Chapter: Biochemistry: The Behavior of Proteins: Enzymes, Mechanisms, and Control
Families of Enzymes: Proteases
Families of Enzymes: Proteases
Large
numbers of enzymes catalyze similar functions. Many oxidation–reduction
reactions take place, each catalyzed by a specific enzyme. We have already seen
that kinases transfer phosphate groups. Still other enzymes catalyze hydrolytic
reactions. Enzymes that have similar functions may have widely varying
structures. The important feature that they have in common is an active site
that can catalyze the reaction in question. A number of different enzymes
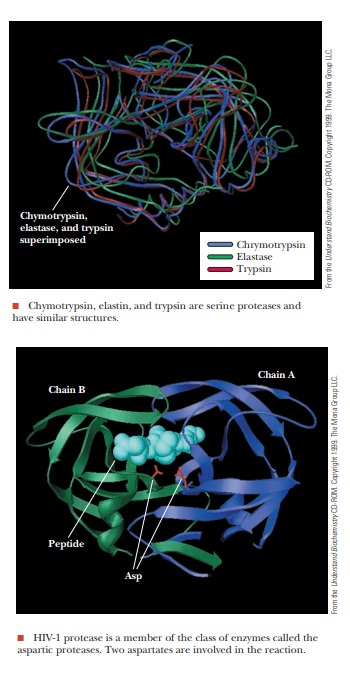
catalyze the hydrolysis of proteins. Chymotrypsin is one example of the class
of serine proteases, but many others are known, including elastase, which
catalyzes the degradation of the connective tissue protein elastin and the
digestive enzyme trypsin. (Recall that we first saw trypsin in its role in
protein sequencing.) All these enzymes are similar in structure. Other
proteases employ other essential amino acid residues as the nucleophile in the
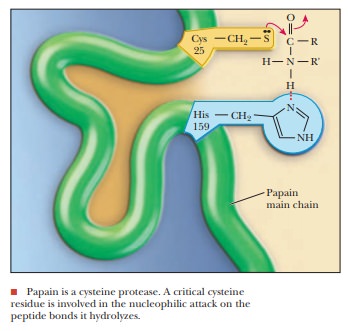
active site. Papain, the basis of commercial meat tenderizers, is a proteolytic
enzyme derived from papayas. However, it has a cysteine rather than a serine as
the nucleophile in its active site. Aspartyl proteases differ still more widely
in structure from the common serine proteases. A pair of aspartate side chains,
sometimes on different subunits, participates in the reaction mechanism. A
number of aspartyl proteases, such as the digestive enzyme pepsin, are known.
However, the most notorious aspartyl protease is the one necessary for the
maturation of the human immunodeficiency virus, HIV-1 protease.
Related Topics