Chapter: Optical Communication and Networking : Transmission Characteristics of Optical Fiber
Fiber bend loss
Fiber bend loss
Optical
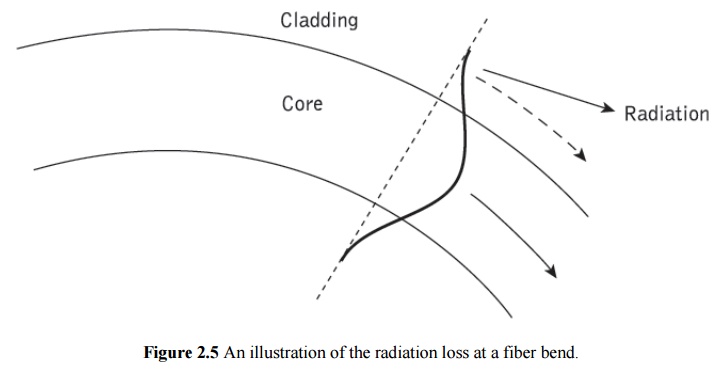
fibers suffer radiation losses at bends or curves on their paths. This is due
to the energy in the evanescent field at the bend exceeding the velocity of
light in the cladding and hence the guidance mechanism is inhibited, which
causes light energy to be radiated from the fiber. An illustration of this
situation is shown in Figure 2.5. The part of the mode which is on the outside of
the bend is required to travel faster than that on the inside so that a
wavefront perpendicular to the direction of propagation is maintained.
Hence,
part of the mode in the cladding needs to travel faster than the velocity of
light in that medium. As this is not possible, the energy associated with this
part of the mode is lost through radiation. The loss can generally be
represented by a radiation attenuation coefficient which has the form:
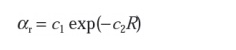
Where R is the radius of curvature of the
fiber bend and c1, c2 are constants which are independent
of R. Furthermore, large bending
losses tend to occur in multimode fibers at a critical radius of curvature Rc which may be estimated from:

It may be
observed from the expression given in Eq. (2.8) that potential macrobending
losses may be reduced by:
ü designing
fibers with large relative refractive index differences;
ü operating
at the shortest wavelength possible.
The above
criteria for the reduction of bend losses also apply to single-mode fibers. One
theory, based on the concept of a single quasi-guided mode, provides an
expression from which the critical radius of curvature for a single-mode fiber Rcs can be estimated as

where λc
is the cutoff wavelength for the single-mode fiber. Hence again, for a specific
single-mode fiber (i.e. a fixed relative index difference and cutoff
wavelength), the critical wavelength of the radiated light becomes
progressively shorter as the bend radius is decreased.
Related Topics