Chapter: Medical Surgical Nursing: Management of Patients With Musculoskeletal Trauma
Elbow - Fracture
ELBOW
Fractures of the distal humerus result from motor vehicle
crashes, falls on the elbow (in the extended or flexed position), or a direct
blow. These fractures may result in injury to the median, radial, or ulnar
nerves.
The patient is evaluated
for paresthesia and signs of compro-mised circulation in the forearm and hand.
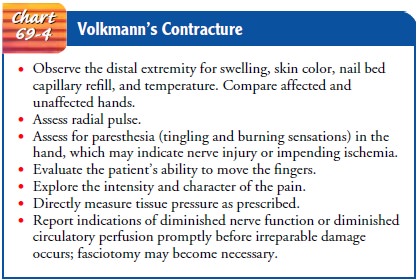
The most serious complication of a supracondylar fracture of the humerus is
Volk-mann’s ischemic contracture (a compartment syndrome), which results from
antecubital swelling or damage to the brachial artery (Chart 69-4). The nurse
needs to monitor the patient regularly for compromised neurovascular status and
signs of compartment syndrome.
Other potential complications are damage to the joint
articu-lar surfaces and hemarthrosis (blood in the joint). If hemarthro-sis is
present, the physician may aspirate the joint to remove the blood, thereby
relieving the pressure and pain.
Management
The goal of therapy is prompt reduction and stabilization
of the distal humerus fracture, followed by controlled active motion after
swelling has subsided and healing has begun. If the fracture is not displaced,
the arm is immobilized in a cast or posterior splint with the elbow at 45 to 90
degrees of flexion and in a sling for 4 to 6 weeks. Then a thermoplastic splint
is used to support the fracture and rehabilitation exercises are begun.
Usually, a displaced fracture is treated with open
reduction and internal fixation. Excision of bone fragments may be neces-sary.
Additional external support with a splint is then applied. Active finger
exercises are encouraged. Gentle ROM exercise of the injured joint is begun
about 1 week after internal fixation. Motion promotes healing of injured joints
by producing move-ment of synovial fluid into the articular cartilage. Active
exercise of the elbow is performed as prescribed to prevent residual
limi-tation of motion.
Related Topics