Chapter: Electrical machines : Synchronous Generator
E.M.F. equation of an elementary alternator single phase
E.M.F. equation of an elementary
alternator single phase
Let us
assume that this generator has an armature winding consisting of a total number
of full pitched concentrated coils C, each coil having a given number of turns Nc. Then the total number of
turns in any given phase of a single-phase generator armature is
N p = CNc
According
to Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction the average voltage induced in a
single turn of two coil sides is
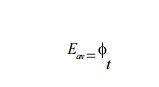
The
voltage induced in one conductor is 2ϕ/(1/n) = 2ϕs, where
n=speed of rotation in r.p.s, for a 2 pole generator. Furthermore, when a coil
consisting of Nc turns
rotates in a uniform magnetic field, at a uniform speed, the average voltage
induced in an armature coil is
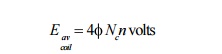
where ϕ is the number of lines of flux
(in Webers) per pole, Nc
is number of turns per coil, n is the relative speed in revolutions/second
(rps) between the coil of Nc
turns and the magnetic field ϕ.
A speed n
of 1 rps will produce a frequency f
of 1 Hz. Since f is directly
proportional and equivalent to n, (for a 2-pole generator) for all the series
turns in any phase,
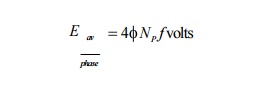
The
effective rms value of a sinusoidal ac voltage is 1.11 times the average value.
The effective ac voltage per phase is
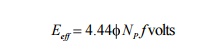
Related Topics