Chapter: Genetics and Molecular Biology: Protein Synthesis
Fidelity of Aminoacylation - Protein Synthesis
Fidelity of Aminoacylation
The aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are remarkable
enzymes since they recognize amino acids and their cognate tRNA molecules and
join them together. Inaccuracies in either recognition process could be highly
deleterious because choosing the wrong amino acid or the wrong tRNA would
ultimately yield a protein with an incorrect sequence. We know,
however, from measurements on peptides highly
purified from proteins of known sequence, that the overall frequency of
misincorporation, at least of charged amino acids, is only about 1/1000.
Let us first consider the process of choosing the
correct amino acid. The greatest difficulty in accurate translation appears to
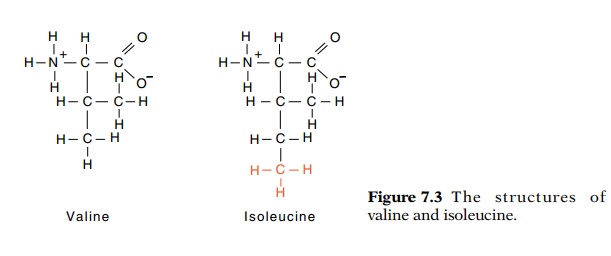
be in discrimi-nating between two highly similar amino acids. Valine and
isoleucine are an example since replacing a hydrogen on valine with a methyl
group yields isoleucine (Fig. 7.3). The valyl-tRNA synthetase should not have
trouble in discriminating against isoleucine because isoleucine is larger than
valine and probably does not fit into the active site on the enzyme. The reverse
situation is more of a problem. Valine will form all of the contacts to the
enzyme that isoleucine can form except for those to the missing methyl group.
How much specificity could the absence of these contacts provide? Estimates of
the differences in binding energy predict about a 200-fold discrimination, but
since the actual error rate is found to be much lower, something in addition to
a simple discrimination based on one binding reaction must contribute to
specificity. An addi-tional step in the overall reaction in the form of editing
by the synthetase increases the accuracy.
Although
isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase can form a valyl adenylate com-plex, upon the
addition of tRNAIle the tRNA is activated and then the
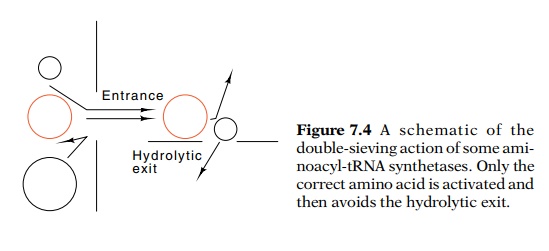
complex is immediately hydrolyzed. One way to think
of this process is that activation is a two-step sieving process (Fig. 7.4). It
permits the correct amino acid and similar but smaller amino acids to be
activated. Then all amino acids smaller than the correct amino acid have a
hydrolytic pathway available for removal of the misacylated amino acid. DNA
synthesis and DNA cutting by restriction enzymes also use two-step error
checking to achieve high accuracy. In the case of protein synthesis, fidelity
is increased by identifying the amino acid several times, and for the DNA
cutting enzymes, the nucleotide sequence is read more than once.
Related Topics