Chapter: Biochemistry: The Metabolism of Nitrogen
Feedback Inhibition in Nitrogen Metabolism
Feedback Inhibition in Nitrogen
Metabolism
The biosynthetic pathways that produce amino acids and the bases of
nucleotides (purines and pyrimidines) are long and complex, requiring a large
investment of energy by the organism. If there is a high level of some end
product, such as an amino acid or a nucleotide, the cell saves energy by not
making that compound. However, the cell needs a signal to tell it to stop
producing more of that particular compound. The signal is frequently part of a feedback inhibition mechanism, in which
the end product of a metabolic pathway inhibits an enzyme at the beginning of
the pathway. We saw an example of such a control mechanism. This enzyme
catalyzes one of the early stages of pyrimidine nucleotide biosynthesis, and it
is inhibited by the end product of that pathway—namely, cytidine triphosphate
(CTP). Feedback inhibition is frequently encountered in the biosynthesis of
amino acids and nucleotides. Another prime example of allosteric regulation by
feedback inhibition is found in the activity of the enzyme glutamine synthetase,
one of the key enzymes in amino acid biosynthesis (Figure 23.4). Nine
allosteric inhibitors are involved here (glycine, alanine, serine, histidine,
tryptophan, CTP, AMP, carbamoyl phosphate, and glucosamine-6-phosphate).
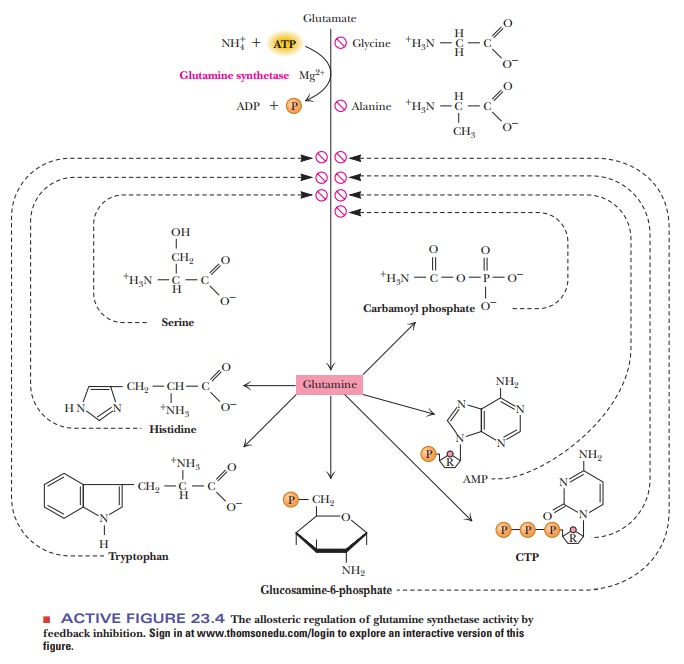
Glycine, alanine, and serine are key indicators of amino acid
metabolism in the cell. Each of the other six compounds represents an end
product of a biosynthetic pathway that depends on glutamine. Feedback
inhibition is very effective because a single product molecule can inhibit an
enzyme capable of synthesizing many hundreds or thousands of product molecules.
Summary
Because the biosynthetic pathways for many nitrogen-containing
com-pounds are long and complex, organisms save energy by inactivating these
pathways when the compounds in question are not needed. This is frequently
achieved by feedback inhibition.
Related Topics