Environmental Issues - Eutrophication | 12th Zoology : Chapter 13 : Environmental Issues
Chapter: 12th Zoology : Chapter 13 : Environmental Issues
Eutrophication
Eutrophication
When run-off from land containing nutrients
reaches water bodies like lakes, it results in dense growth of plant life. This
phenomenon is called Eutrophication. Natural aging of lakes also leads
to nutrient enrichment of its water. In a lake, the water is cold and clear (oligotrophic
stage), supporting little life. With time, streams draining into
the lake introduce nutrients such as nitrates and phosphates, which encourage
the growth of aquatic organisms. Aquatic plants and animal life grow rapidly,
and organic remains begin to be deposited on the lake bottom (mesotrophic
stage) (Fig. 13.5).
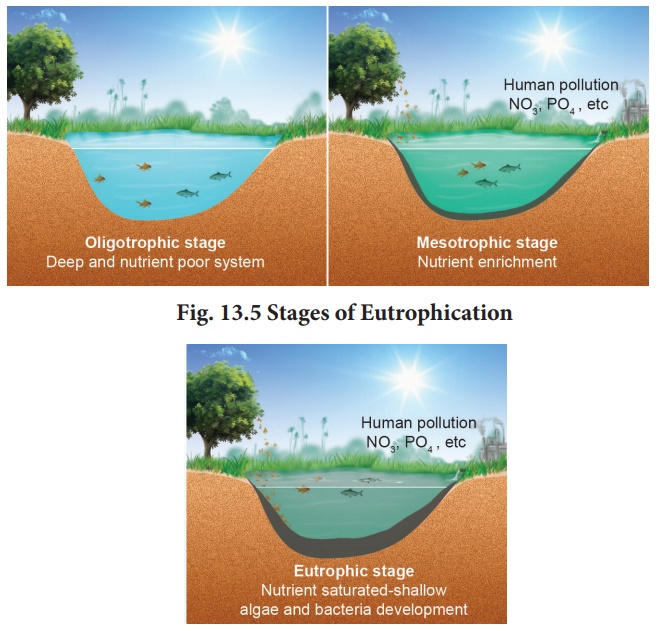
Pollutants from anthropogenic activities like
effluents from the industries and homes can radically accelerate the aging
process. This phenomenon is known as Cultural or Accelerated
Eutrophication.
Nutrients stimulate the growth of algae, water
hyacinth and can cause clogging of canals, rivers and lakes as well as,
displacing native plants. It causes unsightly foam and unpleasant odours, and
deprives the water of dissolved oxygen.
Integrated Wastewater Management
Wastewater Treatment
Wastewater or sewage originates from domestic
waste waters, industrial wastes and animal wastes. Realizing the importance of
clean potable water, the Government passed the Water (Prevention and Control of
Pollution) Act in 1974, which made it mandatory to treat wastewater in
treatment plants. The treatment can be carried out by three ways:
1. Physical methods
2. Chemical methods
3. Biological methods
1. Physical methods of wastewater treatment
Wastewaters containing insoluble substances or
colloids are treated through processes such as flotation, sedimentation,
filtration and centrifugal separation.
2. Chemical methods of Wastewater treatment
Chemical methods of wastewater treatment
include:
• Generation of insoluble solids.
• Produce an insoluble gas.
• Produce biologically degradable substances from
a non-biodegradable substance.
• Oxidize or reduce to produce a
non-objectionable substance.
3. Biological methods of Wastewater treatment
(1) Bioremediation of wastewater includes the
aerobic treatment (oxidation ponds, aeration lagoons) and anaerobic treatment
(anaerobic bioreactors, anaerobic lagoons).
(2) Phytoremediation of wastewater includes constructed wetlands, Root Zone Wastewater Treatment (RZWT), and Decentralized Waste Water Treatment System (DEWATS) (Fig. 13.6 a).

Case Study: Auroville, located in South India near
Puducherry has been experimenting with natural wastewater recycling systems
(Fig:13.6a). Such treatment plants have now also been implemented in Aravind
Eye Hospital, Puducherry (Fig.13.6 b) and the Chennai Mathematical
Institute, Siruseri IT Park, Chennai.
Related Topics