FaradayŌĆÖs experiments, FlemingŌĆÖs Right Hand Rule - Electromagnetic Induction | 9th Science : Magnetism and Electromagnetism
Chapter: 9th Science : Magnetism and Electromagnetism
Electromagnetic Induction
Electromagnetic Induction
When it was shown by
Oersted that magnetic field is produced around a conductor carrying current,
the reverse effect was also attempted. In 1831, Michael Faraday explained the
possibility of producing an e.m.f across the conductor when the magnetic flux
linked with the conductor is changed. In order to demonstrate this Faraday
conducted the following experiments.
1. FaradayŌĆÖs experiments
Experiment 1
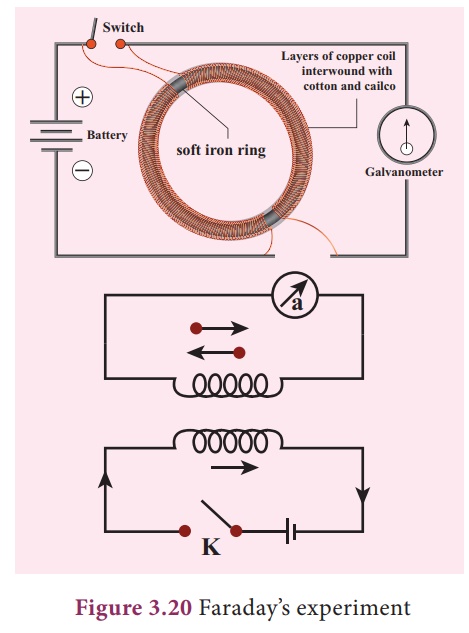
In this experiment, two
coils were wound on a soft iron ring (separated from each other). The coil on
the left is connected to a battery and a switch K. A galvanometer is attached
to the coil on the right. When the switch is put ŌĆśonŌĆÖ, at that instant, there
is a deflection in the galvanometer. Likewise, when the switch is put ŌĆśoff ŌĆÖ,
again there is a deflection ŌĆō but in the opposite direction. This proves the
generation of current.
Experiment 2
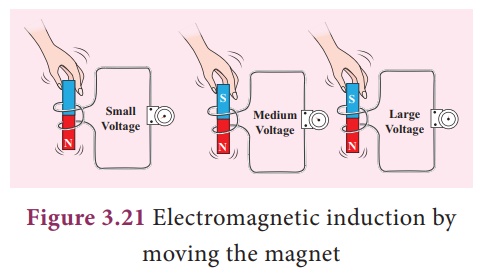
In this experiment,
current (or voltage) is generated by the movement of the magnet in and out of
the coil. The greater the number of turns, the higher is the voltage generated.
Experiment 3
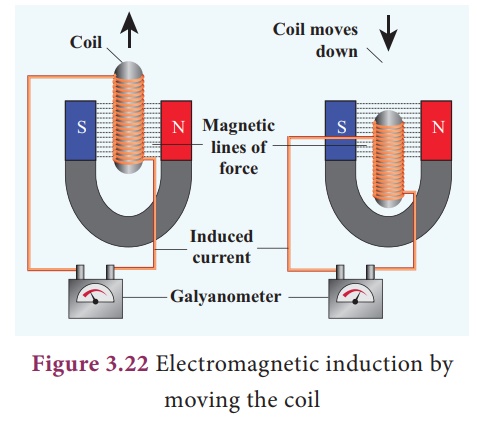
In this experiment, the
magnet is stationary, but the coil is moved in and out of the magnetic field
(indicated by the magnetic lines of force). Here also, current is induced.
All these observations
made Faraday to conclude that whenever there is a change in the magnetic flux
linked with a closed circuit an emf is produced and the amount of emf induced
varies directly as the rate at which the flux changes. This emf is known as
induced emf and the phenomenon of producing an induced emf due to change in the
magnetic flux linked with a closed circuit is known as electromagnetic
induction.
Note:
The direction of the
induced current was given by LenzŌĆÖs law, which states that the induced current
in the coil flows in such a direction as to oppose the change that causes it.
The direction of induced current can also be given by another rule called
FlemingŌĆÖs Right Hand Rule.
2. FlemingŌĆÖs Right Hand Rule
Fleming formulated Right
Hand Rule to find the direction of flow of current when a conductor is placed
in a changing magnetic field as he formulated Left Hand Rule to find the
direction of the force in a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic
field.
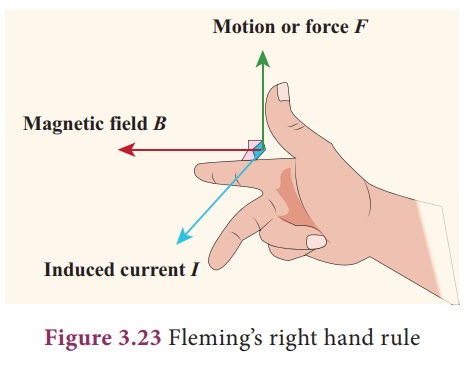
Stretch the thumb, fore
finger and middle finger of your right hand mutually perpendicular to each
other. If the fore finger indicates the direction of magnetic field and the
thumb indicates the direction of motion of the conductor, then the middle
finger will indicate the direction of induced current. FlemingŌĆÖs Right hand
rule is also called ŌĆ£generator ruleŌĆØ.
Related Topics