Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Organic Inorganic Physical Chemistry Higher secondary school College Notes
Enthalpy of combustion - Bomb calorimeter
Enthalpy of combustion
Generally combustion reactions occur in oxygen
atmosphere (excess oxygen) with evolution of heat. These reactions are
exothermic in nature. Enthalpy changes of combustion reactions are used in
industrial heating and in rocket fuels and in domestic fuels.
(QWKDOS\
FKDQJH RI FRPEXVWLRQ
ûcH, of a substance at a given temperature is defined as the enthalpy change of
the reaction accompanying the complete combustion of one mole of the substance
in presence of excess oxygen at that temperature. The enthalpy change of
combustion of substances in their standard states are known as standard
enthalpy change RI FRPEXVWLRQ
ûcH). These values are useful to experimentally
determine the
standard enthalpy change of formation of organic compounds.
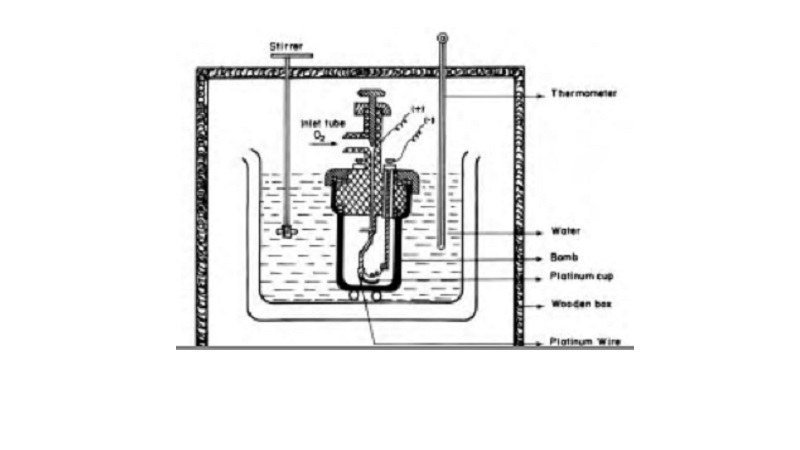
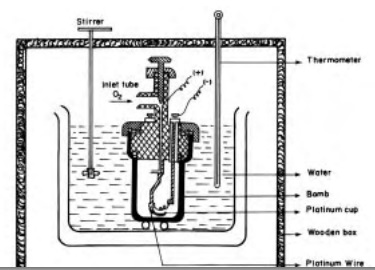
Bomb calorimeter
Enthalpy changes of combustion of chemical
substances are experimentally determined using a bomb calorimeter.
The bomb
calorimeter apparatus is shown in Fig.12.3. The inner vessel or the bomb and
its cover are made of strong steel. The cover is fitted tightly to the vessel
by means of metal lid and screws. A weighed amount of the substance is taken in
a platinum cup or boat connected with electrical wires for striking an arc
instantly to kindle combustion. The bomb is then tightly closed and pressurised
with excess oxygen. The bomb is lowered in water which is placed inside the
calorimeter. A stirrer is placed in the space between the wall of the
calorimeter and the bomb, so that water can be stirred, uniformly. The reaction
is started in the bomb by heating the substance through electrical heating.
During burning, the exothermic heat generated inside the bomb raises the
temperature of the surrounding water bath. The enthalpy measurements in this
case corresponds to the heat of reaction at constant volume. Although the
temperature rise is small (only by few degrees), the temperature change can be
measured accurately using Beckmann thermometer.
In a typical bomb calorimeter experiment, a weighed sample of benzoic
acid (w) is placed in the bomb which is then filled with excess oxygen and
sealed. Ignition is brought about electrically. The rise in temperature (∆T) is
noted. Water equivalent of the calorimeter is known from the standard value of
enthalpy of combustion of benzoic acid.
∆HcoC6H5COOH(s) = -3227 kJ mol-1
∆HcoC6H5COOH x ( w / M2 ) = wc ∆T
(where M2 = mol.wt benzoic acid).
Knowing wc
value, the enthalpy of combustion of any other substance is determined adopting the similar procedure and
using the substance in place of benzoic acid. By this experiment, the enthalpy
of combustion at constant volume ∆HcVol) is known
∆Hco(Vol) = wc ∆T
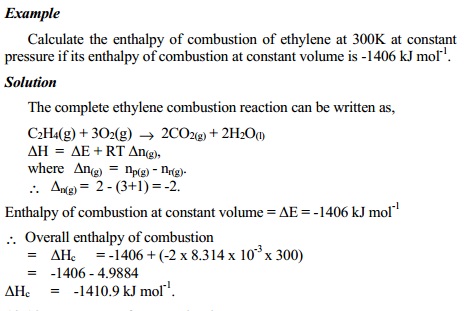
Enthalpy of combustion at constant pressure of the substance is
calculated from the equation,
∆Hco(Pr)
= ∆ Hc0(Vol) + ∆ n(g)RT
and ∆n(g) is known from the difference in the number of moles
of the products
and reactants in the completely balanced equation of combustion of the
substance with excess oxygen.
Related Topics