Chapter: Biochemistry: Biochemical Techniques
Electrophoresis: principle, Types
Electrophoresis
1. General
principle: Many
important biological molecules such as amino acids, peptides, proteins, nucleotides and nucleic acids posses ionisable
groups and can therefore be made to exists in solution as electrically charged
species either as cations (+) or anions (-). When a mixture of these components
are subjected to electric field, they migrate differentially and thus can be
separated.
2. Types of electrophoresis
(i) low voltage thin sheet electrophoresis;
(ii) high voltage electrophoresis, (iii) gel electrophoresis – native poly
acrylamide gel electrophoresis and sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS) poly
acrylamide gel electrophoresis, (iv) isoelectric focussing and (v)
isotachophoresis.
Gel electrophoresis
The most commonly used electrophoresis is gel
electrophoresis. In this technique either agarose or poly acrylamide is used as
supporting media. Electrophoresis units are available for running either
vertical or horizontal gel systems. Vertical slab gel units are commercially
available and routinely used to separate proteins in acrylamide gels. The gel
is formed between two glass plates that are clamped together but held apart by
plastic spacers. Gel dimensions are mostly 12 cm x 14 cm with a thickness of
0.5 mm to 1.0 mm. A plastic comb is placed in the gel solution and removed
after polymersization to provide loading wells for the samples. When the
apparatus is assembled, the lower electrophoresis tank buffer surrounds the gel
plates and effect cooling of the gel plates.
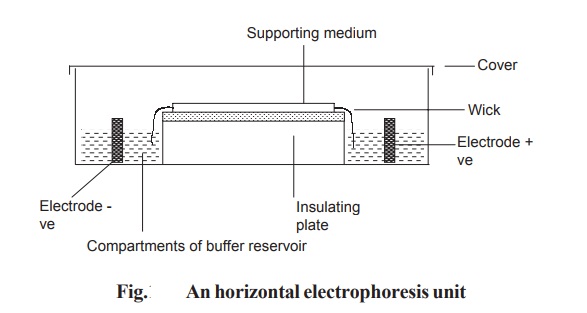
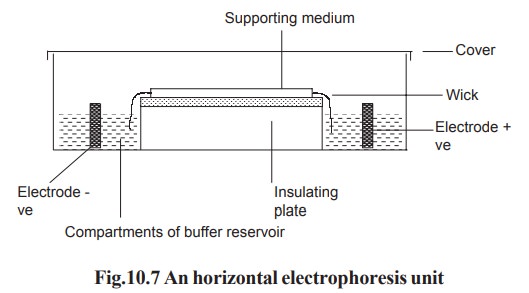
In horizontal gel system, the gel is cast on a
glass or a plastic sheet and placed on a cooling plate. Connection between the
gel and electrode buffer is made by using a thick wetted filter paper (wick).
The power pack supplies direct current between the electrodes in the
electrophoresis unit. All electrophoresis is carried out in appropriate buffer
to maintain constant state of ionization of the components being separated. Any
variation in pH may alter the over all charge and so the mobility of the
molecules being separated (Fig. 10.7).
Agarose Gels: Agarose is a linear
polysaccharide made up of repeating units of agarobiose which contains
galactose and 3, 6 anhydro galactose. This is isolated from seaweeds. Agaroses
gel is usually prepared at the concentration of 1-3% solutions. The gels can be
prepared by suspending dry agarose in suitable aqueous buffer then boiling the
mixture until a clear solution forms. This is poured and allowed to cool to
room temperature to form a rigid gel. Agarose gels are used for the
electrophoresis of both proteins and nucleic acids.
Polyacrylamide Gels: Electrophoresis in acrylamide gels is referred as PAGE being an abbreviation for PolyAcrylamide Gel Electrophoresis. Polyacrylamide gels are prepared by dissolving required quantity of acrylamide with a small amount of N, N’-methylene bisacrylamide in suitable buffer. The polymerization is initiated by ammonium persulphate and N, N, N’, N’-tetramethylene diamine (TEMED).The polymerization is free radical mediated reaction. Sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS) polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis is the most widely used method for analyzing protein mixture qualitatively. It is particularly useful for monitoring protein purification. SDS is an anionic detergent. Samples to be run on SDS-PAGE are first boiled for 5 minutes in sample buffer containing beta mercapitoethanol and SDS. The mercapto ethanol reduces any disulphide bridges and cleave the protein into different sub-units. So, by this electrophoresis different units of proteins can be identified.
unit Detection of separated components
·
Proteins
can be detected by using the dye-solution Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250 (CBB).
Staining is usually carried out using 0.1% CBB in methanol : acetic acid :
water in the ratio 5:1:5. The protein bands will look blue in colour.
·
Glycoproteins
are detected by using periodic acid – schiff (PAS) stain. The bands will appear
in red colour.
·
Nucleic
acids can be detected by using the fluorescent dye ethidium bromide. The
nucleic acids bands will appear colourless in black background.
Related Topics