Chapter: Electrical machines : Synchronous Generator
Effect of Change of Excitation
Effect of Change of Excitation:
A change
in the excitation of an alternator running in parallel with other affects only
its KVA output; it does not affect the KW output. A change in the excitation,
thus, affects only the power factor of its output. Let two similar alternators
of the same rating be operating in parallel, receiving equal power inputs from
their prime movers. Neglecting losses, their kW outputs are therefore equal. If
their excitations are the same, they induce the same emf, and since they are in
parallel their terminal voltages are also the same. When delivering a total
load of I amperes at a power-factor of cos
Ф, each alternator delivers half
the total current and I1 = I2 = I/2.
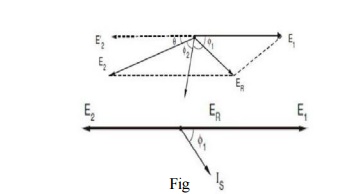
Since
their induced emfs are the same, there is no resultant emf acting around the
local circuit formed by their two armature windings, so that the synchronizing
current, Is, is
zero. Since the armature resistance is neglected, the vector difference between
E1 = E2 and V is equal
to, I1Xs1 I2Xs2 , this vector leading the current I by 900,
where XS1 and XS2 are the synchronous reactances of the two alternators
respectively.
Now
consider the effect of reducing the excitation of the second alternator. E2 is therefore reduced as shown
in Figure. This reduces the terminal voltage slightly, so let the excitation of
the first alternator be increased so as to bring the terminal voltage back to
its original value. Since the two alternator inputs are unchanged and losses
are neglected, the two kW outputs are the same as before. The current I2 is changed due to the change in
E2, but the active components of
both I1 and I2 remain unaltered. It can be
observed that there is a small change in the load angles of the two
alternators, this angle being slightly increased in the case of the weakly
excited alternator and slightly decreased in the case of the strongly excited
alternator. It can also be observed that I1 + I2 = I, the total load current.
Related Topics