Chapter: Medical Physiology: The Autonomic Nervous System and the Adrenal Medulla
Excitatory and Inhibitory Actions of Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Stimulation
Excitatory and Inhibitory Actions of Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Stimulation
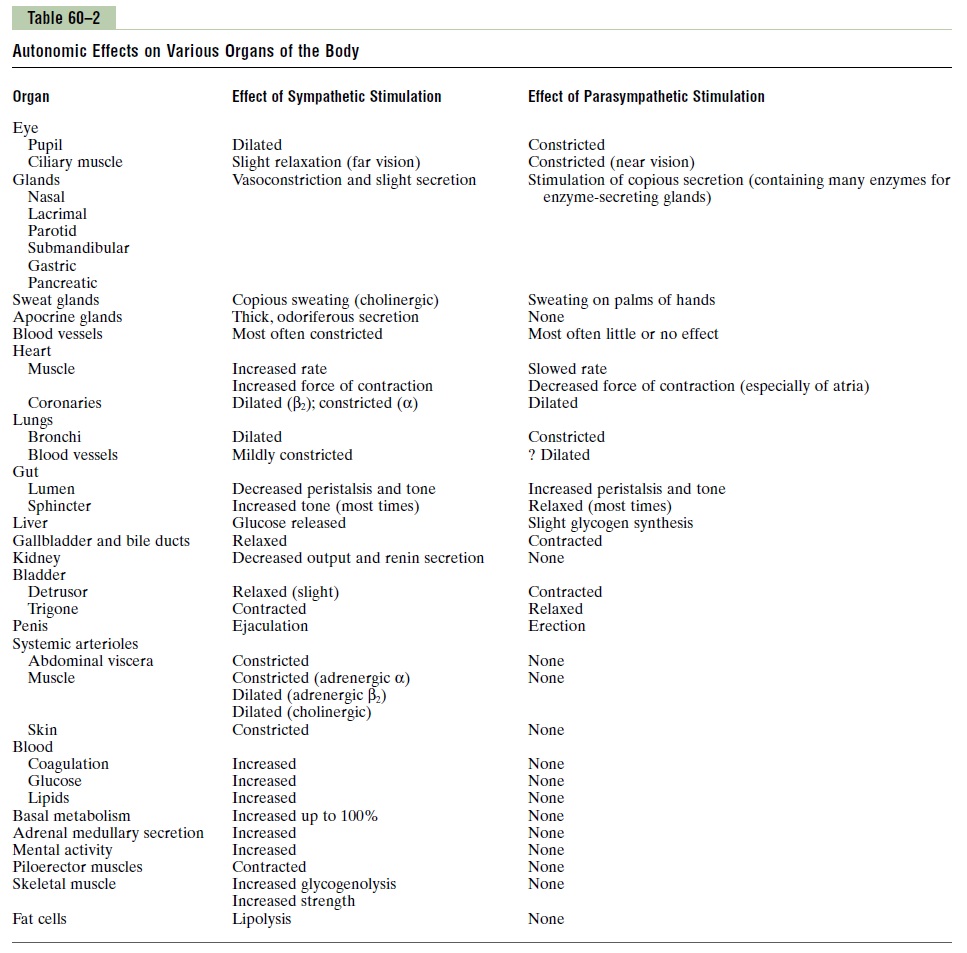
Table 60–2 lists the effects on different visceral func-tions of the body caused by stimulating either the parasympathetic nerves or the sympathetic nerves. From this table, it can be seen again that sympatheticstimulation causes excitatory effects in some organs but inhibitory effects in others. Likewise, parasympathetic stimulation causes excitation in some but inhibition in others. Also, when sympathetic stimulation excites aparticular organ, parasympathetic stimulation some-times inhibits it, demonstrating that the two systems occasionally act reciprocally to each other. But most organs are dominantly controlled by one or the other of the two systems.
There is no generalization one can use to explain whether sympathetic or parasympathetic stimulation will cause excitation or inhibition of a particular organ. Therefore, to understand sympathetic and parasympa-thetic function, one must learn all the separate func-tions of these two nervous systems on each organ, as listed in Table 60–2. Some of these functions need to be clarified in still greater detail, as follows.
Related Topics