products and services provided on credit
•
Identify the appropriate credit policy
•
Inventory
Management
•
Identify the level of inventory which allows for
uninterrupted production
•
Reduces the investment in raw materials, minimizes
reordering costs and hence increases cash flow
Inventory Management
A
company's merchandise, raw materials, and finished and unfinished products
which have not yet been sold. These are considered liquid assets, since they
can be converted into cash quite easily.
Policies,
procedures, and techniques employed in maintaining the optimum number or amount
of each inventory item. The objective of inventory management is to provide
uninterrupted production, sales, and/or customer-service levels at the minimum
cost.
Techniques: -
•
ABC
•
JIT
•
FSN
•
VED
•
BILLS OF MATERIAL
•
BIN CARDS
•
EOQ-ECONOMIC RE-ORDER QUANTITY
•
INVENTORY/TURNOVER
Inventory Management
Importance:-
– TRANSCATIONS
MOTIVE:
It emphasizes the need to maintain inventories to facilitate smooth
production and sales operations
– PRECAUTIONARY
MOTIVE: -
It necessitates holding of inventories to guard against the risk of
unpredictable changes in demand and supply forces and other factors
– SPECULATIVE
MOTIVE: -
It influences the decision to increase or reduce inventory levels to
take the advantage of price level fluctuations
Conflicting
needs : -
– To maintain a large size of inventories of raw
materials and WIP for efficient and smooth production and of finished goods for
uninterrupted sales operations
– To maintain a minimum investment in
inventories to maximize profitability
Objective: -
– determine and maintain optimum level of
inventory investment
– to maintain sufficient inventory for the
smooth production and sales operations
– to avoid excessive and inadequate levels of
inventories
– Making adequate inventories available for production
& sales when required.
Benefits of holding inventories:
Avoiding losses of sales avoid
non-supply of goods at times demands by understands.
Reducing
ordering costs cost associated with individual order such as typing approving
mailiyet can be reduced.
Achieving
efficient production run Supply of sufficient inventories protects against
shortage of raw materials that may interrupt production operation.
Cost of holding inventories:-
Ordering
cost cost which are associated with placing of orders to purchase raw materials
& components. Salary, rent. “More the order the more will be ordering costs
vice verse”.
Carrying
costs cost involved in holding or
carrying inventories like insurance. Charger for covering risk, thefts. It
includes opportunity cost.
Money
blocked in inventories been invested. It would earn a certain return. Loss of
such return may be considered opportunity cost.
Models of inventory mgt:-
Several
models & methods have been developed in recent past for determing the
optimum level of inventories.
Classified into two types:-
Deterministic models:-
There is
no uncertainty associated with demand supply of inventory.
Probabilistic models:-
It always
some degree of uncertainty associated with demand pattern & lead times of
inventories.
Unusually
deterministic models associated:
Economic
ordering quantity.(EOQ)
ABC
analysis.
Inventory
return over ratio.
EOQ:
Important
decision to be taken by a firm in inventory mgt is how much to buy at a time.
This is called EOQ.
EOQ give
solution to other problem like: How frequently to buy? When to buy? What should
be the reserve stock?
Assumptions:-
EOQ is
based on certain assumption.
The firm
knows how much items of particular inventories will be used or demanded. Use of
inventories/sales made by the firm remains constant, or unchanged.
The
moment inventories reach the zero level, the order of inventory is placed
without delay. These assumptions are also called limitations of EOQ.
Determination of EOQ:-
Ordering cost:
Cost concerned
with the placing of an order to acquire inventories. Yes it way from time to
time depending upon the no of items orders places & no of items ordered in
each order.
Carrying cost:
Cost
related to carrying or keeping inventories in a firm.
Ex: interest
on investment, obsolescence, losses, insurance, premium.
Volume of
inventory & carrying cost.
EOQ can
be determined by an approach.
The order-formula approach:-
There are
number of mathematical formula to calculate EOQ. The most frequently used formula
is
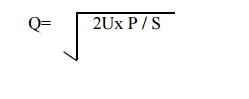
Q = EOQ.
U =
Quantity purchased in a year/month.
P = Cost
of placing an order. (ordering cost)
S =
Annual/ monthly cost of storage of one unit known (carrying cost)
Trial & Error Approach:-
Carrying
& ordering cost should be studied “order formula approach”.
Graphic Approach:
EOQ can
found by drawing a graph.
ABC Analysis:-
A – Items
with highest value.
B – Items
with relatively low value.
C – Items
with least valuable.
A – items
maintain bare minimum necessary level of inventories.
B – items
will be kept under reasonable control.
C – items
would be under simple control.
FSN – Fast moving, Slow moving, Non-moving.
Fast
moving in order of have smooth production.High demand – adequate inventory of
these items maintained
Slow
moving items:-Slowly moving indicated by a low turnover ratio needed to
maintain at minimum level.
Dormant/obsolete
items have no demand these should be disposed of a early as possible to curb
further losses caused by them.
Inventory turnover Ratio:
=Cost of
goods consumed or sold during year/ Average inventory during the year x 100
Related Topics